Thus, assessing an individual’s diabetes risk status, discussing the risk and, referring the patient to a proven community‐based diabetes prevention program is an important role for the primary care practitioner. RCTs of structured lifestyle modification have consistently demonstrated that caloric reduction plus increased physical activity leading to modest weight loss reduces the risk of incident type 2 diabetes in adults at high risk by 50–70%.
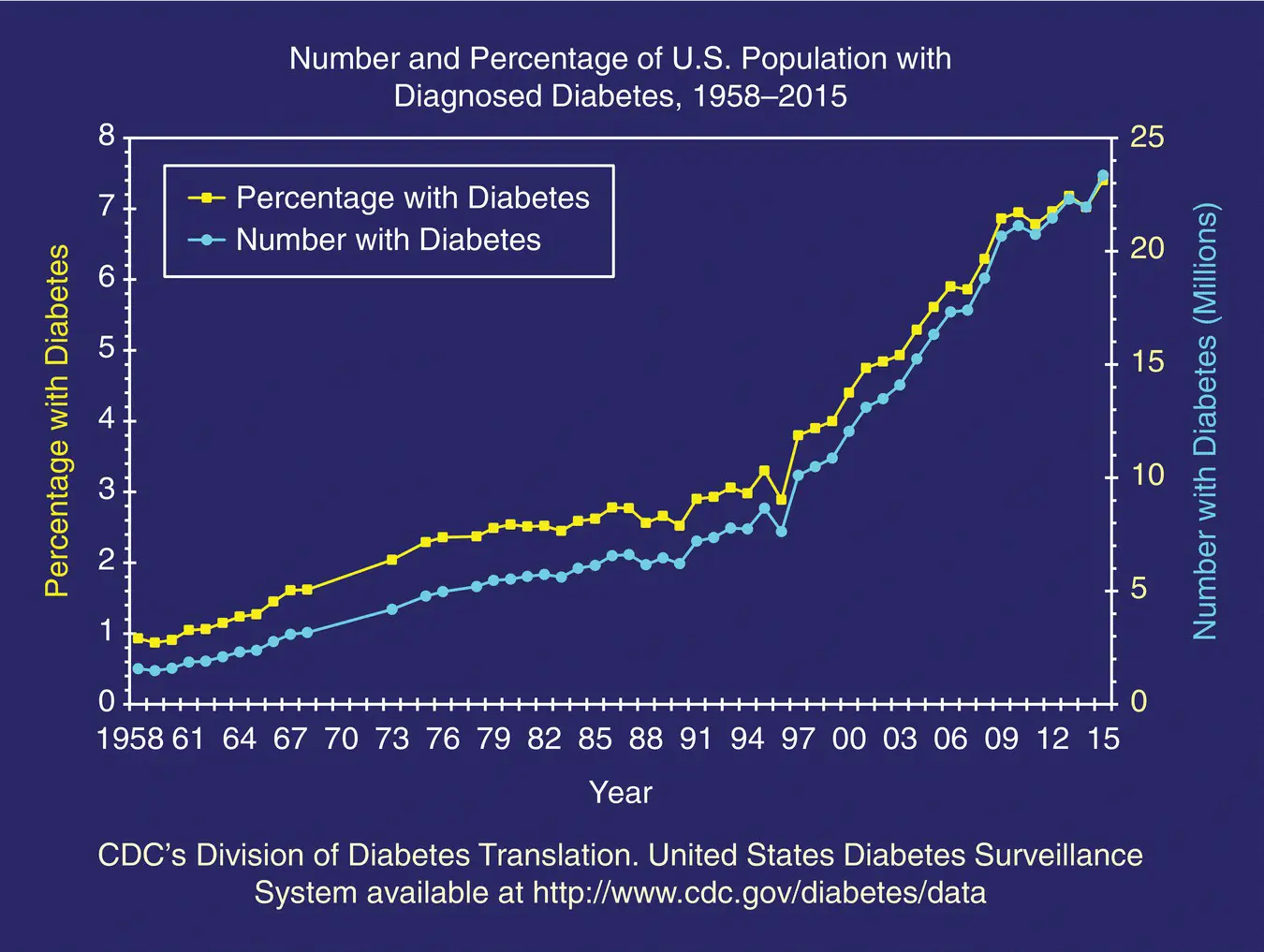
Figure 4.3 An alarming trend in the USA with increasing numbers of patients. CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation. United States Diabetes Surveillance System.
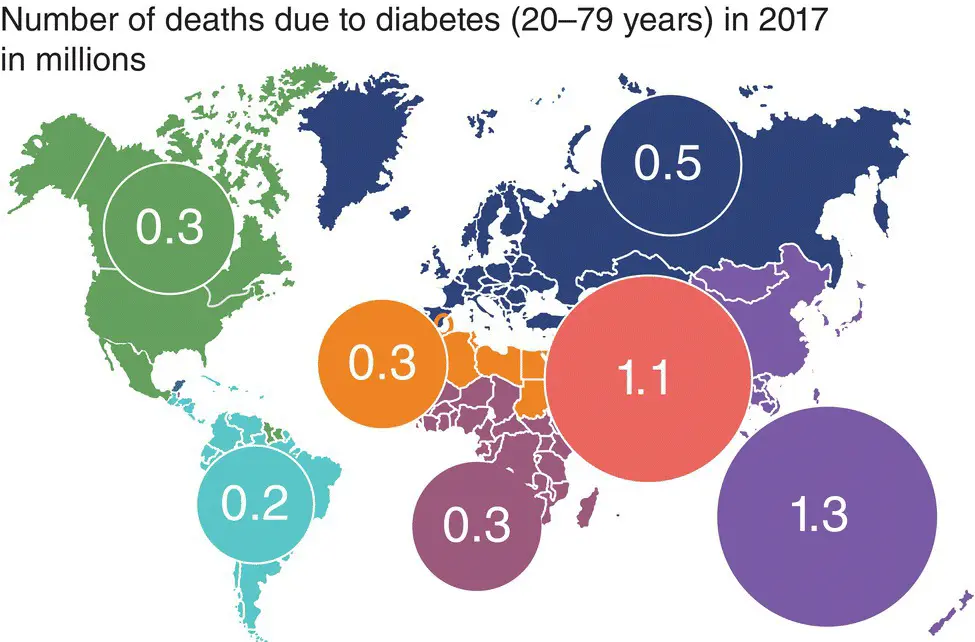

Figure 4.4 Mortality rates due to diabetes‐related complications. IDF Atlas, 2017.
The Diabetes Prevention program (DPP) recruited 3234 middle‐aged overweight or obese adults with impaired glucose tolerance, who were then randomised to one of three treatment groups: (i) a lifestyle intervention that employed behavioural counselling to promote caloric reduction and physical activity; (ii) metformin therapy; or (iii) placebo metformin therapy. The lifestyle intervention group achieved an initial weight loss of ∼6% of body weight after 12 months, reducing to ∼4% after 3 years, and an increase in self‐reported physical activity (equivalent to brisk walking) from 100 to 190 minutes per week. Compared to their counterparts in the control group, participants in the lifestyle intervention group showed a 58% reduction in incident diabetes over 4 years. This benefit was evident in men and women across different ethnic groups and it was even greater among older age participants ( Figure 4.10).
The intensive and quite costly lifestyle intervention used in the DPP trial was designed to give maximum efficacy with limited consideration for the ease or sustainability of delivering the program in a real world community setting. Thus, two barriers have hampered the widespread implementation of the DPP findings to the growing population of people who might benefit: (i) the cost of the one‐to‐one lifestyle coaching and intervention format; and (ii) limitations in the practicalities of identifying suitable patients, optimising referral pathways and maintaining patient participation.
In the UK, the ambition is to achieve a country‐wide, evidence‐based type 2 diabetes prevention program, known as ‘The Healthier You ’ programme, to prevent or delay diabetes in those identified to be at high risk. The scheme was rolled out in 2016, and participants undergo an intensive 9‐month programme that includes at least 13 face‐to‐face interactions and at least 16 hours of contact time. So far, >50,000 referrals have been made with attendance rates over 40% across diverse socio‐economic groups ( Figure 4.11).
Providing access to structured diabetes education
Diabetes education is key to successful day‐to‐day diabetes management, yet few patients are offered high quality education, in part because of myths that it doesn’t really work. However, randomised trials, and a meta‐analysis, have shown that group‐based diabetes self‐management education results in statistically significant improvements in key clinical (HbA1c, fasting glucose), lifestyle (diabetes knowledge and self‐management skills), and psycho‐social outcomes. As a result, diabetes education is recommended by NICE and SIGN ( Table 4.1).
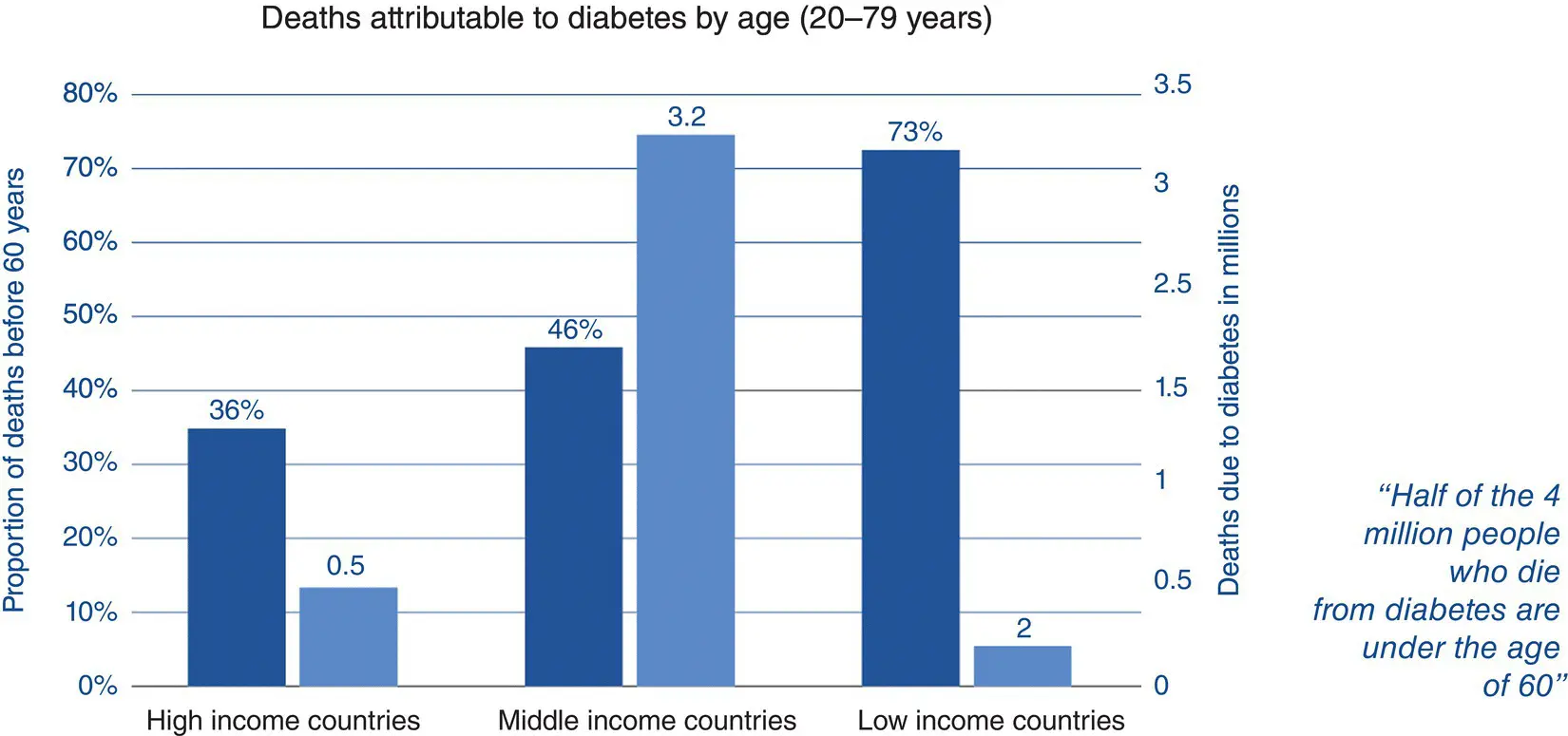
Figure 4.5 Premature mortality affects low‐, medium‐ and high‐income countries. IDF Atlas, 2017.
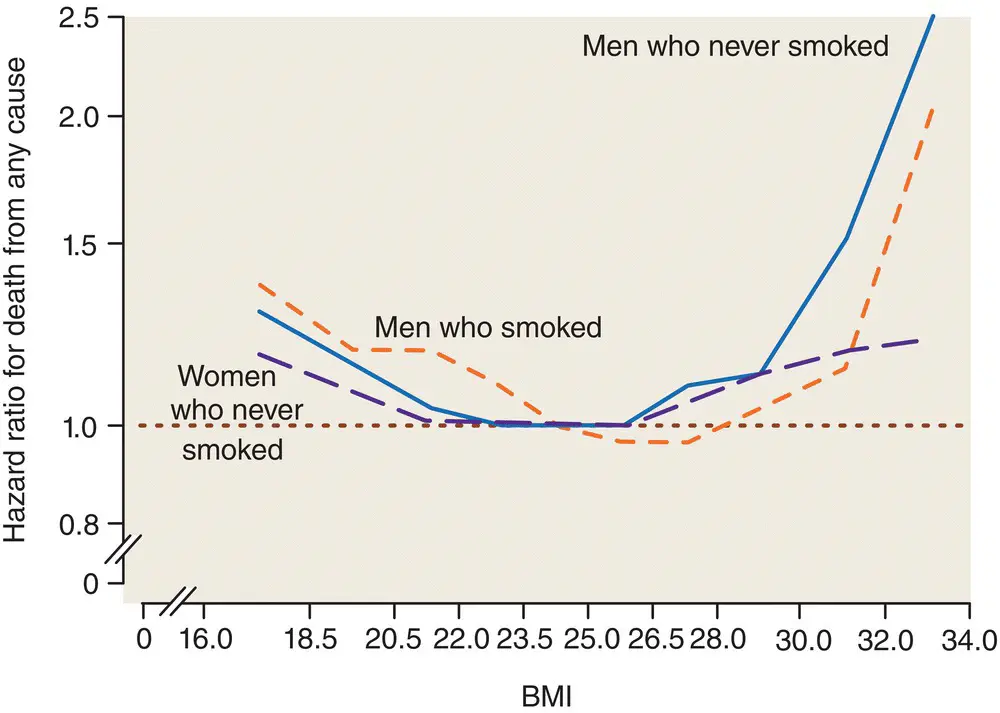
Figure 4.6 The relationship between Body Mass Index and the hazard ratio for death from any cause. Data for men according to smoking status, relative to females who never smoked, in a large Asian cohort study. Obesity carries an increased risk of several unwanted health outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease and certain forms of cancer.
Adapted from Jee et al. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 779–787.
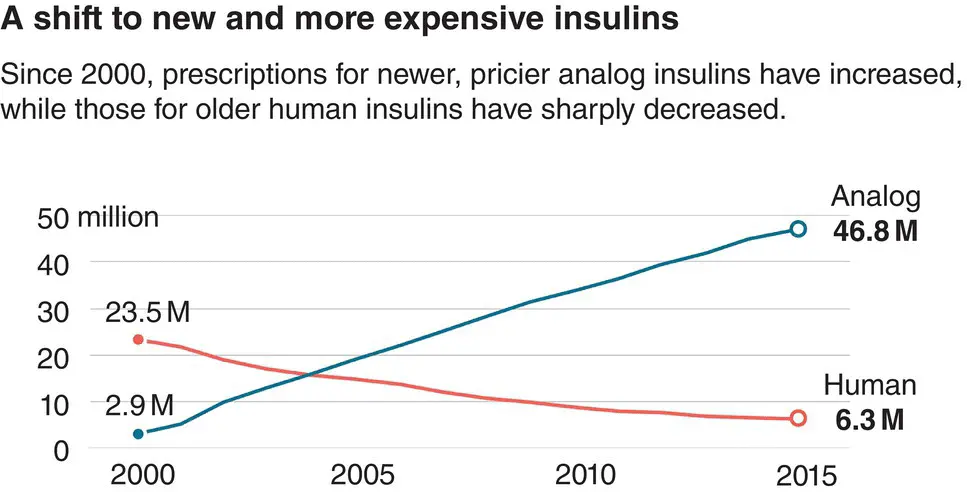
Figure 4.7 Healthcare expenditure on diabetes is rising steeply. IDF Atlas, 2017.

Figure 4.8 In the USA the costs of providing diabetes care are enormous. Based on Rowley et.al. 2016. Diabetes 2030: Insights from Yesterday, Today, and Future Trends.
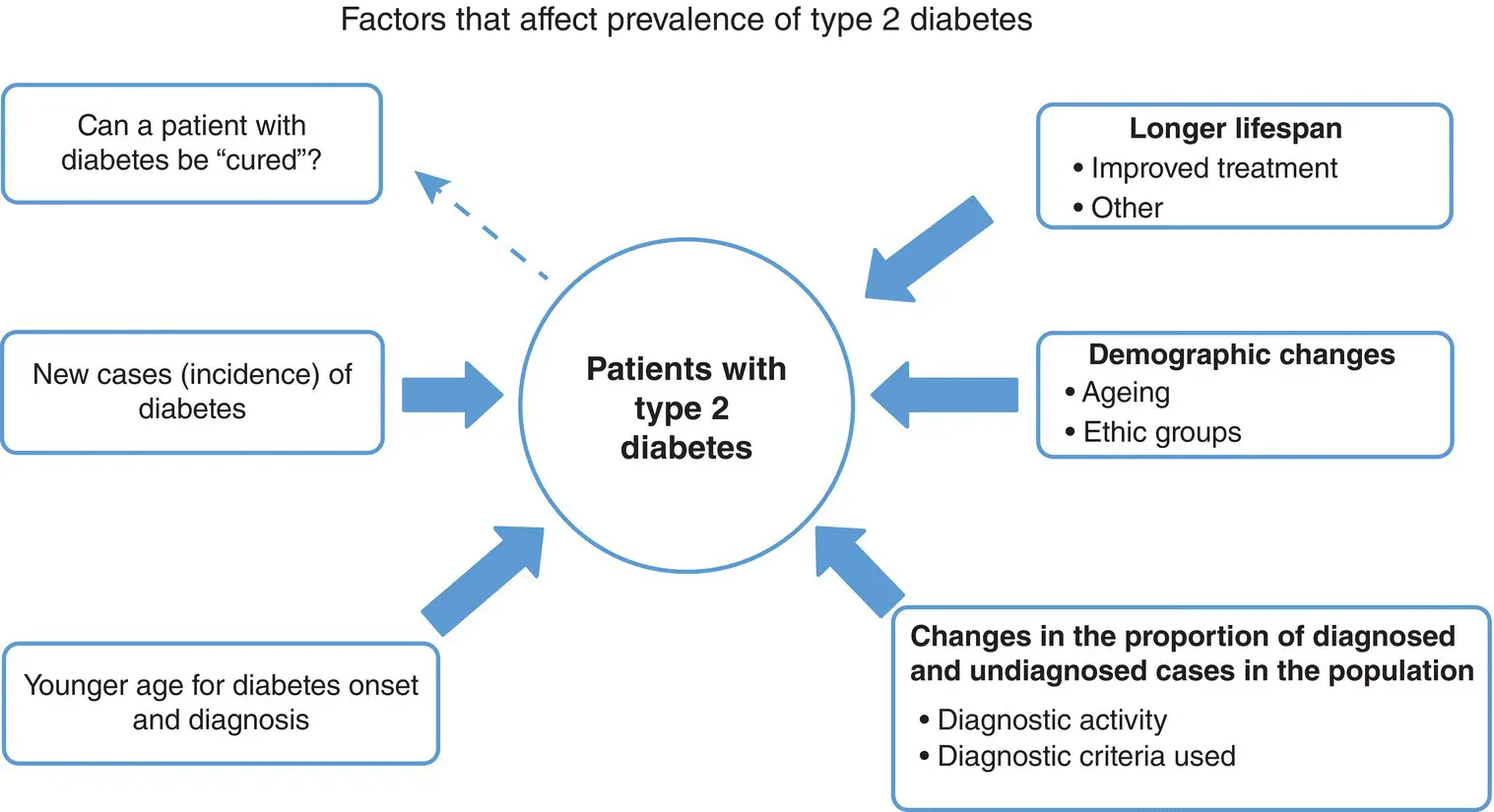
Figure 4.9 Factors affecting the numbers of patients with type 2 diabetes.
The definition of structured patient education is: ‘A planned and graded programme that is comprehensive in scope, flexible in content, responsive to an individual’s clinical and psychological needs and adaptable to his or her educational and cultural background’. Work initially undertaken to support people with type 1 diabetes identified three different levels of patient education:
| Level 1: |
Basic skills at diagnosis |
| Level 2: |
Content on living with diabetes |
| Level 3: |
Content on managing diabetes |
A systematic review of group‐based education for people with type 2 diabetes assessed 21 RCTs and concluded that education achieved reductions in HbA1c of 0.46% at 1 year, reduced body weight at 1 year and significant improvements in self‐empowerment, knowledge and satisfaction.
In the UK, audits of two major education programmes for type 2 diabetes, the X‐PERT and DESMOND diabetes programmes, have shown clinical benefits that are highly cost effective. The cost of delivering these courses is circa £70, which means that diabetes education could be provided to everyone in the UK with type 2 diabetes for £40m per year over 5 years (i.e <0.6% of what the NHS currently spends on diabetes). Lay educators, partnering healthcare professionals, can also deliver effective education to patients with type 2 diabetes.
Table 4.1 Criteria that define structured patient education in the NICE guidance.
| A philosophy of educationAn evidence‐based curriculum meeting the needs of an individualAims and learning outcomes that support self managementDelivered by a trained educator with an understanding of educational theoryQuality assured and audited |
In type 1 diabetes the evidence for group‐based education is extremely strong. The DAFNE programme – which costs £308 per person for a 5‐day course – achieves long‐term improvements in glycaemic control, less hypoglycaemia and improved quality of life. The UK Department of Health estimates that in the long run the DAFNE course could save the NHS £48m per year if it was made accessible to everyone in the UK with type 1 diabetes.
Читать дальше



















