Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A rich examination of the technologies supporting secure digital information transfers from respected leaders in the field Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: A Handbook for the 21ST Century
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction

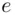 , namely that
, namely that 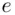 is relatively prime to
is relatively prime to 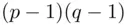 , there exists a unique integer
, there exists a unique integer 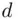 (
( 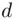 for deciphering) which is greater than 1 but less than
for deciphering) which is greater than 1 but less than 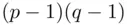 and is such that the remainder of
and is such that the remainder of 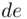 when divided by
when divided by 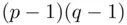 is 1. It is easy for Bob to calculate
is 1. It is easy for Bob to calculate 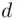 , using a method related to the Euclidean Algorithm (see Chapter 19), since Bob knows
, using a method related to the Euclidean Algorithm (see Chapter 19), since Bob knows 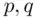 which are the factors of
which are the factors of 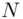 . There may be other deciphering indices that are easier to work with (see Remark 3.1part 2and a more general method in item 3 of the formal algorithm overleaf).
. There may be other deciphering indices that are easier to work with (see Remark 3.1part 2and a more general method in item 3 of the formal algorithm overleaf).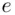 and
and 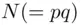 in a public directory under his name. He keeps secret the primes
in a public directory under his name. He keeps secret the primes 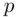 and
and 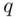 :
:  is Bob's private key and the pair
is Bob's private key and the pair 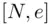 is Bob's public key.
is Bob's public key.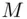 to transmit to Bob. Alice converts
to transmit to Bob. Alice converts 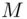 to a number between 1 and
to a number between 1 and 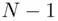 represented in binary (which we also denote by
represented in binary (which we also denote by 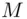 ). If
). If 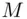 is too large, Alice breaks
is too large, Alice breaks 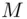 into blocks, each of which is less than
into blocks, each of which is less than 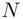 . Let us assume, for simplicity, that
. Let us assume, for simplicity, that 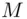 is less than
is less than 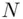 . Then, Alice enciphers
. Then, Alice enciphers 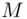 by calculating the cipher text
by calculating the cipher text 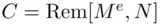 . Note that Rem
. Note that Rem 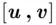 means the remainder when
means the remainder when 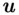 is divided by
is divided by 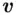 , so in other words Alice multiplies
, so in other words Alice multiplies 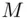 by itself
by itself 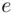 times and gets the remainder upon division by
times and gets the remainder upon division by 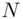 . This can be done quickly using the “repeated squaring” method and the principle described earlier. Note that
. This can be done quickly using the “repeated squaring” method and the principle described earlier. Note that 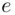 can be any positive integer relatively prime to
can be any positive integer relatively prime to  and
and  . However, suppose
. However, suppose 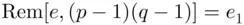 . Then it can be shown that
. Then it can be shown that 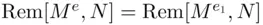 , and so we may as well assume that
, and so we may as well assume that 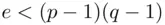 .
.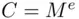 , he in turn multiplies
, he in turn multiplies 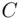 by itself
by itself 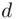 times and gets the remainder upon division by
times and gets the remainder upon division by 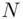 . As explained in our earlier example, the calculation can be simplified. This remainder is in fact equal to
. As explained in our earlier example, the calculation can be simplified. This remainder is in fact equal to 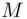 , the original message.
, the original message.










