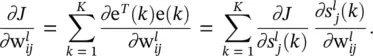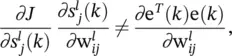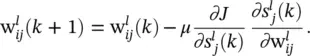Savo G. Glisic - Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Savo G. Glisic - Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A practical overview of the implementation of artificial intelligence and quantum computing technology in large-scale communication networks Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks

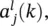 representing the output of a neuron in a layer, is given by the corresponding vector of delayed activations written as
representing the output of a neuron in a layer, is given by the corresponding vector of delayed activations written as 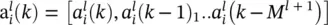 . Again, at the edges we have
. Again, at the edges we have 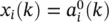 and
and 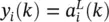 . Instead of Table 3.1, a complete set of definitions is summarized in Table 3.2. The form of the two tables demonstrates a high level of similarity.
. Instead of Table 3.1, a complete set of definitions is summarized in Table 3.2. The form of the two tables demonstrates a high level of similarity.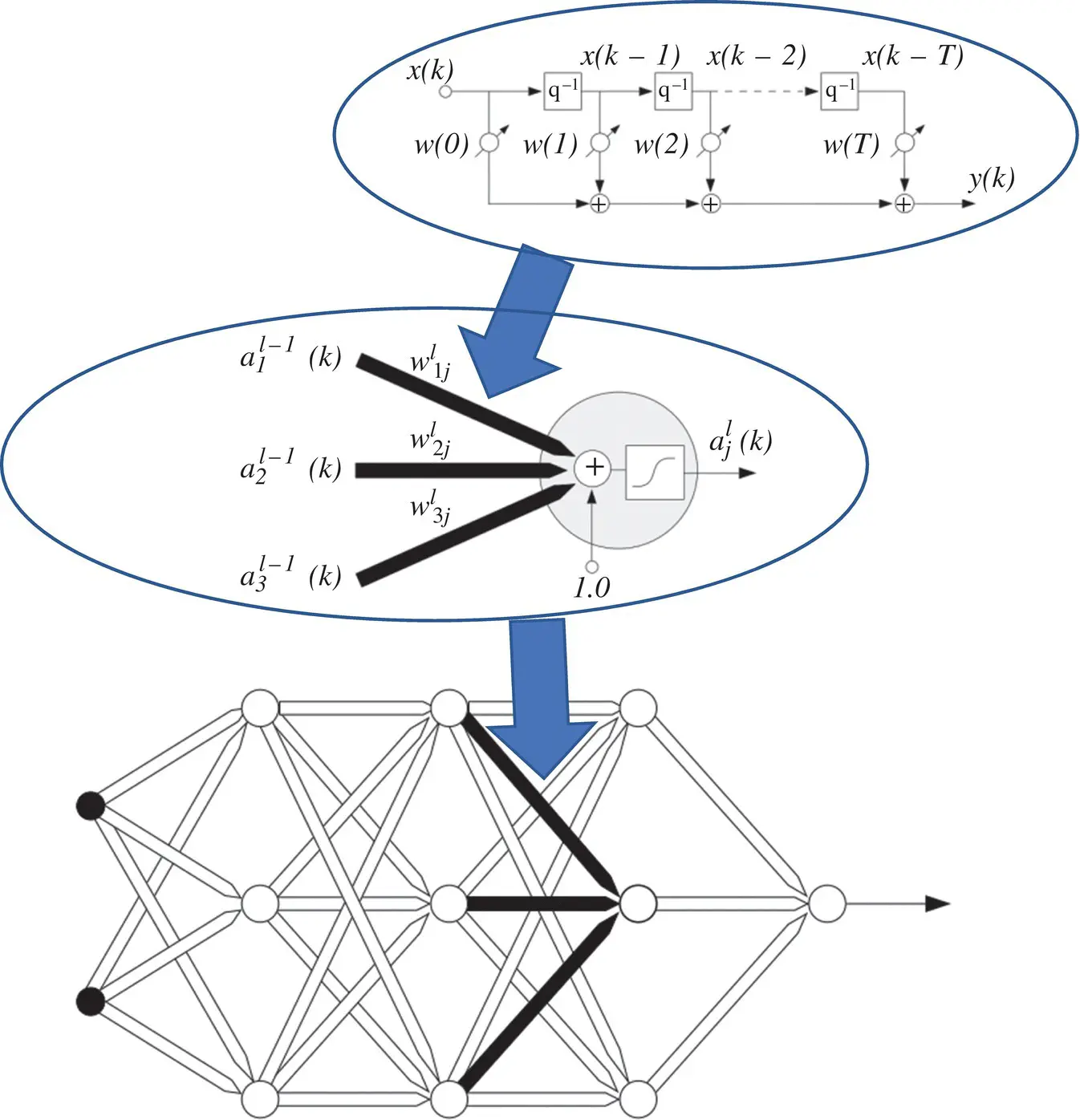
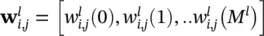
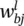
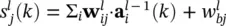
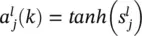
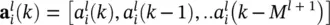
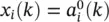
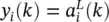
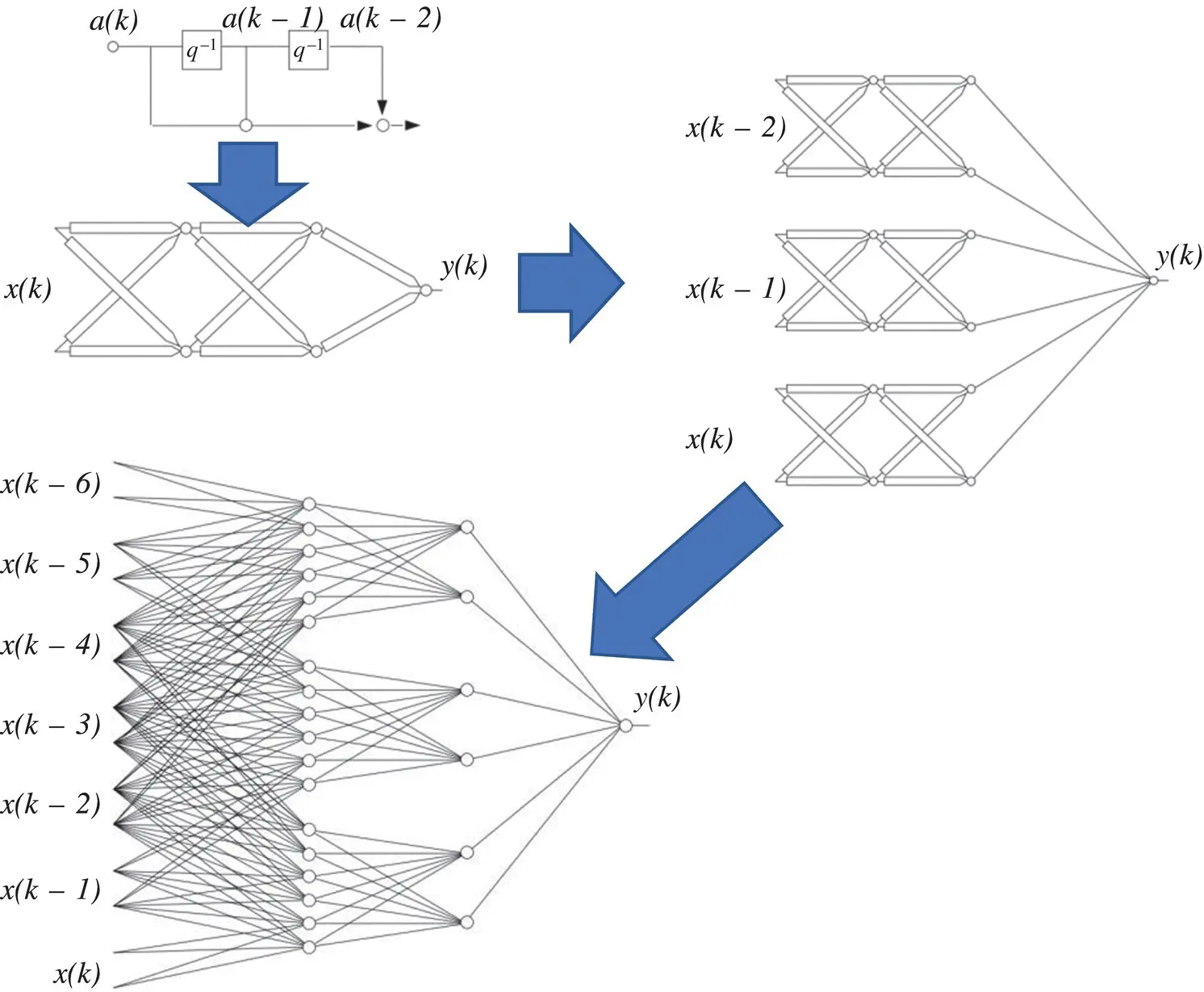
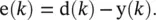
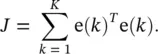
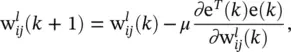
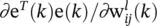 is the instantaneous gradient estimate, and μ is the learning rate. However, deriving an expression for this parameter results in an overlapping of number of chain rules. A simple backpropagation ‐ like formulation does not exist anymore.
is the instantaneous gradient estimate, and μ is the learning rate. However, deriving an expression for this parameter results in an overlapping of number of chain rules. A simple backpropagation ‐ like formulation does not exist anymore.