Savo G. Glisic - Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Savo G. Glisic - Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A practical overview of the implementation of artificial intelligence and quantum computing technology in large-scale communication networks Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks

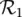 , we have R 1= Low × Low ; for rule
, we have R 1= Low × Low ; for rule 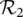 , we obtain R 2= Moderate × High ; and finally for rule
, we obtain R 2= Moderate × High ; and finally for rule 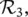 R 3= High × Low . The fuzzy relation R , which represents the entire rule base, is the union (element‐wise maximum) of the relations R i:
R 3= High × Low . The fuzzy relation R , which represents the entire rule base, is the union (element‐wise maximum) of the relations R i:

 , that is,
, that is, 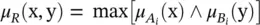 .
.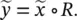

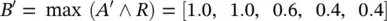
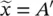 , for which the output value B ′ is given by the relational composition:
, for which the output value B ′ is given by the relational composition: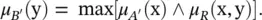
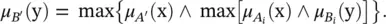
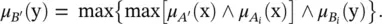
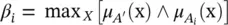 as the degree of fulfillment of the i‐ th rule’s antecedent. The output fuzzy set of the linguistic model is thus
as the degree of fulfillment of the i‐ th rule’s antecedent. The output fuzzy set of the linguistic model is thus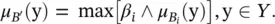
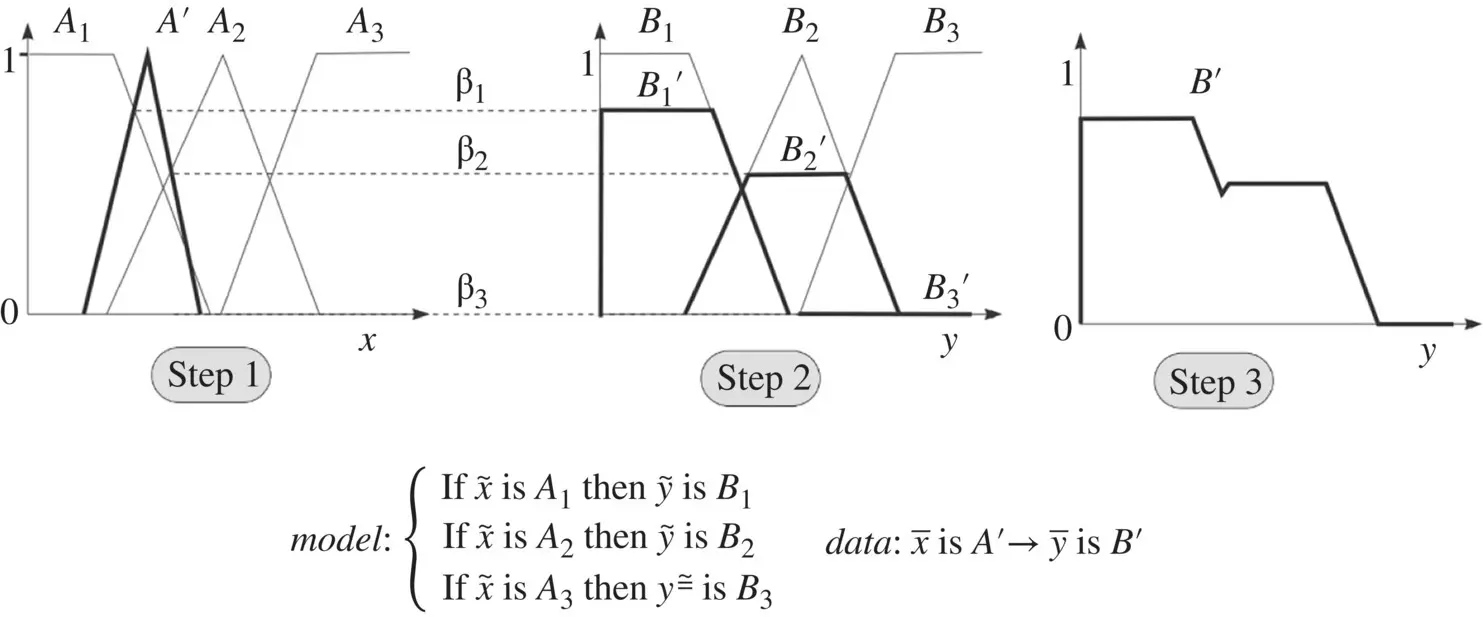
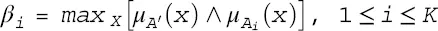 . Note that for a singleton fuzzy set (
. Note that for a singleton fuzzy set ( 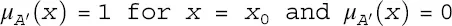 otherwise) the equation for βi simplifies to
otherwise) the equation for βi simplifies to 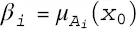 . 2. Derive the output fuzzy sets
. 2. Derive the output fuzzy sets  . 3. Aggregate the output fuzzy sets
. 3. Aggregate the output fuzzy sets  .
.











