Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Explore a unified view of differential equations through the use of the generalized ODE from leading academics in mathematics Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications
Generalized Ordinary Differential Equations in Abstract Spaces and Applications

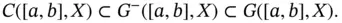
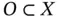 . By
. By 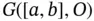 , we mean the set of all elements
, we mean the set of all elements 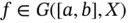 for which
for which 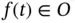 for every
for every 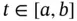 . Thus, it is clear that
. Thus, it is clear that 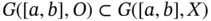 and the range of
and the range of 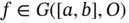 belongs to
belongs to 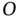 . Note that, for a given
. Note that, for a given 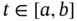 ,
, 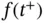 and
and 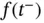 do not necessarily belong to
do not necessarily belong to 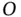 .
.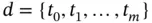 of points in the closed interval
of points in the closed interval 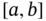 such that
such that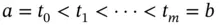
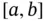 . We write simply
. We write simply 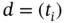 . Given a division
. Given a division 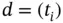 of
of 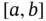 , its elements are usually denoted by
, its elements are usually denoted by 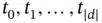 , where, from now on,
, where, from now on, 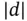 denotes the number of intervals in which
denotes the number of intervals in which 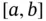 is divided through the division
is divided through the division 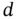 . The set of all divisions
. The set of all divisions 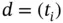 of
of 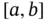 is denoted by
is denoted by 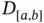 .
.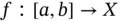 is called a step function , if there is a division
is called a step function , if there is a division 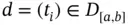 such that for each
such that for each 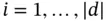 ,
, 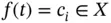 , for all
, for all 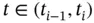 . We denote by
. We denote by 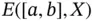 the set of all step functions
the set of all step functions 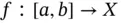 .
.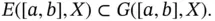 Moreover, we have the following important result which is a general version of the result presented in [127, Theorem I.3.1].
Moreover, we have the following important result which is a general version of the result presented in [127, Theorem I.3.1].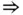 (ii), (ii)
(ii), (ii) 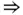 (iii) and, then, (iii)
(iii) and, then, (iii) 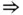 (i).
(i).










