2.2.2 Purine–Pyrimidine Mismatches
Mismatched base pairs between purine and pyrimidine nucleobases are known as transition mismatches. G·T and G·U mismatches can form two hydrogen bonds, which are usually known as typical “wobble” base pairs, by shifting the nucleobase geometry from that of Watson–Crick base pairs ( Figure 2.2). These mismatches are one of the most stable mismatches in DNA and RNA duplexes ( Tables 2.1and 2.2). G·U base pair is frequently observed in natural RNAs. It is because that both guanine and uracil take anti conformation in their glycosidic bond angles that are the same with Watson–Crick base pairs and the distance and geometric arrangement of C1′ atoms of the sugars do not largely change compared with the canonical duplex. Thus, there is no significant worsening of base stacking and littler perturbation of the duplex conformation. Adenine and cytosine also form two hydrogen bonds as similar way as the G·T(U) mismatch when the adenine nucleobase is protonated ( Figure 2.2). Formation of the A +·C mismatched base pair is demonstrated by X-ray diffraction analysis using dodecamer oligonucleotide strand [7]. However, neutral A·C mismatches are in equilibrium between the wobble and reverse wobble forms, each of which only forms one hydrogen bond. Thus, A·C mismatch is much less stable than G·T(U) mismatch in a physiological condition ( Tables 2.1and 2.2).
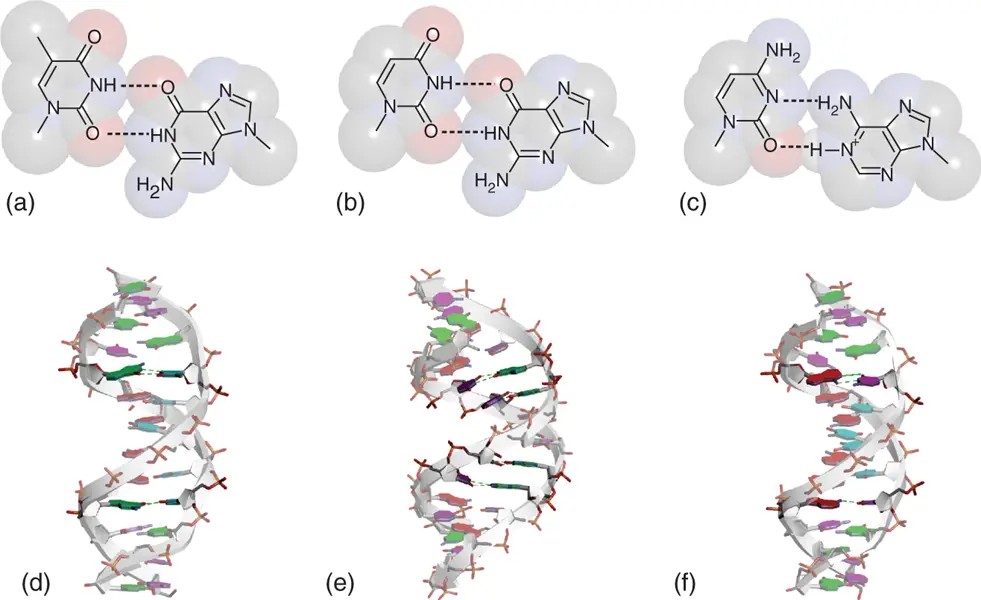
Figure 2.2 Wobble base pairs in duplexes. Chemical structures of G-T (a), G-U (b), and A +-C (c) wobble base pairs. N1 atom of adenine nucleobase is protonated. (d) Structure of B-form DNA duplex containing G-T wobble base pairs (PDB ID: 113D). (e) Structure of A-form RNA duplex containing two consecutive G-U wobble base pairs (PDB ID: 433D). (f) Structure of B-form DNA duplex containing A +-C wobble base pairs (PDB ID: 1D99). Nucleobases forming the wobble base pairs are emphasized dark. Hydrogen bonds in the wobble base pairs are shown in dashed lines.
2.2.3 Purine–Purine Mismatches
Purine–purine and pyrimidine–pyrimidine mismatches are known as transversion mismatches. There are G·A, G·G, and A·A mismatches in the purine–purine mismatch. Among them, G·A mismatch forms relatively stable unusual base pairs in both DNA and RNA duplexes ( Tables 2.1and 2.2). It is highly polymorphic depending on sequence compositions. In DNA duplexes containing G·A mismatches that form two hydrogen bonds, various combinations of anti and syn were observed in their glycosidic bond angles ( Figure 2.3). G·G mismatch potentially adopts a base paring with two hydrogen bonds, in which two guanosines are symmetrically or asymmetrically oriented with anti and syn conformation in their glycosidic bond angles ( Figure 2.3). When the asymmetric G·G base pairs face each other in rotation, four guanines form a symmetric quartet as described later ( Chapter 3). Recent X-ray diffraction analyses also demonstrated polymorphic feature of the G·G mismatch by showing that with syn–syn combination in the glycosidic bond angles in the presence of chromomycin A3, which binds minor groove of the mismatched place and supports the structure analysis [8]. Detailed structure of A·A mismatch is rarely determined by X-ray diffraction analysis. It is considered that the mismatch is dynamically fluctuated and not able to be a particular structural state.
Table 2.1 Thermodynamic parameters for duplex formations in 1M NaCl by DNA oligonucleotides containing mismatches a) .
|
|
−Δ H ° |
−Δ S ° |
−Δ 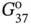 |
T m |
| Sequence |
XY |
(kcal mol −1) |
(cal mol −1) K −1) |
(kcal mol −1) |
(°C at 10 −4M) |
5′CAAA X AAAG |
CG |
64.5 |
183 |
7.7 |
42.9 |
3′GTTT Y TTTC |
GC |
62.8 |
179 |
7.3 |
40.8 |
|
AT |
68.0 |
196 |
7.2 |
40.1 |
|
TA |
58.6 |
168 |
6.5 |
36.8 |
|
GG |
53.5 |
158 |
4.5 |
25.6 |
|
TG |
55.6 |
165 |
4.4 |
25.7 |
|
GA |
52.6 |
156 |
4.2 |
23.9 |
|
GT |
46.7 |
137 |
4.2 |
22.3 |
|
AG |
39.9 |
116 |
3.9 |
18.0 |
|
AA |
36.9 |
107 |
3.7 |
15.0 |
|
CT |
53.2 |
161 |
3.3 |
19.1 |
|
TC |
50.0 |
151 |
3.2 |
17.5 |
|
CA |
(40.3) b) |
(120) b) |
(3.1) b) |
(13) b) |
|
TT |
(54.6) b) |
(167) b) |
(2.8) b) |
(17) b) |
|
AC |
(35.8) b) |
(106) b) |
(2.9) b) |
(9) b) |
|
CC |
(55.3) b) |
(171) b) |
(2.3) b) |
(15) b) |
5′CAACTTGATATTAATA + |
Mismatch |
|
|
|
|
3′GTTGAACTATAATTAT |
– |
102.1 |
289 |
12.4 |
55.8 |
3′GTTGAGCTATAATTAT |
TG |
92.6 |
266 |
10.1 |
49.4 |
3′GTTGAACTATAGTTAT |
TG |
95.5 |
274 |
10.5 |
50.5 |
3′GTTGAACTCTAATTAT |
TC |
98.4 |
286 |
9.7 |
47.3 |
3′GTTGAATTATAATTAT |
GT |
91.3 |
264 |
9.4 |
47.1 |
3′GTTGAACCATAATTAT |
AC |
90.9 |
265 |
8.7 |
44.6 |
3′GTTGAACAATAATTAT |
AA |
92.0 |
267 |
9.26 |
46.2 |
a)Values are summarized ones in a reference [6].
b)Values in parenthesis are significantly less accurate estimated using flat lower baselines in their melting analyses.
Table 2.2 Free energy increments for tandem mismatches in RNA oligonucleotides in 1M NaCl a) , b) .
| Mismatch |
YZ ZY |
5′ CGX YZX′ CG 3′ |
UG |
GU |
GA |
AG |
UU |
GG |
CA |
CU |
UC |
CC |
AC |
AA |
3′ GCX′ ZYX GC 5′ |
GU |
UG |
AG |
GA |
UU |
GG |
AC |
UC |
CU |
CC |
CA |
AA |
| Closing base pair |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X/X′ |
G/C |
−4.9 |
−4.1 |
−2.6 |
−1.3 |
−0.5 |
|
1.0 |
1.1 |
|
|
0.9 |
1.5 |
|
C/G |
−4.2 |
−1.1 |
−0.7 |
−0.7 |
−0.4 |
0.8 |
1.1 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
1.3 |
|
U/A |
−2.6 |
−0.3 |
0.7 |
|
1.1 |
|
[1.9] C |
2.2 |
2.8 |
|
|
2.8 |
|
A/U |
−1.9 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
|
0.6 |
|
2.3 |
|
|
|
2.5 |
2.8 |
a)Values are summarized ones in a reference [6].
Читать дальше