Chris McCain - Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Chris McCain - Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Город: Indianapolis, Год выпуска: 2008, ISBN: 2008, Издательство: WILEY Wiley Publishing, Inc., Жанр: Программы, ОС и Сети, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3
- Автор:
- Издательство:WILEY Wiley Publishing, Inc.
- Жанр:
- Год:2008
- Город:Indianapolis
- ISBN:978-0-470-18313-7
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3 — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
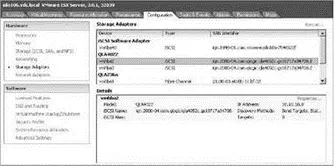
Figure 4.22Supported iSCSI HBA devices will automatically be found and can be configured in the BIOS of the ESX host.
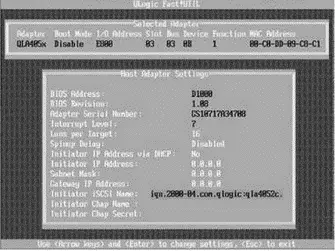
Figure 4.23The BIOS of the QLogic card provides an opportunity to configure the iSCSI HBA. If it's not configured in the BIOS, the defaults pass into the configuration display in the VI Client.
At the time this book was written, the only supported iSCSI HBA was a specific set of QLogic cards in the 4050 series. Although a card may work, if it is not on the compatibility list, obtaining support from VMware will be challenging. As with other hardware situations in VI3, always check the VMware compatibility guide prior to purchasing or installing an iSCSI HBA.
To modify the setting of an iSCSI HBA, perform the following steps:
1. In the Storage Adapters node on the Configuration tab, select the appropriate iSCSI HBA (i.e., vmhba2 or vmhba3) from the list and click the Properties link.
2. Click the Configure button.
3. For a custom iSCSI qualified name, enter a new iSCSI name and iSCSI alias in the respective text boxes.
4. If desired, entire the static IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server for the iSCSI HBA.
5. Click OK. Do not click Close.
Once you've configured the iSCSI HBA with the appropriate IP information, you must configure it to accurately find the target available via iSCSI storage devices. ESX provides for the two types of target identification:
♦ Static discovery
♦ Dynamic discovery
As the names suggest, one method involves manual configuration of target information (static) while the other involves a less cumbersome, administratively easier means of finding storage (dynamic). The dynamic discovery method is also referred to as the SendTargets method in light of the SendTarget request made by the ESX host. To dynamically discover the available storage targets, you must configure the host manually with the IP address of at least one node. Ironically, when configuring a host to perform a SendTarget request (dynamic discovery), you configure a target on the Dynamic Discovery tab of the iSCSI initiator Properties box, and all of the dynamically identified targets appear on the Static Discovery tab. You perform static assignment as well on the Dynamic Discovery tab so that dynamic targets appear on the Static Discovery tab. Figure 4.24 details the SendTargets method of iSCSI LUN discovery.
The hardware-initiated iSCSI allows for either dynamic or static discovery of targets. The iSCSI software initiator built into ESX 3.0 only allows for the SendTargets discovery method.
To configure the iSCSI HBA for target discovery using the SendTargets method, perform the following steps:
1. In the iSCSI Initiator Properties dialog box, select the Dynamic Discovery tab and click the Add button.
2. Enter the IP address of the iSCSI device and the port number (if it has been changed from the default port of 3260).
3. Click Close.
4. Click the Rescan link.
5. Review the Static Discovery tab of the iSCSI HBA properties.
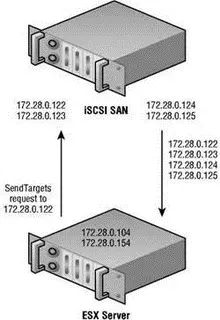
Figure 4.24The SendTargets iSCSI LUN discovery method requires that you manually configure at least one iSCSI target to issue a SendTargets request. The iSCSI device will then return information about all the targets available.
In this section I've hinted, or, better yet, blatantly stated, that iSCSI storage networks should be isolated from the other IP networks already configured in your infrastructure. However, this is not always a possibility due to such factors as budget constraints, IP addressing challenges, host limitations, and more. If you cannot isolate the iSCSI storage network, you can configure the storage device and the ESX nodes to use the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). CHAP provides a secure means of authenticating a user account without the need for exchanging the password over publicly accessible networks.
To configure an iSCSI HBA to authenticate using CHAP, follow these steps:
1. From the Storage Adapters node on the Configuration page, select the iSCSI HBA to be configured and click the Properties link.
2. Select the CHAP Authentication tab and click Configure.
3. Insert a custom name in the CHAP Name text box or select the Use Initiator Name checkbox.
4. Type a strong and secure string in the Chap Secret text box.
5. Click OK.
6. Click Close.
Software-initiated iSCSI is a cheaper solution than the iSCSI HBA hardware initiation because it does not require any special hardware. Software-based iSCSI initiation, as the name suggests, begins in the VMkernel and utilizes a normal Ethernet adapter installed on the ESX Server host. Unlike the iSCSI HBA solution, software initiation relies on a set of drivers and a TCP/IP stack that resides in the VMkernel. In addition, the iSCSI software initiator, of which there is only one, uses the name vmhba32 as opposed to being enumerated with the rest of the HBAs within a host. Figure 4.25 outlines the architectural differences between the hardware and software initiation mechanisms on ESX Server.
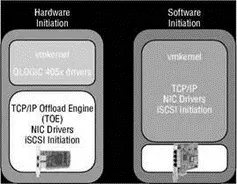
Figure 4.25ESX Server supports using an iSCSI HBA hardware-based initiation, which reduces overhead on the VMkernel. For a cheaper solution, ESX Server also supports a software-based initiation that does not require specialized hardware.
Using the iSCSI software initiation built into ESX Server provides an easy means of configuring the host to communicate with the iSCSI storage device. The iSCSI software initiator uses the SendTargets method for obtaining information about target devices. The SendTargets request requires the manual entry of one of the IP addresses on the storage device. The software initiator will then query the provided IP address in search of all additional targets.
To enable iSCSI software initiation on an ESX Server, perform the following steps:
1. Enable the Software iSCSI client in the firewall of the ESX Server host as shown in Figure 4.26:
♦ On the Configuration tab of the ESX host, click the Security Profile link.
♦ Click the Properties link.
♦ Enable the Software iSCSI Client checkbox,
or
♦ Open an SSH session with root privileges and type the following commands:
esxcfg-firewall -r swISCSIClient
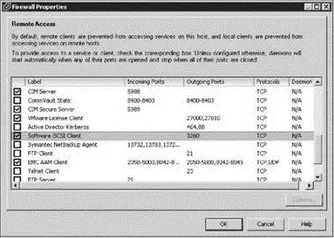
Figure 4.26The iSCSI software must be enabled in the Service Console firewall.
2. Create a virtual switch with a VMkernel port and a Service Console (vswif) port. Bind the virtual switch to a physical network adapter connected to the dedicated storage network. Figure 4.27 shows a correctly configured switch for use in connecting to an iSCSI storage device.
Log on to an ESX host using an SSH session and elevate the permissions using # su — if necessary. Follow these steps:
1. Add a new port group named Storageto the virtual switch on the dedicated storage network:
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












