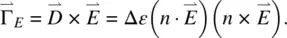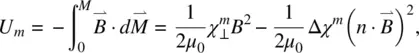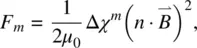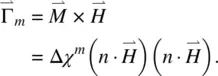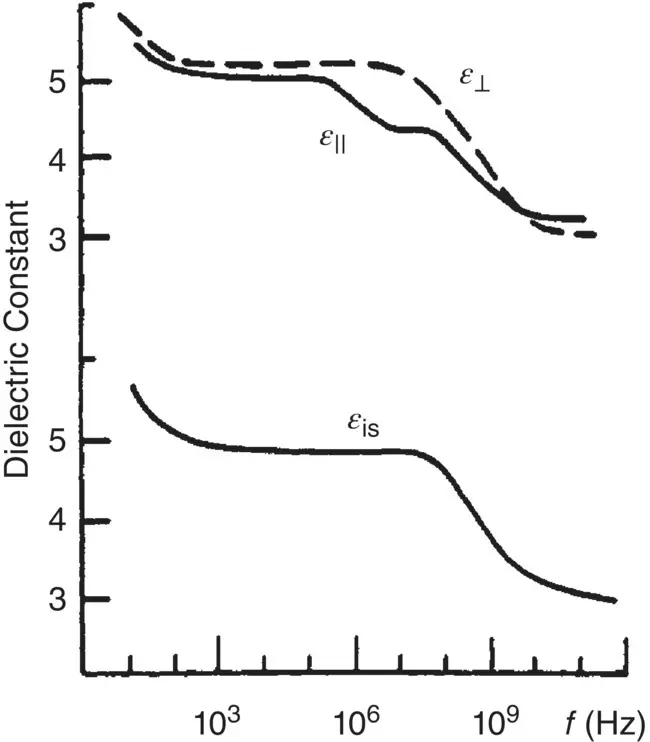
Figure 3.4. Dispersion data of the dielectric constant ε ||and ε ⊥for the nematic and isotropic phase of the liquid crystal 4‐methoxy‐4′‐ n ‐butylazoxy‐benzene.
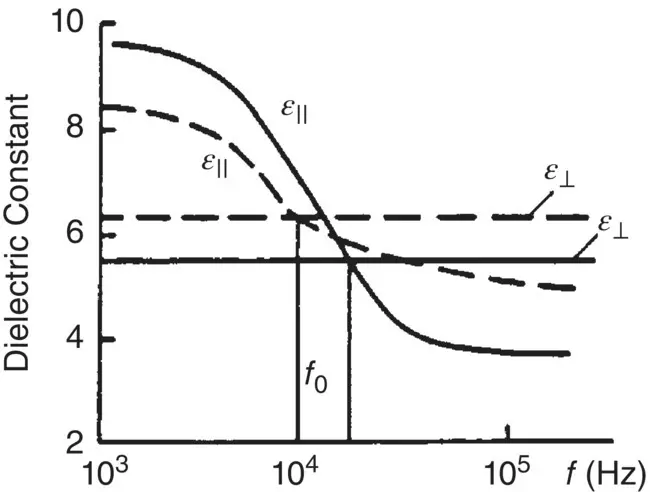
Figure 3.5. Dispersion data of the dielectric constant ε ||and ε ⊥for the nematic and isotropic phase of the liquid crystal phenylbenzoate.
For electro‐optical applications, the dielectric relaxation behavior of ε ||and ε ⊥for the different classes of nematic liquid crystals, and the relationships between the molecular structures and the dielectric constant, is obviously very important. This topic, however, is beyond the scope of this chapter, and the reader is referred to Blinov [8] and Khoo and Wu [9] and the references quoted therein for more detailed information.
Pure organic liquids are dielectric (i.e. nonconducting [ σ = 0]). The electric conductivities of liquid crystals are due to some impurities or ions. In general, σ ||is larger than σ ⊥. Electrical conduction plays an important role in electro‐optical applications of liquid crystals in terms of stability and instability, chemical degradation, and lifetime of the device [9]. Typically, σ ||and σ ⊥are on the order of 10 −10S −1cm −1for pure nematics. As in almost all materials, these conductivities could be varied by several orders of magnitude with the use of appropriate dopants.
The magnetic susceptibility of a material is defined in terms of the magnetization 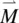 ,the magnetic induction
,the magnetic induction 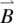 , and the magnetic strength
, and the magnetic strength 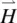 by
by
(3.20) 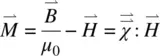
and
(3.21) 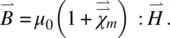
The magnetic susceptibility tensor 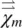 is anisotropic. For a uniaxial material such as a nematic, the magnetic susceptibility takes the form
is anisotropic. For a uniaxial material such as a nematic, the magnetic susceptibility takes the form
(3.22) 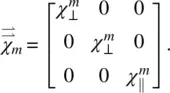
Note that this is similar to the dielectric constant 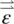 .
.
Nematic liquid crystals, in fact, liquid crystals in general, are diamagnetic. Therefore, 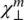 and
and 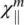 are negative of vanishingly small magnitude. As a result of the smallness of these magnetic susceptibilities, the magnetic interactions among the molecules comprising the liquid crystal are small (in comparison with their interaction with the externally applied field). Consequently, the local field acting on the molecules differs very little from the external field, and in general, magnetic measurements are the preferred method to study liquid crystal order parameters and other physical processes.
are negative of vanishingly small magnitude. As a result of the smallness of these magnetic susceptibilities, the magnetic interactions among the molecules comprising the liquid crystal are small (in comparison with their interaction with the externally applied field). Consequently, the local field acting on the molecules differs very little from the external field, and in general, magnetic measurements are the preferred method to study liquid crystal order parameters and other physical processes.
3.3.2. Free Energy and Torques by Electric and Magnetic Fields
In this section, we consider the interactions of nematic liquid crystals with applied fields (electric or magnetic); we will limit our discussion to only dielectric and diamagnetic interactions.
For a generally applied (dc, low frequency, or optical) electric field 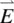 , the displacement
, the displacement  may be written in the form
may be written in the form
(3.23) 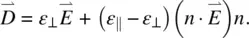
The electric interaction energy density is therefore
(3.24) 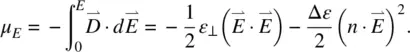
Note that the first term on the right‐hand side of Eq. (3.24)is independent of the orientation of the director axis. It can therefore be neglected in the director axis deformation energy. Accordingly, the free‐energy density term associated with the application of an electric field is given by
(3.25) 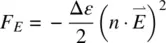
in SI units (in cgs units, 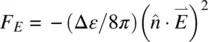 ). The molecular torque produced by the electric field is given by
). The molecular torque produced by the electric field is given by
(3.26) 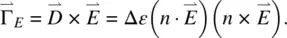
Similar considerations for the magnetic field yield a magnetic energy density term U mgiven by
(3.27) 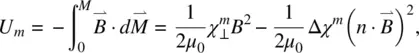
a magnetic free‐energy density (associated with director axis reorientation) F mgiven by
(3.28) 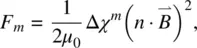
and a magnetic torque density
(3.29) 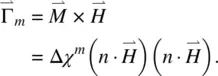
These electric and magnetic torques play a central role in various field‐induced effects in liquid crystals.
3.4. OPTICAL DIELECTRIC CONSTANTS AND REFRACTIVE INDICES
Читать дальше



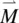 ,the magnetic induction
,the magnetic induction 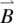 , and the magnetic strength
, and the magnetic strength 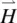 by
by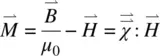
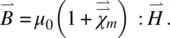
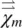 is anisotropic. For a uniaxial material such as a nematic, the magnetic susceptibility takes the form
is anisotropic. For a uniaxial material such as a nematic, the magnetic susceptibility takes the form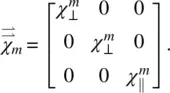
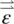 .
.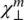 and
and 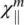 are negative of vanishingly small magnitude. As a result of the smallness of these magnetic susceptibilities, the magnetic interactions among the molecules comprising the liquid crystal are small (in comparison with their interaction with the externally applied field). Consequently, the local field acting on the molecules differs very little from the external field, and in general, magnetic measurements are the preferred method to study liquid crystal order parameters and other physical processes.
are negative of vanishingly small magnitude. As a result of the smallness of these magnetic susceptibilities, the magnetic interactions among the molecules comprising the liquid crystal are small (in comparison with their interaction with the externally applied field). Consequently, the local field acting on the molecules differs very little from the external field, and in general, magnetic measurements are the preferred method to study liquid crystal order parameters and other physical processes.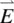 , the displacement
, the displacement  may be written in the form
may be written in the form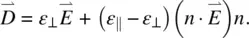
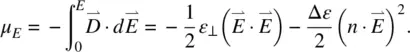
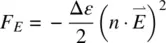
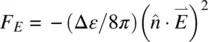 ). The molecular torque produced by the electric field is given by
). The molecular torque produced by the electric field is given by