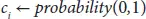1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...18 We observed that by applying ensemble method of type majority voting on the algorithms Decision tree, Random Forest, Naive Bayes, and K means, we could achieve an accuracy of 91.56%. To additionally improve the precision, we proposed the following algorithm. The design of the proposed method is as given in Figure 1.12.
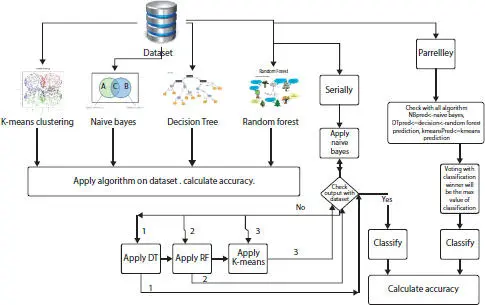
Figure 1.12 Proposed architecture.
Algorithm 1.1Probabilistic optimization.
initialization
d ← dataset
a1 ← Naive_Bayes_output ← ApplyNaiveBayes(d)
a2 ← Decision_tree_output ← ApplyDesisionTree(d)
a3 ← Random_tree_output ← ApplyRandomForest(d)
a4 ← K_Means_output ← ApplyKmeans(d)
winner(0, 1) ← Voting(a1, a2, a3, a4)
op ← winner_of_max_count(0,1)
if op ≠ desired_output then
Probability_calculation of each column with output 0 or 1
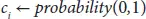
end
For each value in c i
count ← c i/2
For k to count
Add the probability (Find the max column with which probability matches)
Number of columns selected as ti
wi ← Weightage of selected columns
αi ← Append the weightage with the input of data
Find mean square error with the training and find lowest (MSE) parameter. Calculate the Euclidean distance

Find the minimum distance using this formula.
If probability of data > 0.5 and MSE < 0.5 and ED < 0.2
Classify as 1
else
Classify as 0
The following block diagram explains the flow of Algorithm 1.1.
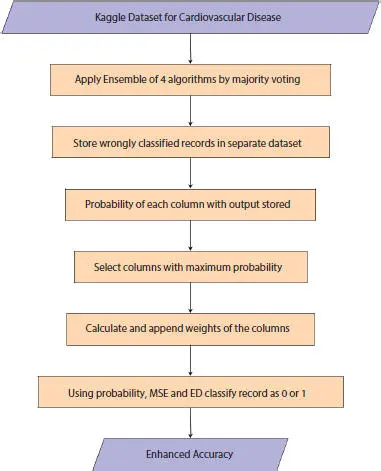
The working of the algorithm is explained briefly as follows.
1 1. The ensemble method of the four algorithms (Decision Tree, Random Forest, Naive Bayes, and K Means) is applied by majority voting and classification is obtained on presence or absence of cardiopathy.
2 2. The wrongly classified records are stored in a separate dataset.
3 3. The probability of each column with output is calculated and stored. For example, considering age, the probability of heart disease for age greater than 45 is more than otherwise.
4 4. We calculate those columns for which probability is maximum.
5 5. Only select these columns for further analysis.
6 6. Calculate the weights of these columns using formula y = mx + c for linear data using Multiple linear regression.
7 7. For non-linear data wherein the chances of misclassification are more, more complex functions such as tanh, sigmoid, and relu are used for calculating the weights.
8 8. Append the weights to the column at the time of classification.
9 9. Calculate the mean square error and Euclidean distance.
10 10. Finally, based on probability, mean square error and Euclidean distance, we classify the records as 1 or 0 which indicates presence/absence of heart disease.
11 11. Hence, accuracy achieved is higher than using the classical ensemble method.
Hence, our proposed methodology achieves a precision that not only surpasses the individual methods but also overshoots the combination method and the precision achieved thus is quite competitive.
An ensemble of classifiers is a collection of classification models whose singular forecasts are joined, by means of weighted or unweighted casting a ballot to dole out a classification mark to each new pattern. There is no single best method of creating successful ensemble methods and is being actively researched. Predicting heart disease has been a topic of interest for researchers for a long time. We therefore check the accuracy of the heart disease prediction using an ensemble of classifiers. For our study, we chose the best performing algorithms whose individual predictions made them classify as strong classifiers. We used a combination of Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, Random Forest, and K means algorithm. Since no single algorithm can guarantee maximum performance under all circumstances, we use the majority voting method to best classify the records. The dataset used for this purpose was Kaggle dataset for cardiovascular disease which has 70,000 records on which we achieved an accuracy of 91.56%.
However, we realized the potential of further increasing the accuracy by analyzing those records which were wrongly classified by all/most of the algorithms. The reason for it could be high bias, high variance, low precision, or low recall. So, we identified those columns/attributes which were causing the data to be misclassified by assigning probabilities to each tuple in the column and combining those probabilities by using conditional probability. Hence, we focused only on those columns which would result in accurate prediction by increasing the weight of those columns and feature reduction. Hence, by using the probabilistic approach, we could effectively remove the anomalies and increase the prediction accuracy.
1. Heart Disease Facts Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, [Online], Available: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm. [Accessed: 27-Apr-2019].
2. Thenmozhi, K. and Deepika, P., Heart disease prediction using classification with different decision tree techniques. Int. J. Eng. Res. Gen. Sci. , 2, 6, 6–11, 2014.
3. Kaggle Dataset, Cardiovascular Disease dataset, Available: https://www.kaggle.com/sulianova/cardiovascular-disease-dataset.
4. Kannan, R. and Vasanthi, V., Machine learning algorithms with ROC curve for predicting and diagnosing the heart disease, in: Soft Computing and Medical Bioinformatics , pp. 63–72, Springer Singapore, Jun 2018.
5. Latha, C.B.C. and Jeeva, S.C., Improving the accuracy of prediction of heart disease risk based on ensemble classification techniques. Inform. Med. Unlocked , 16, 100203, 2019.
6. Mohan, S., Thirumalai, C., Srivastava, G., Effective heart disease prediction using hybrid machine learning techniques. IEEE Access , 7, 81542–81554, 2019.
7. Thaiparnit, S., Kritsanasung, S., Chumuang, N., A classification for patients with heart disease based on hoeffding tree, in: 2019 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE) , Jul 2019, IEEE.
8. Atallah, R. and Al-Mousa, A., Heart Disease Detection Using Machine Learning Majority Voting Ensemble Method. 2019 2nd International Conference on new Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS) , 9-11 Oct. 2019.
9. Alim, M.A. and Habib, S., Robust Heart Disease Prediction: A Novel Approach based on Significant Feature and Ensemble learning Model. 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET) .
10. Pouriyeh, S., A Comprehensive Investigation and Comparison of Machine Learning Techniques in the Domain of Heart Disease. 22nd IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication (ISCC 2017): Workshops - ICTS4eHealth , 2017.
11. Aridas, C., Kotsiantis, S., Vrahatis, M., Increasing Diversity in Random Forests Using Naive Bayes. IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations , September 2016.
Читать дальше