Anil K. Chopra - Earthquake Engineering for Concrete Dams
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Anil K. Chopra - Earthquake Engineering for Concrete Dams» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Earthquake Engineering for Concrete Dams
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Earthquake Engineering for Concrete Dams: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Earthquake Engineering for Concrete Dams»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
offers a comprehensive, integrated view of this progress over the last fifty years. The book offers an understanding of the limitations of the various methods of dynamic analysis used in practice and develops modern methods that overcome these limitations.
This important book:
Develops procedures for dynamic analysis of two-dimensional and three-dimensional models of concrete dams Identifies system parameters that influence their response Demonstrates the effects of dam–water–foundation interaction on earthquake response Identifies factors that must be included in earthquake analysis of concrete dams Examines design earthquakes as defined by various regulatory bodies and organizations Presents modern methods for establishing design spectra and selecting ground motions Illustrates application of dynamic analysis procedures to the design of new dams and safety evaluation of existing dams. Written for graduate students, researchers, and professional engineers,
offers a comprehensive view of the current procedures and methods for seismic analysis, design, and safety evaluation of concrete dams.

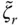 , of the equivalent SDF system ( Figure 2.6.4), are more complicated than its effects on the vibration period. As the wave reflection coefficient, α , decreases from unity, ζ rincreases monotonically from zero for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s, but the trends are more complicated for smaller values of Ω r, i.e. larger values of E s. This latter, unexpected behavior in ζ rresults from the previously observed effects of reservoir bottom absorption on the natural vibration frequency,
, of the equivalent SDF system ( Figure 2.6.4), are more complicated than its effects on the vibration period. As the wave reflection coefficient, α , decreases from unity, ζ rincreases monotonically from zero for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s, but the trends are more complicated for smaller values of Ω r, i.e. larger values of E s. This latter, unexpected behavior in ζ rresults from the previously observed effects of reservoir bottom absorption on the natural vibration frequency, 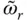 , of the equivalent SDF system ( Eq. 2.6.11), which is the frequency at which the added damping, ζ r, is evaluated ( Eq. 2.6.13). The added damping ratio depends on the relative values of
, of the equivalent SDF system ( Eq. 2.6.11), which is the frequency at which the added damping, ζ r, is evaluated ( Eq. 2.6.13). The added damping ratio depends on the relative values of 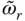 and
and 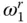 ; recall that the latter is the fundamental natural vibration frequency of the impounded water. As Ω rdecreases (i.e. E sincreases, implying that the dam becomes stiffer),
; recall that the latter is the fundamental natural vibration frequency of the impounded water. As Ω rdecreases (i.e. E sincreases, implying that the dam becomes stiffer), 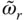 approaches
approaches 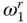 , and the imaginary‐valued component of the hydrodynamic term,
, and the imaginary‐valued component of the hydrodynamic term, 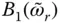 , increases as α decreases from unity to zero, thus increasing ζ r. Figure 2.6.3also shows that the wave reflection coefficient, α , has a larger effect on the added damping for smaller values of Ω rthan for larger Ω r. If the reservoir bottom is absorptive ( α < 1), the added damping ratio ζ rincreases as Ω rdecreases, with the rate of increase becoming smaller as α decreases.
, increases as α decreases from unity to zero, thus increasing ζ r. Figure 2.6.3also shows that the wave reflection coefficient, α , has a larger effect on the added damping for smaller values of Ω rthan for larger Ω r. If the reservoir bottom is absorptive ( α < 1), the added damping ratio ζ rincreases as Ω rdecreases, with the rate of increase becoming smaller as α decreases.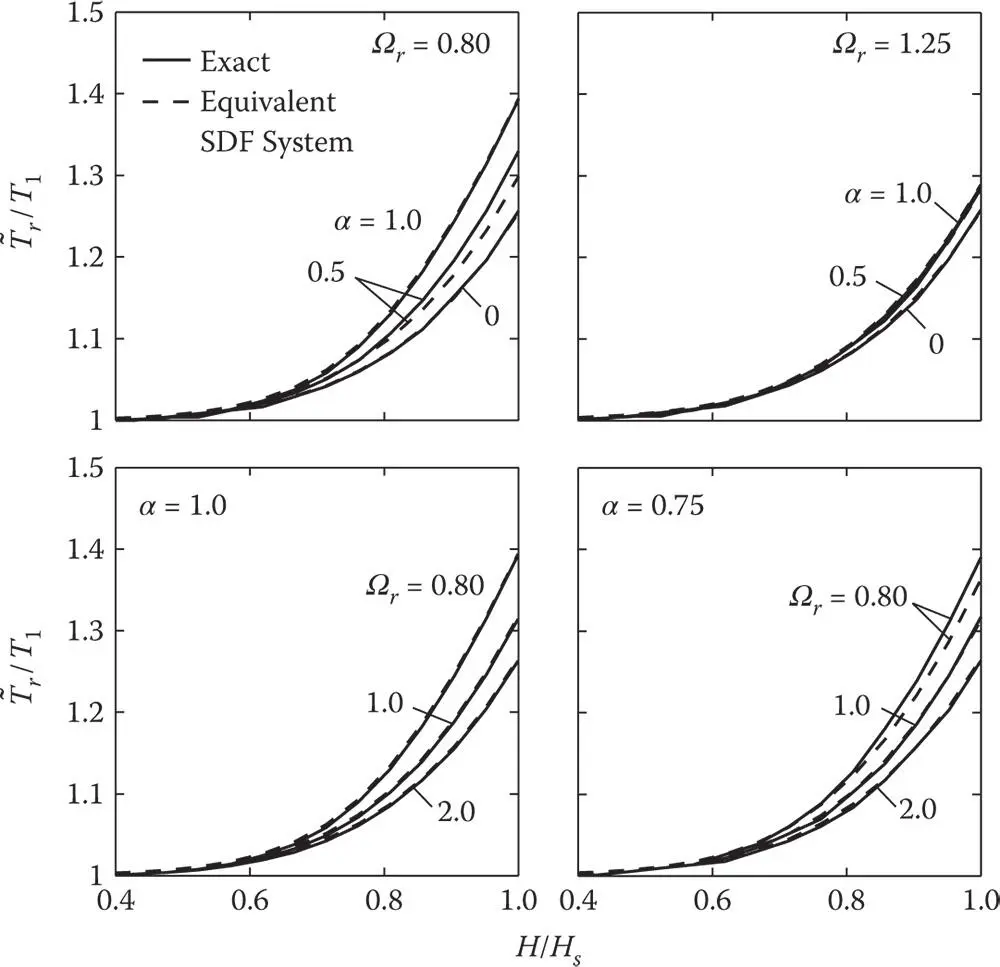
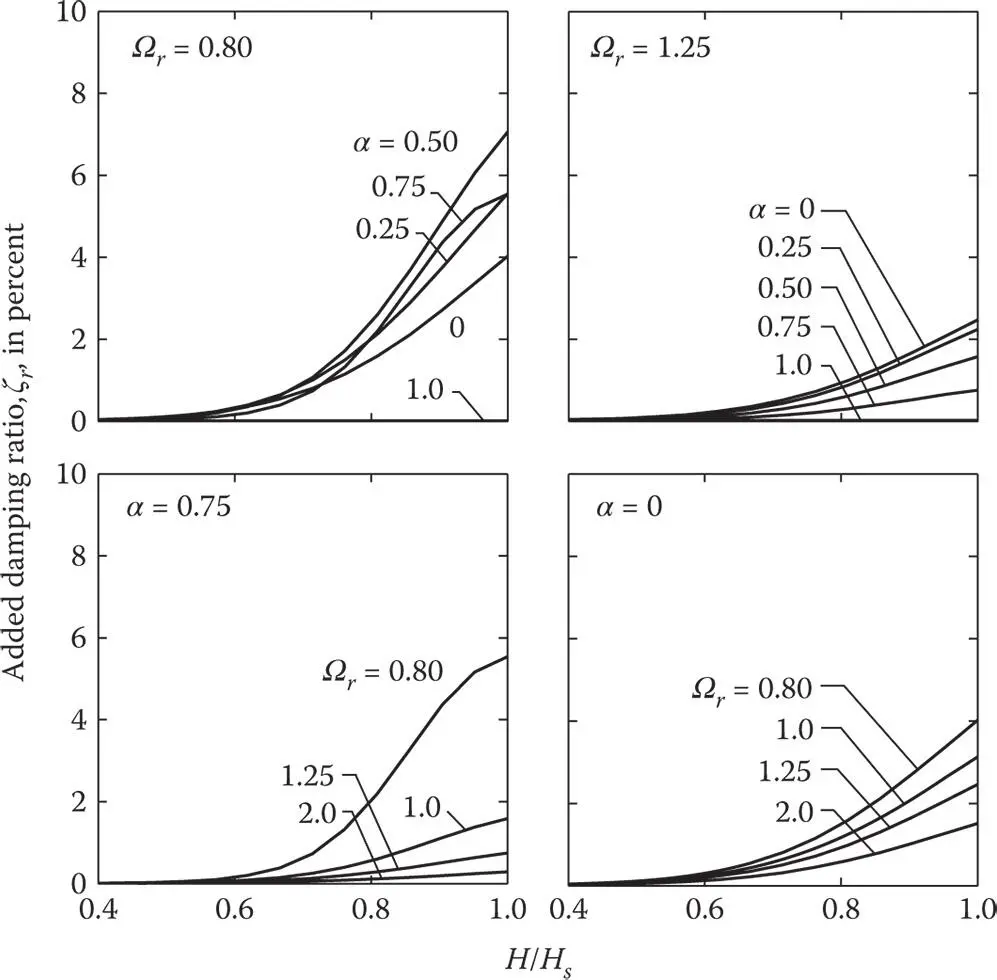
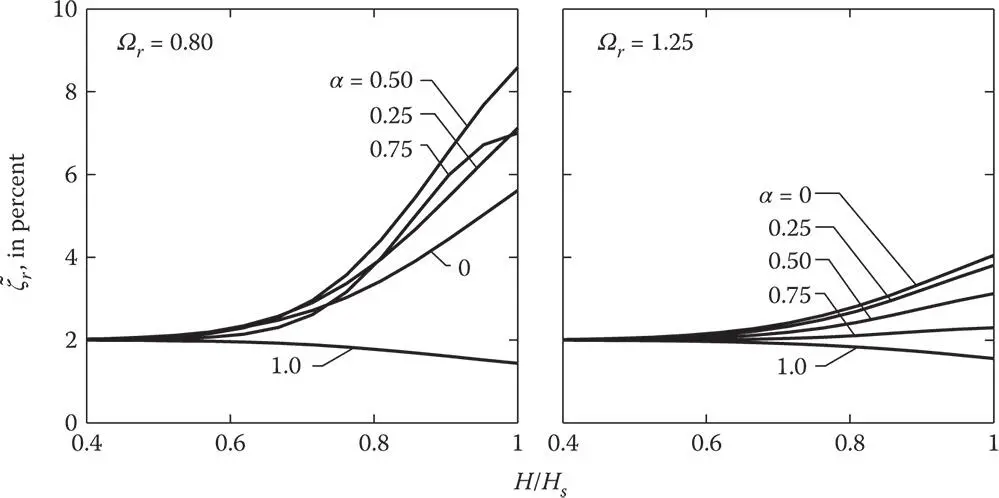
 of the equivalent SDF system representing dams on rigid foundation with impounded water; ζ 1= 2%.
of the equivalent SDF system representing dams on rigid foundation with impounded water; ζ 1= 2%.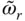 is less than ω 1, Eq. (2.6.12)indicates that dam–water interaction reduces the effectiveness of the structural damping. Unless this reduction is compensated by the added damping ζ rdue to reservoir bottom absorption, the overall damping ratio, ζ r, will be less than ζ 1( Figure 2.6.4).
is less than ω 1, Eq. (2.6.12)indicates that dam–water interaction reduces the effectiveness of the structural damping. Unless this reduction is compensated by the added damping ζ rdue to reservoir bottom absorption, the overall damping ratio, ζ r, will be less than ζ 1( Figure 2.6.4).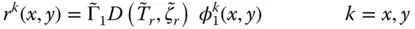
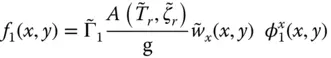
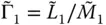 ;
;  and
and 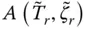 are the ordinates of the deformation and pseudo‐acceleration response spectra at the natural vibration period
are the ordinates of the deformation and pseudo‐acceleration response spectra at the natural vibration period 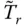 and damping ratio
and damping ratio 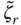 of the equivalent SDF system, and
of the equivalent SDF system, and 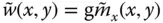 with
with 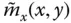 defined by Eqs. (2.6.5a)and (2.6.6). Substituting these equations in Eq. (2.6.15)gives the final expression for the equivalent static lateral forces (Chopra 1978):
defined by Eqs. (2.6.5a)and (2.6.6). Substituting these equations in Eq. (2.6.15)gives the final expression for the equivalent static lateral forces (Chopra 1978):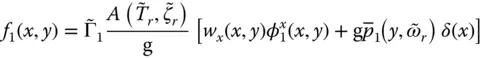
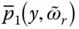 at the upstream face, increases Γ 1, and modifies the period and damping ratio where the spectral ordinate is determined.
at the upstream face, increases Γ 1, and modifies the period and damping ratio where the spectral ordinate is determined.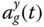 if the boundary is rigid, resulting in Eq. (2.3.3), repeated here for convenience:
if the boundary is rigid, resulting in Eq. (2.3.3), repeated here for convenience:










