In 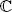 n, the complex Euclidean inner product is defined by:
n, the complex Euclidean inner product is defined by:
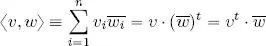
where v = ( v 1, v 2, . . . , v n), w = ( w 1, w 2, . . . , w n) ∈ 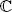 nare written with their components in relation to any given, but fixed, basis
nare written with their components in relation to any given, but fixed, basis  in
in 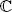 n.
n.
The symbol 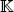 will be used throughout to represent either ℝ or
will be used throughout to represent either ℝ or 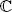 in the context of properties which are valid independently of the reality or complexity of the inner product.
in the context of properties which are valid independently of the reality or complexity of the inner product.
THEOREM 1.1.– Let ( V , 〈 , 〉) be an inner product space. We have:
1) 〈 v , 0 V〉 = 0 ∀ v ∈ V ;
2) if 〈 u, w 〉 = 〈 v, w 〉 ∀ w ∈ V , then u and v must coincide;
3) 〈 v, w 〉 = 0 ∀ v ∈ V  w = 0 V, i.e. the null vector is the only vector which is orthogonal to all of the other vectors.
w = 0 V, i.e. the null vector is the only vector which is orthogonal to all of the other vectors.
PROOF.–
1) 〈 v , 0 V〉 = 〈 v , 0 V+ 0 V〉 = 〈 v , 0 V〉 + 〈 v , 0 V〉 by linearity, i.e. 〈 v , 0 V〉 − 〈 v , 0 V〉 = 0 = 〈 v , 0 V〉.
2) 〈 u, w 〉 = 〈 v, w 〉 ∀ w ∈ V implies, by linearity, that 〈 u − v, w 〉 = 0 ∀ w ∈ V and thus, notably, considering w = u − v , we obtain 〈 u − v, u − v 〉 = 0, implying, due to the definite positiveness of the inner product, that u − v = 0 V, i.e. u = v .
3) If w = 0 V, then 〈 v, w 〉 = 0 ∀ v ∈ V using property (1). Inversely, by hypothesis, it holds that 〈 v, w 〉 = 0 = 〈 v , 0 V〉 ∀ v ∈ V , but then property (2) implies that w = 0 V.
Finally, let us consider a typical property of the complex inner product, which results directly from a property of complex numbers.
THEOREM 1.2.– Let ( V , 〈 , 〉) be a complex inner product space. Thus:
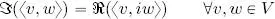
PROOF.– Consider any complex number z = a + ib , so − iz = b − ia , hence b = ℑ ( z ) = ℜ (− iz ). Taking z = 〈 v, w 〉, we obtain ℑ (〈 v, w 〉) = ℜ (− i 〈 v, w 〉) = ℜ (〈 v, iw 〉) by sesquilinearity.
1.2. The norm associated with an inner product and normed vector spaces
If ( V , 〈, 〉) is an inner product space over 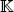 , then a norm on V can be defined as follows:
, then a norm on V can be defined as follows:

Note that ‖ v ‖ is well defined since 〈 v, v 〉 ≽ 0 ∀ v ∈ V . Once a norm has been established, it is always possible to define a distance between two vectors v, w in V : d ( v, w ) = ‖ v − w ‖.
The vector v ∈ V such that ‖ v ‖= 1 is known as a unit vector . Every vector v ∈ V can be normalized to produce a unit vector, simply by dividing it by its norm.
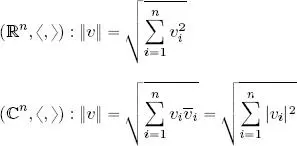
Three properties of the norm, which should already be known, are listed below. Taking any v, w ∈ V , and any α ∈ 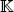 :
:
1) ‖ v ‖≽ 0, ‖ v ‖= 0  v = 0 V;
v = 0 V;
2) ‖ αv ‖= | α |‖ v ‖(homogeneity);
3) ‖ v + w ‖≼ ‖ v ‖+ ‖ w ‖(triangle inequality).
DEFINITION 1.4 (normed vector space).– A normed vector space is a pair ( V , ‖ ‖) given by a vector space V and a function, called a norm , 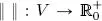 , satisfying the three properties listed above.
, satisfying the three properties listed above.
A norm ‖ ‖ is Hilbertian if there exists an inner product 〈 , 〉 on V such that 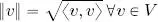 .
.
Canonically, an inner product space is therefore a normed vector space. Counterexamples can be used to show that the reverse is not generally true.
Note that, by definition, 〈 v, v 〉 = ‖ v ‖ ‖ v ‖, but, in general, the magnitude of the inner product between two different vectors is dominated by the product of their norms. This is the result of the well-known inequality shown below.
THEOREM 1.3 (Cauchy-Schwarz inequality).– For all v, w ∈ ( V , 〈 , 〉) we have:

PROOF.– Dozens of proofs of the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality have been produced. One of the most elegant proofs is shown below, followed by the simplest one:
– first proof : if w = 0 V, then the inequality is verified trivially with 0 = 0. If w ≠ 0 V, then we can define 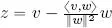 , i.e.
, i.e. 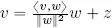 and we note that:
and we note that:
Читать дальше

 n, the complex Euclidean inner product is defined by:
n, the complex Euclidean inner product is defined by: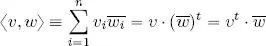
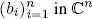 in
in  will be used throughout to represent either ℝ or
will be used throughout to represent either ℝ or  w = 0 V, i.e. the null vector is the only vector which is orthogonal to all of the other vectors.
w = 0 V, i.e. the null vector is the only vector which is orthogonal to all of the other vectors.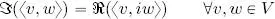

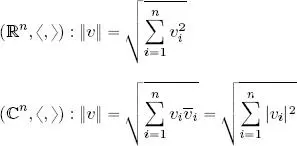
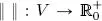 , satisfying the three properties listed above.
, satisfying the three properties listed above.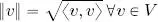 .
.
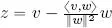 , i.e.
, i.e. 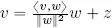 and we note that:
and we note that:










