Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A rich examination of the technologies supporting secure digital information transfers from respected leaders in the field Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: A Handbook for the 21ST Century
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction

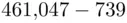 is divisible by
is divisible by 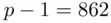 .
. are not divisible by
are not divisible by  ,
, 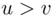 and assume that
and assume that 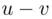 is divisible by
is divisible by 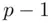 . Then
. Then 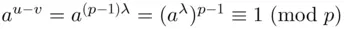 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 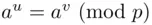 upon multiplying both sides by
upon multiplying both sides by 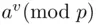 .
.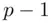 and
and  is
is 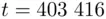 . Then he can find that the remainder of
. Then he can find that the remainder of 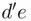 when divided by
when divided by 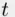 is 1, where
is 1, where 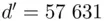 , and use this for a deciphering index instead.
, and use this for a deciphering index instead. from
from 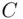 is easier than the factoring problem . For some methods of obtaining
is easier than the factoring problem . For some methods of obtaining 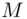 from
from 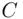 that work in special cases, we refer to the problems. The factoring problem is to obtain
that work in special cases, we refer to the problems. The factoring problem is to obtain 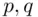 given
given 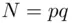 . Once
. Once 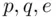 are known, it is easy to find the message
are known, it is easy to find the message 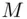 from
from 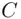 by calculating
by calculating 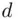 : this is what Bob does. Mathematically, nobody has been able to prove that the factoring problem cannot be solved in a reasonable amount of time. Similarly, it has not been shown that
: this is what Bob does. Mathematically, nobody has been able to prove that the factoring problem cannot be solved in a reasonable amount of time. Similarly, it has not been shown that 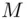 cannot be obtained from
cannot be obtained from 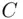 in a reasonable amount of time by some method or another. We point out also that given
in a reasonable amount of time by some method or another. We point out also that given 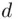 we can find
we can find 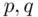 , even when
, even when 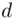 is chosen so that
is chosen so that 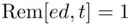 , where
, where  divides
divides 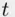 and
and  divides
divides 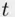 . (See Buchmann [Buc04]). Thus, the problem of finding
. (See Buchmann [Buc04]). Thus, the problem of finding 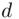 is equivalent to the factoring problem.
is equivalent to the factoring problem.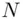 . Let the message be some number
. Let the message be some number 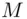 between 0 and
between 0 and 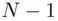 , i.e.
, i.e. 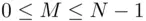 . Our enciphering algorithm now reads: “increase
. Our enciphering algorithm now reads: “increase 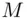 by 7 and get the cipher text
by 7 and get the cipher text 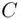 by calculating the remainder upon division by
by calculating the remainder upon division by 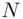 .” For example if
.” For example if 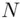 is 55 and
is 55 and 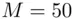 , then
, then  . So Atransmits the cipher text 2. Now, Bmust undo (or decrypt or decipher) 2 to get the original message. Before, our decryption algorithm read “subtract 7 from
. So Atransmits the cipher text 2. Now, Bmust undo (or decrypt or decipher) 2 to get the original message. Before, our decryption algorithm read “subtract 7 from 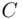 ,” i.e. “add the inverse of 7 to
,” i.e. “add the inverse of 7 to 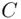 .” We do this now. First, we must get the additive inverse of 7 modulo
.” We do this now. First, we must get the additive inverse of 7 modulo 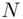 i.e., the inverse of 7 modulo 55 (see Chapter 19). In other words, we must find
i.e., the inverse of 7 modulo 55 (see Chapter 19). In other words, we must find 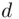 such that
such that 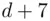 leaves a remainder 0 when divided by 55. In this case,
leaves a remainder 0 when divided by 55. In this case,  is 48. Then, to decipher
is 48. Then, to decipher 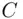 , we increase
, we increase 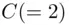 by 48 and obtain the remainder upon division by 55. In this case, we obtain the number 50. This is the original message.
by 48 and obtain the remainder upon division by 55. In this case, we obtain the number 50. This is the original message.










