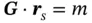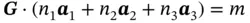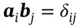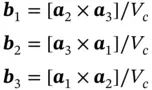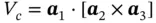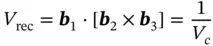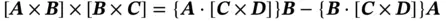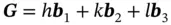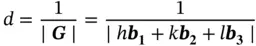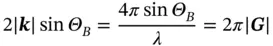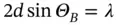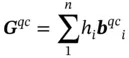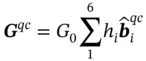and combining Eqs. (1.27, 1.28), we find
(1.29) 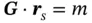
According to Eqs. (1.28, 1.29), different values of k f= k i+ 2 π Gare permitted in a periodic medium, but only those that provide scalar products of certain vectors, G, with all possible vectors, r s, to be integer numbers, m . By substituting Eq. (1.1)into Eq. (1.29), we finally obtain:
(1.30) 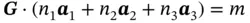
In order to find the set of allowed vectors, G, satisfying Eq. (1.30), the reciprocal space is built, which is based on three non-coplanar vectors b 1, b 2, and b 3. Real (direct) space and reciprocal space are interrelated by the orthogonality (reciprocity) conditions:
(1.31) 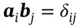
where δ ijis the Kroneckersymbol, equal to 1 for i = j or 0 for i ≠ j ( i , j = 1, 2, 3). To produce the reciprocal space from real space, we use the following mathematical procedure:
(1.32) 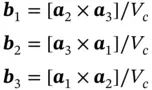
where V cstands for the volume of the parallelepiped (unit cell) built in real space on vectors a 1, a 2, a 3:
(1.33) 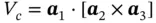
By using Eqs. (1.32, 1.33), it is easy to directly check that the procedure (1.32)provides proper orthogonality conditions (1.31). For example, a 1· b 1= a 1· [ a 2× a 3]/ V c= V c/ V c= 1, whereas a 2 · b 1= a 2 ·[ a 2× a 3]/ V c= 0. Certainly, the volume of the unit cell, V rec, in reciprocal space
(1.34) 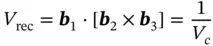
is inverse to V c. To prove this statement, we use the relationship well-known in vector algebra:
(1.35) 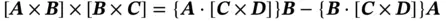
In the reciprocal space, the allowed vectors, G, are linear combinations of the basis vectors, b 1, b 2, b 3:
(1.36) 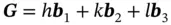
with integer projections ( hkl ), known as Millerindices. The ends of vectors, G, being constructed from the common origin ( 000 ), produce the nodes of a reciprocal lattice. For all vectors, G, Eq. (1.30)is automatically valid due to the orthogonality conditions (1.31). We repeat that in the medium with translational symmetry, only those wavevectors, k f, may exist, which are in rigid interrelation with the initial wavevector k i, satisfying Eq. (1.28). Sometimes Eq. (1.28)is called as quasi-momentum (or quasi-wavevector) conservation law in the medium with translational symmetry, which should be used instead of the momentum conservation law in a homogeneous medium. We remind that the latter law means 2 π G= k f− k i= 0, i.e. k f= k i.
Note that each vector of reciprocal lattice, G = hb 1 + kb 2 + lb 3, is perpendicular to a specific crystallographic plane in real space. This statement directly follows from Eq. (1.29), which defines the geometric plane for the ends of certain vectors, r s, the plane being perpendicular to the vector G( Figure 1.14). Bearing in mind possible wave diffraction when propagating through a periodic medium, it is worth to introduce a set of parallel planes of this type (i.e. those given by Eq. (1.29)), which are separated by the d -spacing
(1.37) 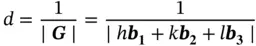
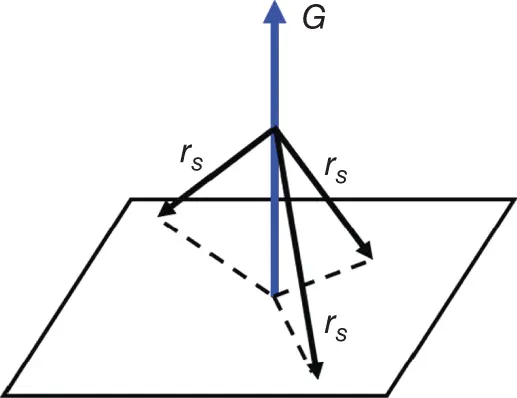
Figure 1.14Sketch of a crystal plane, normal to the vector of reciprocal lattice, G, which contains the ends of vectors, r s, satisfying Eq. (1.29).
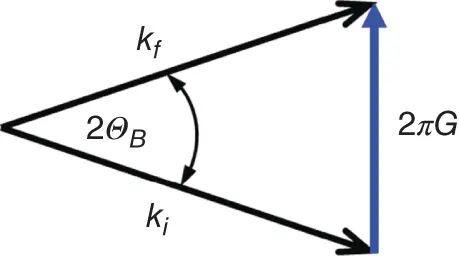
Figure 1.15Graphical interrelation between wavevectors of the incident ( k i) and scattered ( k f) waves and the vector of reciprocal lattice, G.
In fact, using graphical representation of Eq. (1.28)( Figure 1.15) and solving the wavevector triangle, we find (with the aid of Eq. (1.24)) that
(1.38) 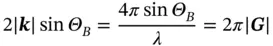
Substituting Eq. (1.37)into Eq. (1.38), we finally obtain the so-called Bragglaw:
(1.39) 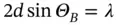
which provides the relationship between the possible directions for the diffracted wave propagation (via Braggangles, Θ B) and inter-planar spacings ( d -spacings), d , in crystals. We stress that if λ > 2 d , Braggdiffraction is not possible.
Note that for quasicrystals, the diffraction conditions (like Eq. (1.28)) can be deduced from the quasi-momentum (quasi-wavevector) conservation law in the n -dimensional space (hyperspace, n > 3), in which the vectors of reciprocal lattice, G qc, are:
(1.40) 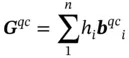
In case of icosahedral symmetry, n = 6, and the set of basis vectors has the following form:
(1.41) 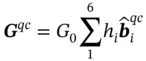
Читать дальше