When traction is applied to a palatally impacted canine in the closed eruption technique, the tooth may move rapidly, sometimes from a considerable distance, deep in the bone. As it exits the bone, it causes the very palpable bulge beneath the thick mucosa of the palate to increase in size. The thick mucosa will, in turn, create difficulty for the tooth to erupt through it. In such a circumstance, it is recommended that a small circular incision be made around the crown tip of the impacted tooth and the tissue removed to an extent that will re‐expose the tooth with an aperture not exceeding the circumference of its crown. Further traction will then erupt the tooth very rapidly. Delay in performing this simple procedure will over‐tax the anchorage unit and simply cause the anchor teeth to intrude and the overall archform to become disrupted.
The final treatment outcome
Several research groups, from various countries, have conducted studies on the effect of the open exposure technique on the post‐treatment pulpal and periodontal status of maxillary canines, following the orthodontic resolution of impacted teeth. A Norwegian group [31] identified an increased depth of periodontal pockets on the distal side of the impacted teeth as well as bone loss on the mesial side. The group from the University of Washington [32] examined patients with impacted canines that had been treated by undefined ‘conservative’ surgical procedures. They identified attachment loss, reduced alveolar bone height and frequent instances of pulp obliteration, discoloration and misalignment. They also found that the previously impacted canines were quite discernible and conspicuous in 75% of the treated cases, which was presumably associated with marred external appearance.
In our own study, our Jerusalem group of researchers examined the results of the treatment, by the closed eruption technique, of palatal canines and found an excellent appearance, with slightly deeper pockets and a 4% loss of alveolar bone support [8]. In addition, in relation to buccally ectopic maxillary canines, we found a minor reduction in the width of the attached gingiva, but otherwise a good general periodontal result [9].
Studies carried out by others have further corroborated the good clinical periodontal results of the use of the closed eruption technique, in both buccal and palatal canine cases [33].
Using a mixed sample of cases of impacted incisors and canines in their study [32], the Washington group carried out a comparison of the open (specifically the apically repositioned flap exposure) and closed procedures. With regard to those treated with the open surgical approach, they found poorer results in both periodontic measurement and aesthetic assessment and, with regard to buccal canines, they identified an increase in clinical crown length and a deterioration and unevenness in the gingival margins ( Figure 5.7). They also noted loss of attachment and alveolar bone, frequently accompanied by vertical positional relapse of the erupted tooth, after the completion of treatment. They reasoned that during the tissue healing that occurs after the surgical repositioning, the horizontal mucosal lines undergo stretching and distortion during the incisal movement of the tooth. Once orthodontic control is released, vertical relapse occurs due to a contraction of these extended mucosal lines. By contrast, in the closed eruption cases, they found that clinical crown length and gingival appearance in the closed eruption group were similar to those of the unaffected (control) side, with a completely normal periodontal attachment and no evidence of post‐treatment relapse in incisor position.
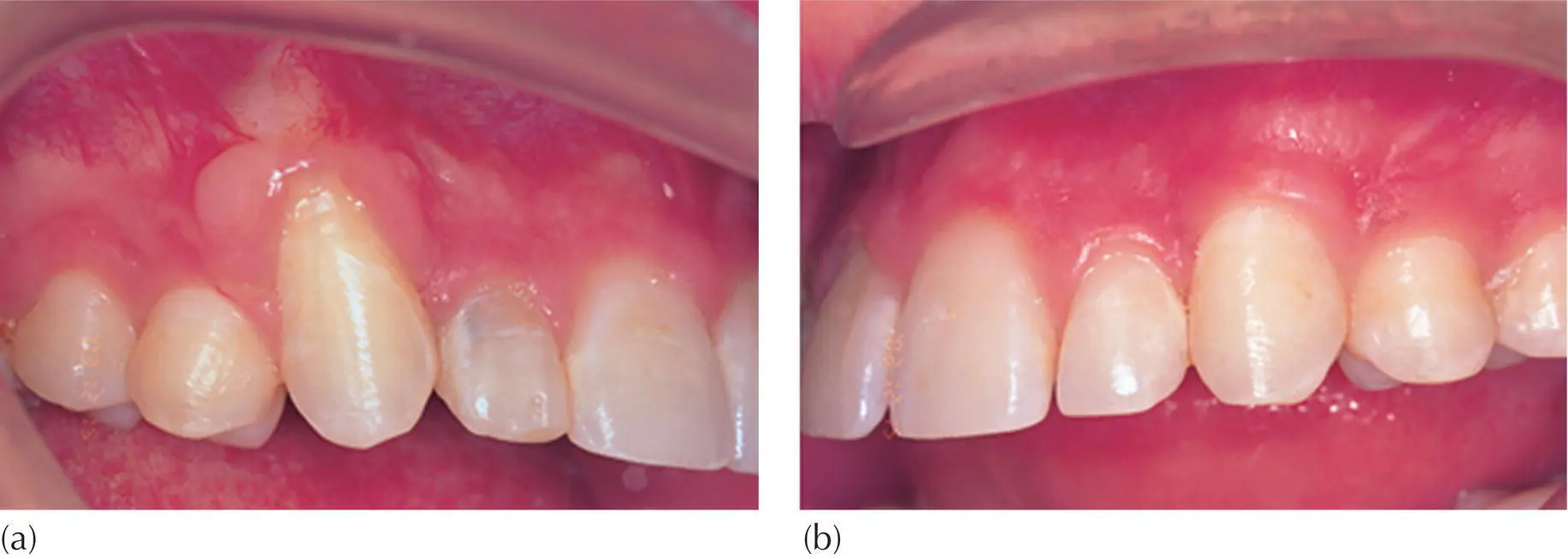
Fig. 5.7 Treatment for the right buccally impacted maxillary canine was performed using an open exposure, apically repositioned flap technique. (a) The post‐treatment outcome shows a thick band of attached gingiva, but a long clinical crown with an unaesthetic lumpy appearance of the gingival margin. (b) The normally erupted canine of the left side is shown for comparison.
Impacted incisors are seen less frequently in the orthodontic office than are impacted canines. This accounts for the relative absence of studies of the results obtained from treatment of impacted incisors. However, based on the differences in the aetiologies of impaction in canines and incisors, it would be reasonable to assume that there could also be differences in the results achieved at the end of treatment.
It was with this in mind that the Jerusalem group [34, 35] undertook a study exclusively relating to maxillary incisors. The findings of the study in the open eruption group showed poor periodontal and aesthetic results, with increased pocket depth and a 10% loss of alveolar bone height. The clinical crowns were elongated and the band of attached gingiva reduced. On the other hand, those treated by the closed surgical procedure showed only minimal changes, with greater bone support, a lesser increase in clinical crown length and better external appearance than in the open surgery group. Crown length and attached gingiva were closely similar to those of the unaffected side, while the bone support level was reduced by between 5% and 6%.
In a later comparative study of open versus closed exposure, similar impacted incisor cases were matched for age, aetiology and location. The overall results favoured the closed surgical exposure method. The open exposure cases showed statistically poorer outcomes, characterized by increased crown length and more significant loss of bone support [9].
A recent split‐mouth investigation of labially impacted maxillary canines was carried out in order to compare the results of a closed eruption surgical exposure of the affected canine with those of the normally erupting antimere. The conclusions were that, at the completion of orthodontic treatment, the previously impacted canines exhibited slight and clinically insignificant periodontal recession, compared with the contralateral normal tooth [33].
It will be clear from the summary of the evidence presented here that a closed surgical exposure approach produces good, predictable, long‐term periodontal and aesthetic results and has advantages over the apically repositioned flap method [34, 35]. It might be appropriate to attribute these advantages to the closer similarity of the full‐flap closed exposure procedure to the natural eruption process.
A Cochrane Collaboration systematic review
The Cochrane Collaboration offers systematic reviews of primary research in human health care and health policy, as well as clinical research in the effects of interventions, for the purposes of prevention, treatment and rehabilitation, in various fields. Existing primary research on a particular topic is collated and, using stringent guidelines, is assessed in order to establish whether or not there is conclusive evidence about a specific treatment. The reviews are updated regularly, ensuring that treatment decisions can be based on the most current and reliable evidence. In this way, these reviews provide us with the ideal framework to objectively adjudicate, without regard to personal subjective preference or bias, the rival claims of those advocating open exposure as opposed to those who advocate closed exposure.
These conflicting opinions were the subject of a Cochrane review that was undertaken in 2008 in the UK [36] and thereafter updated periodically [37–40]. The review only referred to those factors directly related to the surgical aspect and no regard was paid to the age of the patient, the presenting malocclusion or the type of active orthodontic treatment undertaken. The aim was specifically to search the literature for studies involving open and closed surgical exposure of impacted maxillary canines and to compare the outcomes of the two techniques in relation to the claims made by both surgeons and orthodontists. In the 2008 study, however, none of the 191 retrieved studies fulfilled the criteria to be included [36].
Читать дальше