1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...25 Comment:This man presents with typical symptoms of type 2 diabetes and several risk factors (age, obesity, hypertension, family history). The random plasma glucose and HbA1c in the context of symptoms, is diagnostic. He has features of the metabolic syndrome, including hypertension, dyslipidaemia (high triglycerides and low HDL‐cholesterol) and central obesity, and fatty infiltration of the liver is common in this scenario. Susceptibility to infections is typical.
DECODE Study Group. Glucose tolerance and mortality: comparison of WHO and American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria. Lancet 1999; 354: 617–621.
Wong TY, et al. Relation between fasting glucose and retinopathy for diagnosis of diabetes: three population‐based cross‐sectional studies. Lancet 2008; 371: 736–743.
Wild S, et al. Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1047–1053.
Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The prevalence of retinopathy in impaired glucose tolerance and recent‐onset diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabet. Med. 2007; 24: 137–144.
Li G, et al. The long‐term effect of lifestyle interventions to prevent diabetes in the China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: a 20‐year follow‐up study. Lancet 2008; 371: 1783–1789.
Tabak AG, et al. Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the Whitehall II study. Lancet 2009; 373: 2215–2221.
Dabelea D et al SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. Trends in the prevalence of ketoacidosis at diabetes diagnosis: the Search for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics 2014; 133:e938–e945
Herman WH, et al. Early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: a simulation of the results of the Anglo‐Danish‐Dutch study of intensive treatment in people with screen‐detected diabetes in primary care (ADDITION‐Europe). Diabetes Care 2015; 38:1449–1455
1 http://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/en/
2 http://www.diabetes.org/about‐diabetes.jsp
3 http://www.idf.org/home/index.cfm?node=4
1 International Expert Committee International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009; 32:1327–1334
2 Florez JC, et al. TCF7L2 Polymorphisms and progression to diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006; 355: 241–250.
3 Gillies CL, et al. Different strategies for screening and prevention of type 2 diabetes in adults: cost effectiveness analysis. Br. Med. J. 2008; 336: 1180–1184.
4 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes American Diabetes Association Diabetes Care 2017 Jan; 40(Supplement 1): S11–S24. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17‐S005
5 Harris MI, et al. Onset of NIDDM occurs at least 4‐7 years before clinical diagnosis. Diabetes Care 1992; 15: 815–819.
6 Ahlqvist et al. Novel subgroups of adult‐onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data‐driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 2018; 6:361–369
Chapter 4 Public health aspects of diabetes
KEY POINTS
The annual economic burden of diabetes in the USA is estimated at $450 billion in 2016.
The cost‐effectiveness of healthcare interventions in diabetes is a topic of importance.
There are currently circa 425 m patients with diabetes worldwide (2017).
Providing structured education for all patients with diabetes, and implementation of a targeted screening and diabetes prevention programme are public health priorities.
Diabetes has become a major public health challenge in the 21st century ( Figures 4.1and 4.2). Over 26 m people (8% of the population) now have diabetes in the USA and 7 million of these are not even aware of their diagnosis ( Figure 4.3). The prevalence has increased 5‐ to 7‐fold in recent years, and diabetes is responsible for significant reductions in life‐expectancy as well as longterm disabling complications such as blindness, renal failure, lower limb amputation, and premature cardiovascular disease ( Figures 4.4and 4.5).
Overweight and obesity are major factors driving this trend. A recent report from Public Health England suggests that 90% of adults with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese and there is a direct linear relationship between BMI and mortality among type 2 diabetes patients who have never smoked. In those with a smoking history, the relationship is J‐shaped because smoking off‐sets any benefits of a lower BMI. The relationship between HbA1c and any diabetes‐related endpoint is also linear.
Aside from the human costs of diabetes, there is a huge economic impact on the healthcare budget ( Figures 4.6and 4.7). About 75% of the direct costs are attributable to managing the long‐term vascular complications of diabetes, only a relatively small fraction is spent on diabetes treatments and surveillance. Furthermore, 90% of resources are spent on patients with type 2 diabetes. In the USA, the total direct costs of diabetes in 2012 were estimated to be $176b. For an individual patient, the lifetime healthcare costs of diabetes were estimated at $85 200. In the UK, expenditure on diabetes accounts for 9% of the entire NHS budget (approximately £8.8b per year) and is forecast to reach 17% of NHS spending by 2035.
Given that hyperglycaemia has cumulative adverse effects, it makes good clinical and economic sense to maximise glycaemic control and weight reduction in the early years after diagnosis. The UK National Diabetes Audit reported data on 1.9m patients with diabetes and showed that, in the period 2009–2015, 90–95% of patients with type 2 diabetes had 6‐monthly HbA1c monitoring performed and two‐thirds of them achieved the NICE treatment target (applicable at the time) of HbA1c <7.5% (58 mmol/mol). However, there were significant regional variations in achievement of HbA1c targets, and the lowest rates of attainment were among younger age groups (those <40 years and in the 40–64 yr age band).
Declining mortality rates for patients with diabetes, combined with aging population demographics and the increasing prevalence of diabetes risk factors, will likely fuel the continuation of a diabetes epidemic ( Figure 4.8). Clinical management is becoming more complex and more intensive, and therefore more expensive. In particular there has been a shift towards using more expensive analogue insulins ( Figure 4.9)
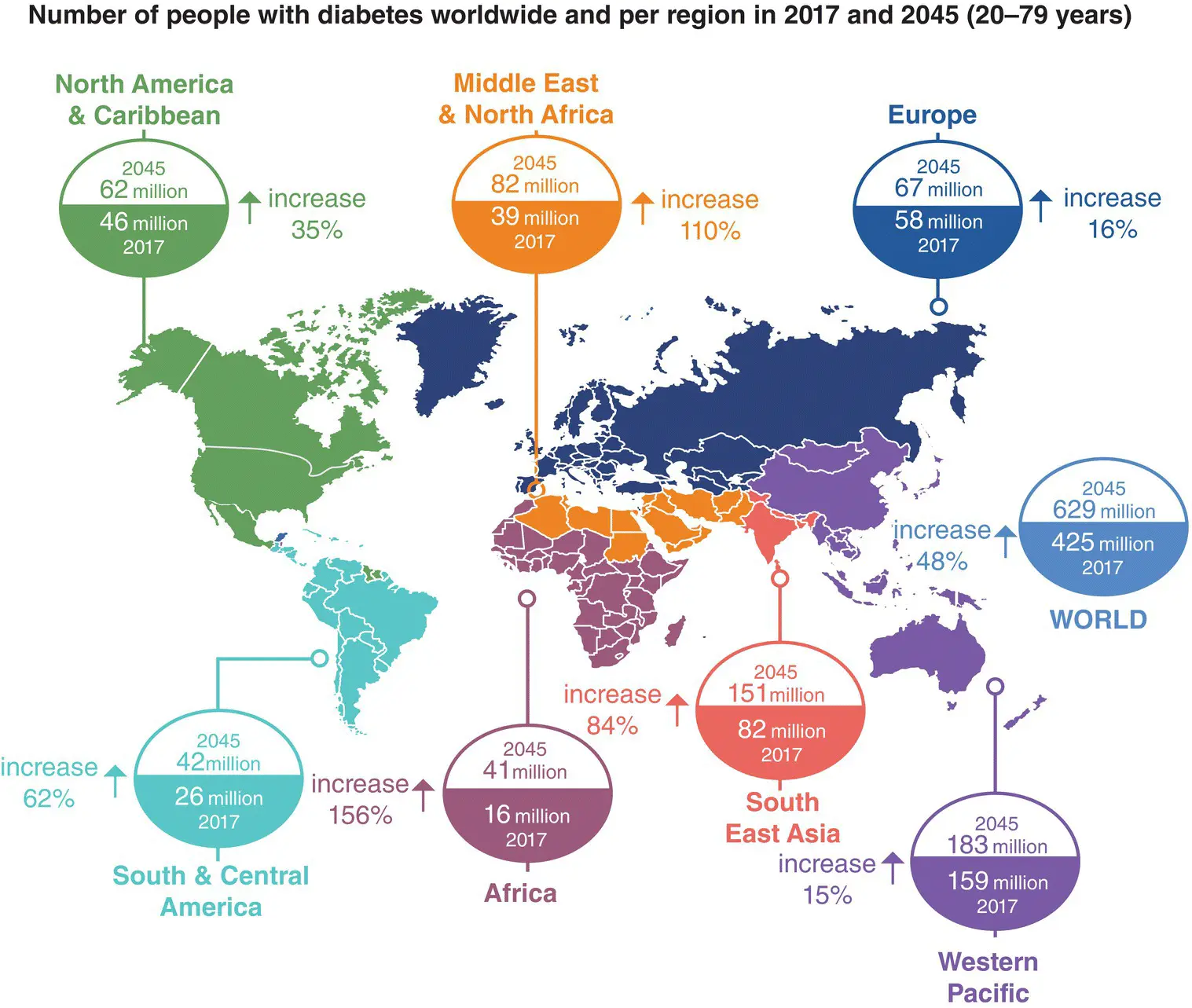
Figure 4.1 Rising numbers of people with diabetes worldwide. IDF Atlas, 2017.
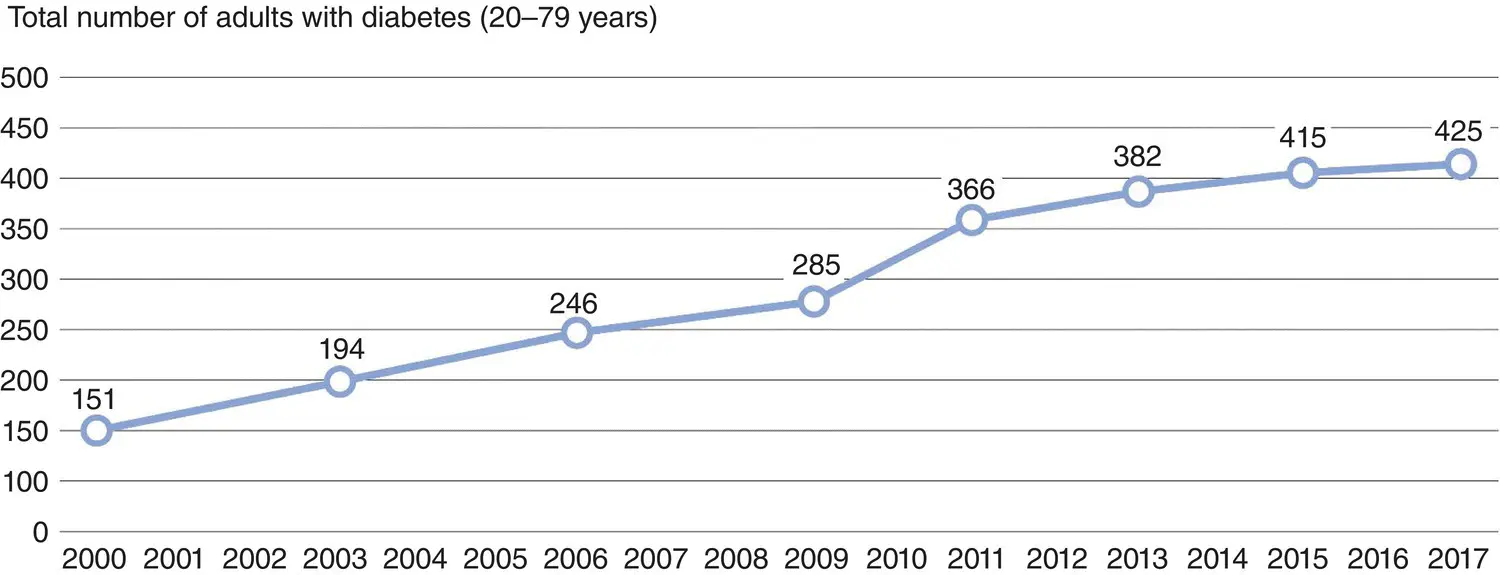
Figure 4.2 There are estimated to be 425 m patients with diabetes worldwide in 2017. IDF Atlas, 2017.
Public health strategies are focused in several key areas:
Primary prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
Primary prevention of diabetes is a public health priority for a number of good reasons: (i) the overall burden of diabetes justifies strategies at a population level: (ii) current treatments are costly, confer risks of serious adverse events (e.g. hypoglycaemia) and often have limited efficacy on key clinical outcomes; (iii) access to, and adherence to, diabetes treatments is still a challenge for many patients; and (iv) prevention of type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modification is likely to confer added benefits in terms of reducing the risks of hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Читать дальше














