Because telescope crowns and nonrigid connectors both require tooth preparations that are more destructive than normal, the selection of one of these would be influenced by the nature of previous destruction of the prospective abutment teeth. The presence of a dowel core or a disto-occlusal amalgam on the premolar, for example, would favor placement of a nonrigid connector on that tooth, while extensive facial and/or lingual restorations on the tilted molar would call for the use of a telescope crown.
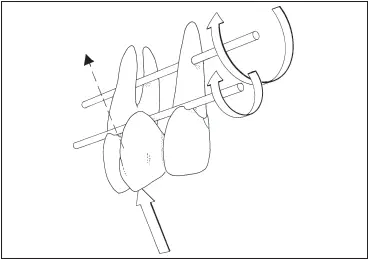
Fig 7-32A fixed partial denture replacing a maxillary canine is subjected to more damaging stresses than that replacing a mandibular canine because the forces are directed outward and the pontic lies farther outside the interabutment axis.v
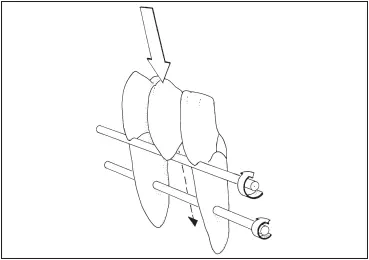
Fig 7-33A fixed partial denture replacing a mandibular canine has a more favorable prognosis than that replacing a maxillary canine because the forces are directed inward and the pontic will be closer to the interabutment axis.
Canine-replacement fixed partial dentures
Fixed partial dentures replacing canines can be difficult because the canine often lies outside the interabutment axis. The prospective abutments are the lateral incisor, usually the weakest tooth in the entire arch, and the first premolar, the weakest posterior tooth. A fixed partial denture replacing a maxillary canine is subjected to more stresses than that replacing a mandibular canine because forces are transmitted outward (labially) on the maxillary arch, against the inside of the curve (its weakest point) ( Fig 7-32). On the mandibular canine, the forces are directed inward (lingually), against the outside of the curve (its strongest point) ( Fig 7-33). Any fixed partial denture replacing a canine should be considered a complex fixed partial denture. No fixed partial denture replacing a canine should replace more than one additional tooth. An edentulous space created by the loss of a canine and any two contiguous teeth is best restored with a removable partial denture.
Cantilever fixed partial dentures
A cantilever fixed partial denture is one that has an abutment or abutments at one end only, with the other end of the pontic remaining unattached. This is a potentially destructive design with the lever arm created by the pontic, and it is frequently misused.
In the routine three-unit fixed partial denture, force that is applied to the pontic is distributed equally to the abutment teeth ( Fig 7-34). If there is only one pontic and it is near the interabutment axis line, less leverage is applied to the abutment teeth and to the retainers than with a cantilever. When a cantilever pontic is employed to replace a missing tooth, forces applied to the pontic have an entirely different effect on the abutment tooth. The pontic acts as a lever that tends to be depressed under forces with a strong occlusal vector ( Fig 7-35).
Prospective abutment teeth for cantilever fixed partial dentures should be evaluated with an eye toward lengthy roots with a favorable configuration, long clinical crowns, good crown-root ratios, and healthy periodontium. 34Generally, cantilever fixed partial dentures should replace only one tooth and have at least two abutments. 35,36
A cantilever can be used for replacing a maxillary lateral incisor ( Fig 7-36). There should be no occlusal contact on the pontic in either centric or lateral excursions. 37The canine must be used as an abutment, and it can serve in the role of solo abutment only if it has a long root and good bone support. There should be a rest on the mesial of the pontic against a rest preparation in an inlay or other metallic restoration on the distal of the central incisor to prevent rotation of the pontic and abutment. The mesial aspect of the pontic can be slightly wrapped around the distal portion of the uninvolved central incisor to stabilize the pontic faciolingually. 37The root configuration of a central incisor makes it an undesirable cantilever abutment.
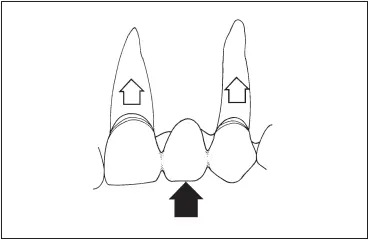
Fig 7-34Forces applied to the pontic of a routine fixed partial denture are transmitted to both abutment teeth.
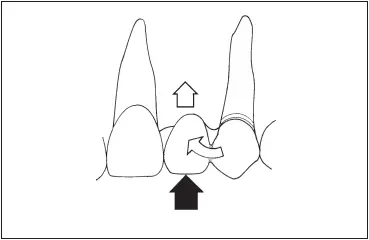
Fig 7-35Forces on the pontic of a cantilever fixed partial denture tend to tip the fixed partial denture or the abutment tooth.
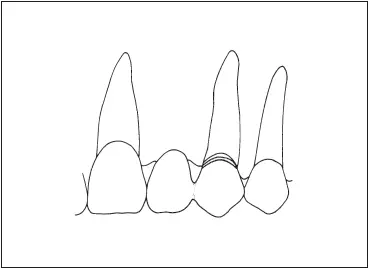
Fig 7-36Cantilever fixed partial denture replacing a maxillary lateral incisor, using the canine as the abutment.
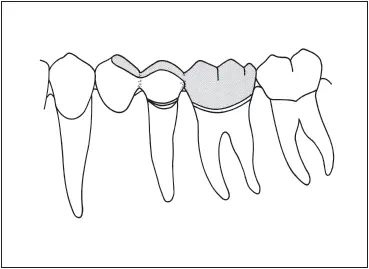
Fig 7-37A cantilever pontic can be used to replace a first premolar if full veneer retainers are used on the second premolar and first molar abutments.
A cantilever pontic can also be used to replace a missing first premolar ( Fig 7-37). This scheme will work best if occlusal contact is limited to the distal fossa. Full veneer retainers are required on both the second premolar and first molar. These teeth must exhibit excellent bone support. This design is attractive if the canine is unmarred and if a full veneer restoration is required for the first molar under any circumstances.
Cantilever fixed partial dentures can also be used to replace molars when there is no distal abutment present. When used judiciously, it is possible to avoid the insertion of a unilateral removable partial denture. 34Most commonly, this type of fixed partial denture is used to replace a first molar, although occasionally it is used to replace a second molar to prevent supereruption of opposing teeth.
When the pontic is loaded occlusally, the adjacent abutment tends to act as a fulcrum, with a lifting tendency on the farthest retainer 38( Fig 7-38). To minimize the leverage effect, the pontic should be kept as small as possible, more nearly representing a premolar than a molar ( Fig 7-39). There should be light occlusal contact with absolutely no contact in any excursion. The pontic should possess maximum occlusogingival height to ensure a rigid prosthesis.
A posterior cantilever pontic places maximum demands on the retentive capacity of the retainer. 39Its use, therefore, should be reserved for those situations in which there is adequate clinical crown length on the abutment teeth to permit preparations of maximum length and retention. The success of cantilevers in the restoration of the periodontally compromised dentition is probably due at least in part to the fact that periodontally involved abutments do have extremely long clinical crowns. While cantilever fixed partial dentures appear to be a conservative restoration, the potential for damage to the abutment teeth requires that they be used sparingly.
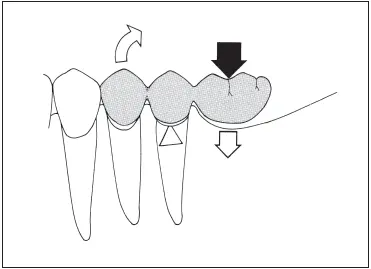
Fig 7-38Forces on a full-size molar cantilever pontic place great stress on the mesial abutment.
Читать дальше



















