1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...37 The invariants of the strain tensors in terms of principal stretches are given by the relations
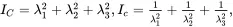 (2.89)
(2.89)
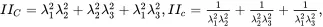 (2.90)
(2.90)
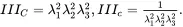 (2.91)
(2.91)
It is clear that
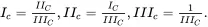 (2.92)
(2.92)
It will be very useful to introduce here the principal values CJ , J = 1, 2, 3, of Green’s deformation tensor defined using the following relations
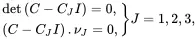 (2.93)
(2.93)
such that the symmetric tensor Cmay be written in the form
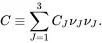 (2.94)
(2.94)
The quantities νJ,J=1,2,3, are orthogonal unit vectors defining the directions of the principal values. They have the following properties
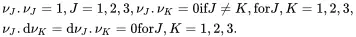 (2.95)
(2.95)
The polar decomposition principle (see, for example, [2, Section 1.5]) states that the deformation gradient may be expressed in the following forms (dyadic and tensor)
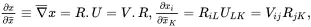 (2.96)
(2.96)
where Ris the orthogonal rigid rotation tensor having the properties R.RT=RT.R=I with det(R)=±1, and where Uand Vare positive-definite symmetric right and left stretch tensors.
It follows from ( 2.84) and ( 2.96) that in tensor form
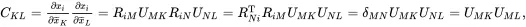 (2.97)
(2.97)
so that in dyadic form
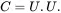 (2.98)
(2.98)
The symmetric tensors Uand Vhave common eigenvalues λJ but different mutually orthogonal eigenvectors νJ such that
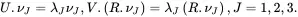 (2.99)
(2.99)
The eigenvalues λJ, J = 1, 2, 3, are the principal stretches and
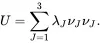 (2.100)
(2.100)
It then follows that the principal values CJ of the Cmay be written in terms of the principal stretches λJ as follows
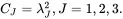 (2.101)
(2.101)
It follows from ( 2.94) that
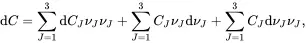 (2.102)
(2.102)
and on multiplying by νK using the properties ( 2.95) it can be shown that
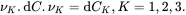 (2.103)
(2.103)
In terms of the principal values C 1, C 2and C 3of the tensor Cand E 1, E 2and E 3of the tensor E, the corresponding invariants may be written as (see [1, Section 1.10])
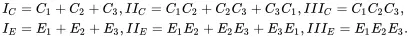 (2.104)
(2.104)
It can be shown that
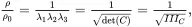 (2.105)
(2.105)
where ρ0 is the uniform mass density before deformation has occurred at some reference temperature T 0and reference pressure p0.
2.11 Field Equations for Infinitesimal Deformations
Continuum mechanics is based upon conservation laws that lead to the basic field equations that are independent of the properties of material to which the laws are applied. The mathematical statement of these laws is now given for the case of infinitesimal deformations where there is no practical distinction between the use of so-called material coordinates and spatial coordinates.
For many practical applications the deformation gradients are sufficiently small for quadratic terms to be neglected when compared with linear terms leading to an infinitesimal deformation theory. The expression ( 2.88) for the Lagrangian strain tensor may then be approximated by υ≅ε where
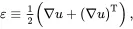 (2.106)
(2.106)
is known as the infinitesimal strain tensor and where ∇ denotes the gradient with respect to the coordinates x. In addition, there is no need to distinguish between the initial and deformed states of the medium so that x≅x¯. Relation ( 2.106) may be written in component form so that
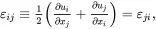 (2.107)
(2.107)
which shows that the infinitesimal strain tensor ε is symmetric.
For a continuous medium having a uniform density distribution ρ0 in its undeformed state, the principle of conservation of mass for infinitesimal deformations is expressed as
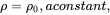 (2.108)
(2.108)
where ρ is the density of the medium during deformation. This equation simply states that the mass of a given set of material points remains constant during any deformation. The local density ρ of the medium measured relative to spatial coordinates will in fact vary because of non-uniform displacement gradients, but this change is negligible for infinitesimal deformation theory where the value of ρ corresponds to the initial density ρ0 prior to deformation, as asserted by ( 2.108).
For the equilibrium situations considered in this book, body forces are neglected so that b= 0 and the equation of motion ( 2.37) reduces in component form to
Читать дальше

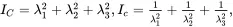 (2.89)
(2.89)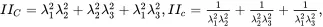 (2.90)
(2.90)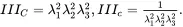 (2.91)
(2.91)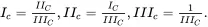 (2.92)
(2.92)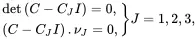 (2.93)
(2.93)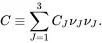 (2.94)
(2.94)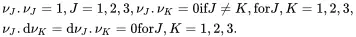 (2.95)
(2.95)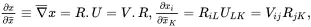 (2.96)
(2.96)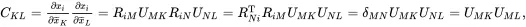 (2.97)
(2.97)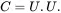 (2.98)
(2.98)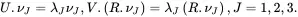 (2.99)
(2.99)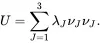 (2.100)
(2.100)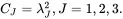 (2.101)
(2.101)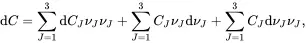 (2.102)
(2.102)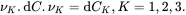 (2.103)
(2.103)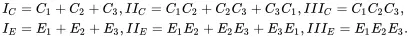 (2.104)
(2.104)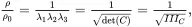 (2.105)
(2.105)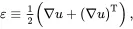 (2.106)
(2.106)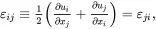 (2.107)
(2.107)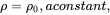 (2.108)
(2.108)










