(bovine heart).
The findings in the human hearts are surprising from the point of view of interpretation, since it is logic to consider its presence in all the evolutionary mammalian chain. It should be assumed that this structure, analyzed in different species, has the common function of providing support to the myocardial band to generate the power needed by any muscle, which is different in diverse mammals. Therefore, its presence is constant in all the hearts studied, both in bovids and humans, but its structural characteristic is different, and this diversity in the intimal analysis of the cardiac fulcrum is undoubtedly associated with the resistance it must oppose to the activity of the myocardial band in hearts of different sizes.
The analysis of a 10-year-old human heart showed in the same place a myxoid-cartilaginous formation with approximately 2 cm diameter (Figure 1.21). A similar finding, both in structure and location, occurred in the heart of a 23-week gestation human fetus (Figures 1.22 and 1.23).
A fact defying logic is having found in the adult human heart a formation presenting consistent characteristics, both to observation and palpation, in the same location and with similar triangular morphology (Figures 1.24 to 1.27). However, the histological analysis revealed a matrix similar to that of a tendon.
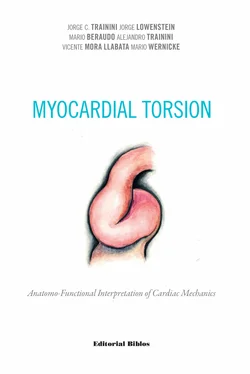
The macroscopic and microscopic observation reveal the muscle fiber attachment to this solid, homogeneous nucleus, which is closely related with the aortic wall on the side of the tricuspid valve. Its configuration has been confirmed histologically. We have called his structure, origin and end of the myocardial band, cardiac fulcrum, as a parallelism and tribute to the definition of the supporting point of a lever expressed by Archimedes of Syracuse (Greek, 288 B.C. – 212 B.C.). It is located anterior to the central fibrous ridge (right trigone) and it clearly shows that the myocardial fibers of the right segment originate in its structure (Figure 1.16) same as the ascending segment courses to meet it in order to attach (Figures 1.18 and 1.19). It should be noted that to visualize the cardiac fulcrum it is essential to unfold the myocardial band. This osseous, cartilaginous or tendinous structure was always present and with the same morphology in all the hearts analyzed by us, albeit with different histological texture. No description of its characteristics or function has been reported in the literature, except the mere mention of its presence as os cordis in bovids.

Figure 1.21. Cardiac fulcrum in a 10-year-old human heart (explant).
Figure 1.22. Human embryo heart (23-week gestation) showing sectioning planes.
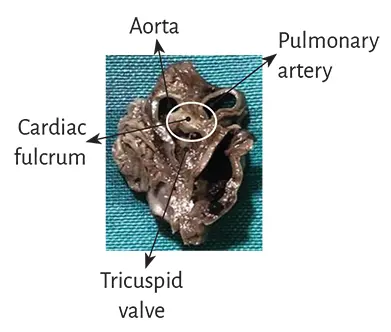
Figure 1.23. Cardiac fulcrum in a 23-week gestation human embryo hear.
Figure 1.24. Fulcrum in the adult human heart.
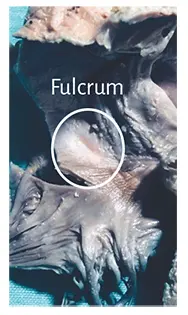
Figure 1.25. Fulcrum in
the adult human heart.
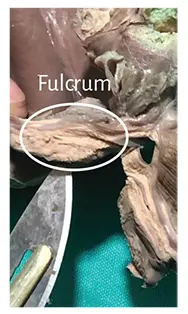
Figure 1.26. Fulcrum resected from
an adult human heart.
Figure 1.27. The drawing shows the myocardial band arrangement at the beginning of its unfolding. The pulmonary artery and the right segment have been separated from the fulcrum to show its intermediate location between the right segment (anterior location) and the ascending segment (posterior location). A: macroscopic image of the fulcrum in the adult human heart. B: microscopic image of the human fulcrum. Notice the myocardial fibers inserting into the tendinous fulcrum matrix
Histology . The microscopic analysis of the bovine cardiac fulcrum shows a trabecular osteochondral matrix with segmental lines. Its general structure resembles the metaphyseal growth of the long bones (Figures 1.28 and 1.29) and increased magnification reveals bone trabeculae with osteoblasts and segmental lines secondary to bone apposition (Figure 1.30).
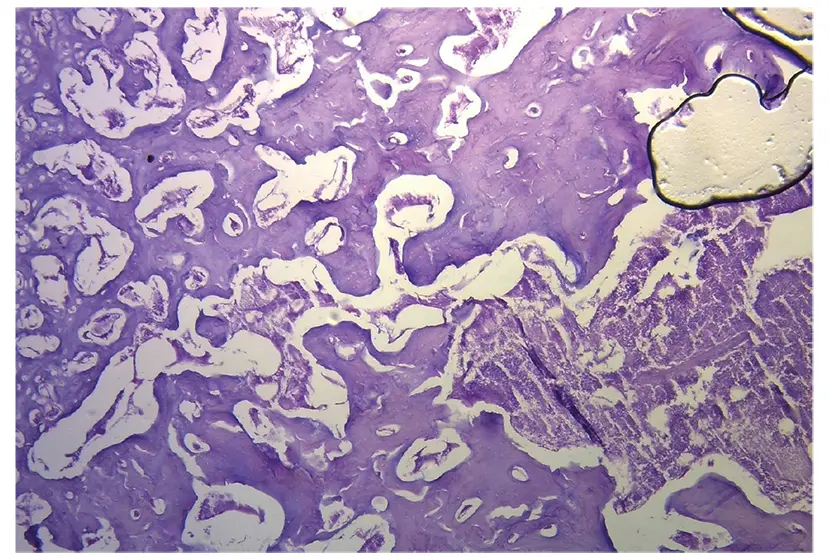
Figure 1.28. Histological section of the cardiac fulcrum showing trabecular bone tissue with osteologic segmental lines (bovine heart). Hematoxylin-eosin stain.
Figure 1.29. Mature trabecular bone forming the cardiac fulcrum tissue (bovine heart). Hematoxylin-eosin stain at low magnification (10×).
Figure 1.30. Cardiac fulcrum trabecular bone with osteoblasts and segmental lines. The structure constitutes the trabecular bone tissue scaffolding similar to the metaphyseal area of growth in long bones. The histological section also shows bone trabeculae with osteoblasts and segmental lines secondary to bone apposition (bovine heart). Hematoxylin-eosin stain at high magnification (40×).
Figure 1.31. Ten year old human heart. Central area of the fulcrum formed by chondroid tissue in a 10-year-old human heart. Hematoxylin-eosin stain.
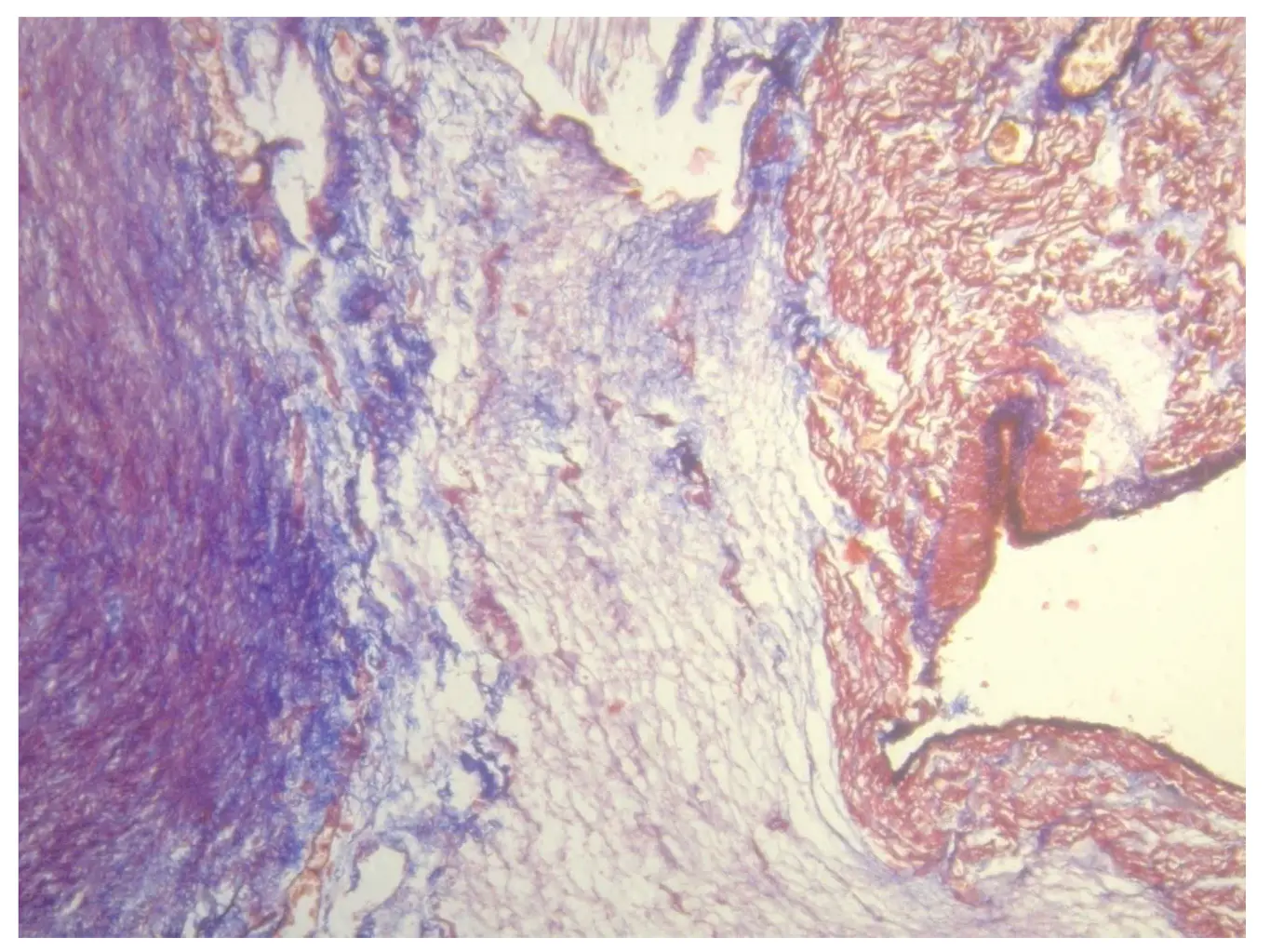
Figure 1.32. Cardiac fulcrum in a 23-week gestation fetus showing prechondroid bluish areas in a myxoid stroma. Masson’s trichrome staining technique.
In the 10-year-old human heart, the histological findings in the cardiac fulcrum were associated with that early age. Figure 1.31 shows a central zone of the fulcrum formed by chondroid tissue. Given the 10-year-old age, it is logical that the fulcrum is smaller and characterized by more chondroid than bone tissue. This finding was repeated in a 23-week old human fetus with the characteristic prechondroid bluish areas in a myxoid stroma (Figure 1.32).
The osseous structure in the bovine os cordis and its relationship with the myxoid-chondroid cardiac fulcrum texture in human hearts, even in gestational stages, is rational for the interpretation analysis. This disparity is associated with the different age evolution from chondroid to osseous material and by the greater force developed in bovids requiring a more rigid supporting point.
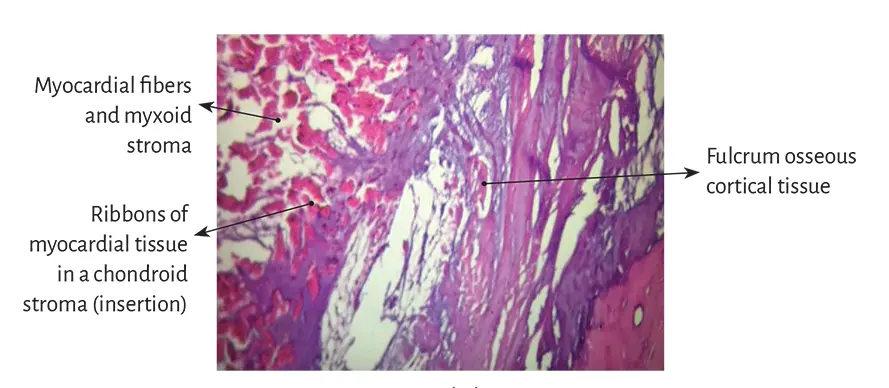
Figure 1.33. Myocardial insertion in
the cardiac fulcrum. Bovine heart.
Figure 1.34. Insertion of myocardial fibers in the fulcrum
chondroid tissue of a bovine heart.
However, the histological analysis of the fulcrum in adult human hearts evidenced a tendinous collagenous matrix, needing an additional clarification. In principle, there is constancy in the detection, site and morphology of the fulcrum in all the hearts analyzed. This means that from a functional point of view, its presence is akin to myocardial band insertion, as established in the histological analysis, becoming a solid point of interpretation to achieve its biomechanical function. And we find this demonstration when the histological examination is directed to the myocardial insertion in the osseous, chondroid or tendinous fulcrum. All the hearts studied presented this myocardial attachment to the rigid structure of the fulcrum, integrating a cardiomyocyte-matrix unit, regardless of its osseous, cartilaginous or tendinous nature (Figures 1.33 to 1.38).
Читать дальше