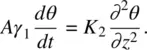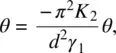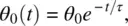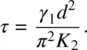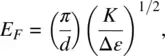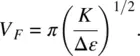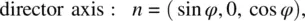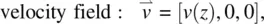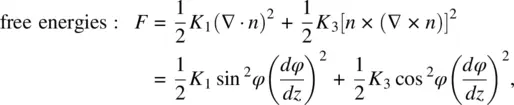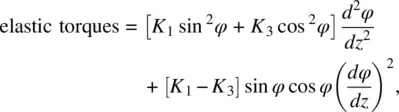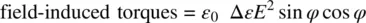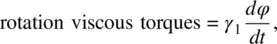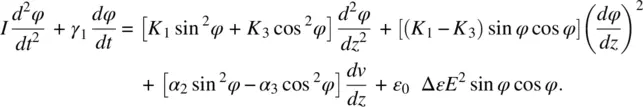For the case where H is abruptly reduced from its value above H F, to 0, Eq. (3.75a)becomes
(3.78) 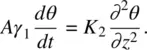
Writing θ ( z , t ) = θ 0sin ( πz / d ) gives
(3.79) 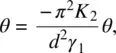
that is,
(3.80) 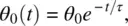
where the relaxation time constant τ is given by
(3.81) 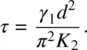
Most practical liquid crystal devices employ ac electric field. Accordingly, the Freedericksz transition field E Fis given by simply replacing Δ χ mwith Δ ε ; i.e. we have
(3.82a) 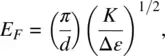
(3.82b) 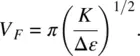
For 5CB [20, 21], k ~ 10 −11N, Δ ε ~ 11 ( ε ||~ 16, ε ⊥~ 5), ε 0= 8.85 × 10 −12F/m, Δ σ / σ ⊥~ 0.5, and V F~ 1 V.
In Chapters 6and 7, we discuss these field‐induced nematic director axis reorientations in detail in the context of electro‐optical switching and display applications.
3.6.2. Reorientation with Flow Coupling
Field‐induced director axis reorientation, accompanied by fluid flow, is quite complicated as it involves much more physical parameters. Consider the interaction geometry shown in Figure 3.13. A homeotropically aligned nematic liquid crystal film is acted on by an electric or a magnetic field in the x ‐direction. Let ϕ denote the director axis reorientation angle from the original alignment direction z . Assume hard‐boundary conditions at the two cell walls at z = 0 and at z = d . The flow is in the x ‐direction, with a z dependence.
The following are the pertinent parameters involved:
(3.83a) 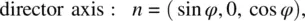
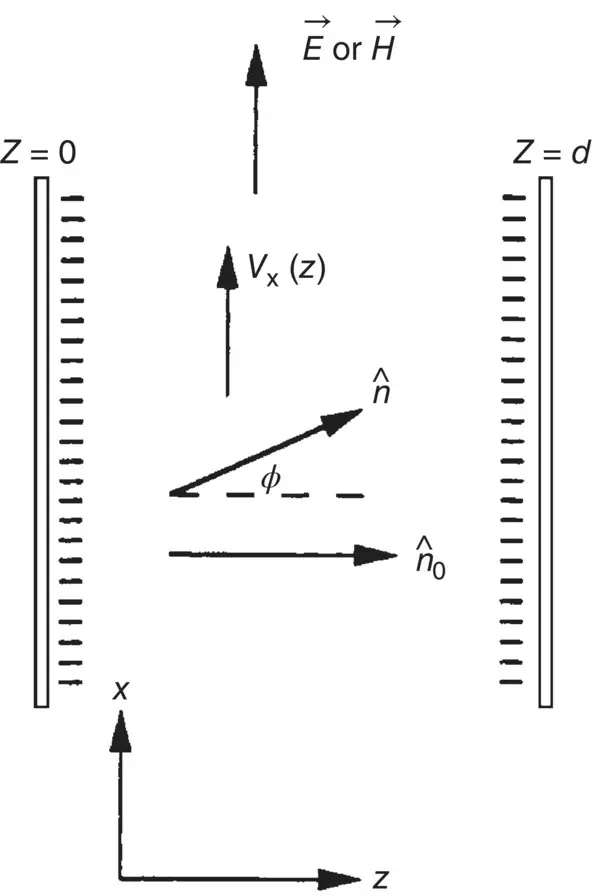
Figure 3.13. Director axis reorientation causing flows.
(3.83b) 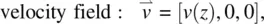
(3.83c) 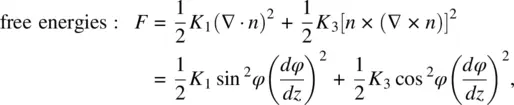
(3.83d) 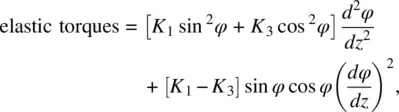
(3.83e) 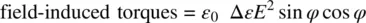
(3.83f) 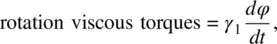
(3.83g) 
Using Eq. (3.65), the equation of motion taking into account these torques, as well as the moment of inertia I of molecules involved, is given by
(3.84) 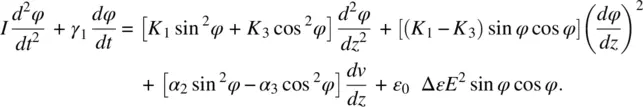
This equation may be solved for various experimental conditions. Optically induced director axis reorientation and flow effects have been studied by two groups [21, 22] using picosecond laser pulses. A solution to the previous equation is also presented in [22].
1 1. Frank, F. C. 1958. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 25: 19.
2 2. Ericksen, J. L. 1969. Liquid Crystals. G. Brown (ed.). New York: Gordon and Breach.
3 3. deGennes, P. G. 1974. Physics of Liquid Crystals. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
4 4. See, for example, Barbero, G., and F. Simoni. 1992. Appl. Phys. Lett. 41: 504; Barbero, G., F. Simoni, and P. Aiello. 1984. J. Appl. Phys. 55: 304; see also Faetti, S. 1991. Physics of Liquid Crystalline Materials. I. C. Khoo and F. Simoni (eds.). Philadelphia: Gordon and Breach.
5 5. Jackson, J. D. 1975. Classical Electrodynamics. New York: Wiley.
6 6. Helfrich, W. 1969. J. Chem. Phys. 51: 4092; see also Ref. 8, Chapter 5.
7 7. Parneix, J. P., A. Chapoton, and E. Constant. 1975. J. Phys. (Paris) 36: 1143.
8 8. Blinov, L. M. 1983. Electro‐Optical and Magneto‐Optical Properties of Liquid Crystals. Chichester: Wiley (Interscience).
9 9. Khoo, I. C., and S. T. Wu. 1993. Optics and Nonlinear Optics of Liquid Crystals. Singapore: World Scientific.
10 10. Vuks, M. F. 1966. Opt. Spektrosk. 60: 644.
11 11. Chandrasekhar, S., and N. V. Madhusudana. 1969. J. Phys. (Paris) Colloq. 30: C4.
12 12. Dunmar, D.A. 1971. Chem. Phys. Lett. 10: 49.
13 13. deJeu, W. H., and P. Bordewijk. 1978. J. Chem. Phys. 68: 109.
14 14. Khoo, I. C., and R. Normandin. 1985. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE‐21: 329.
15 15. Horn, R. G. 1978. J. Phys. (Paris) 39: 105.
16 16. Leslie, F. M. 1966. Quantum J. Mech. Appl. Math. 19: 357.
17 17. Ericksen, J. L. 1966. Phys. Fluids 9: 1205.
18 18. Parodi, O. 1970. J. Phys. (Paris) 31: 581.
19 19. Miesowicz, M. 1935. Nature 17: 261; 1946;158:27.
20 20. See, for example, deJeu, W. H. 1980. Physical Properties of Liquid Crystalline Materials. New York: Gordon and Breech.
21 21. Khoo, I. C., R. G. Lindquist, R. R. Michael, et al. J. Appl. Phys. 69: 3853; Khoo, I. C., and R. Normandin. 1984. J. Appl. Phys. 55: 1416.
22 22. Eichler, H. J., and R. Macdonald. 1991. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67: 2666.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.