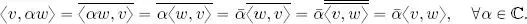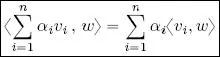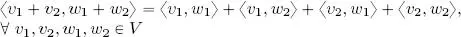
and:
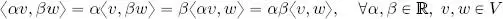
2) symmetrical: 〈 v, w 〉 = 〈 w, v 〉, ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
3) defined: 〈 v, v 〉 = 0  v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;
v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;
4) positive: 〈 v, v 〉 > 0 ∀ v ∈ V , v ≠ 0 V.
Upon reflection, we see that, for a real form over V , the symmetry and bilinearity requirements are equivalent to requiring symmetry and linearity on the left-hand side , that is:
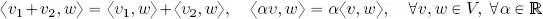
The simplest and most important example of a real inner product is the canonical inner product , defined as follows: let v = ( v 1, v 2, . . . , v n), w = ( w 1, w 2, . . . , w n) be two vectors in ℝ nwritten with their components in relation to any given, but fixed, basis 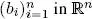 in ℝ n. The canonical inner product of v and w is:
in ℝ n. The canonical inner product of v and w is:
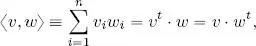
where v tand w tin the final equations are the transposed vectors of v and w , giving us the matrix product of a line vector (treated as a 1 × n matrix) and a column vector (treated as an n × 1 matrix).
The extension of these definitions to complex vector spaces is not particularly straightforward. First, note that if V is a complex vector space, then there is no bilinear and definite-positive transformation over V × V . In this case, any vector v ∈ V would give the following:
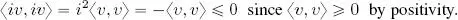
As we shall see, the property of positivity is essential in order to define a norm (and thus a distance, and by extension, a topology) from a complex inner product. To obtain an algebraic structure for complex scalar products which remains compatible with a topological structure, we are therefore forced to abandon the notion of bilinearity, and to search for an alternative.
We could consider antilinearity 2, i.e.
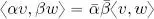
But it has the same problem as bilinearity, 〈 iv, iv 〉 = (− i )(− i )〈 v, v 〉 = i 2〈 v, v 〉 = −〈 v, v 〉 2≼ 0.
A simple analysis shows that, in order to avoid losing the positivity, it is sufficient to request the linearity with respect to one variable and the antilinearity with respect to the other. This property is called sesquilinearity 3.
The choice of the linear and antilinear variable is entirely arbitrary.
By convention, the antilinear component is placed on the right-hand side in mathematics, but on the left-hand side in physics.
We have chosen to adopt the mathematical convention here, i.e. 〈 αv, βw 〉 = α β̅ 〈 v, w 〉.
Next, it is important to note that sesquilinearity and symmetry are incompatible : if both properties were verified, then 〈 v, αw 〉 =  〈 v, w 〉, and also 〈 v, αw 〉 = 〈 αw, v 〉 = α 〈 w, v 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉. Thus, 〈 v, αw 〉 =
〈 v, w 〉, and also 〈 v, αw 〉 = 〈 αw, v 〉 = α 〈 w, v 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉. Thus, 〈 v, αw 〉 =  〈 v, w 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉 which can only be verified if α ∈ ℝ.
〈 v, w 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉 which can only be verified if α ∈ ℝ.
Thus 〈, 〉 cannot be both sesquilinear and symmetrical when working with vectors belonging to a complex vector space.
The example shown above demonstrates that, instead of symmetry, the property which must be verified for every vector pair v, w is 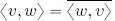 , that is, changing the order of the vectors in 〈, 〉 must be equivalent to complex conjugation.
, that is, changing the order of the vectors in 〈, 〉 must be equivalent to complex conjugation.
A transform which verifies this property is said to be Hermitian 4.
These observations provide full justification for Definition 1.3.
DEFINITION 1.3.– Let V be a complex vector space. The pair ( V , 〈, 〉) is said to be a complex inner product space (or a complex pre-Hilbert space) if 〈, 〉 is a complex form which is:
1) sesquilinear:
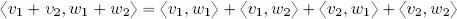
∀ v 1, v 2, w 1, w 2∈ V , and:
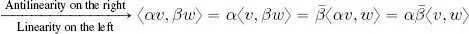
∀ α, β ∈ 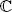 , ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
, ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
2) Hermitian:  , ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
, ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
3) definite: 〈 v, v 〉 = 0  v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;
v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;
4) positive: 〈 v, v 〉 > 0 ∀ v ∈ V , v ≠ 0 V.
As in the case of the canonical inner product, for a complex form over V , the symmetry and sesquilinearity requirement is equivalent to requiring the Hermitian property and linearity on the left-hand side ; if these properties are verified, then:
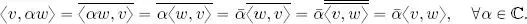
Considering the sum of n , rather than two, vectors, sesquilinearity is represented by the following formulae:
[1.1] 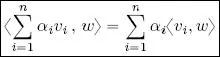
[1.2] 
Читать дальше

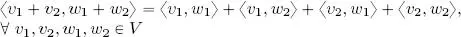
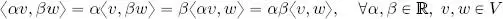
 v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;
v = 0 V, the null vector of the vector space V ;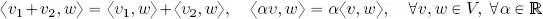
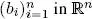 in ℝ n. The canonical inner product of v and w is:
in ℝ n. The canonical inner product of v and w is: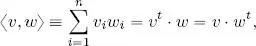
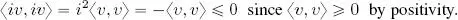
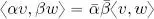
 〈 v, w 〉, and also 〈 v, αw 〉 = 〈 αw, v 〉 = α 〈 w, v 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉. Thus, 〈 v, αw 〉 =
〈 v, w 〉, and also 〈 v, αw 〉 = 〈 αw, v 〉 = α 〈 w, v 〉 = α 〈 v, w 〉. Thus, 〈 v, αw 〉 = 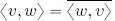 , that is, changing the order of the vectors in 〈, 〉 must be equivalent to complex conjugation.
, that is, changing the order of the vectors in 〈, 〉 must be equivalent to complex conjugation.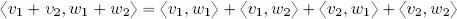
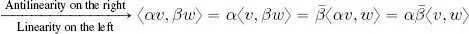
 , ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
, ∀ v, w ∈ V ; , ∀ v, w ∈ V ;
, ∀ v, w ∈ V ;