(2.6.10c) 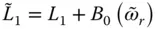
with the generalized mass, damping and force of the equivalent SDF system given by Eq. (2.6.10), a comparison of Eqs. (2.6.7)and (2.6.1)shows that 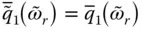 , i.e. the equivalent SDF system gives the exact value for the fundamental resonant response of the dam–water system.
, i.e. the equivalent SDF system gives the exact value for the fundamental resonant response of the dam–water system.
The natural vibration frequency, 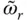 , of the equivalent SDF system is
, of the equivalent SDF system is 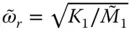 ; substituting
; substituting 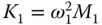 and Eq. (2.6.10a)for
and Eq. (2.6.10a)for 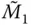 , gives
, gives
(2.6.11) 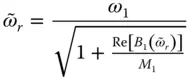
Because 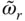 appears on both sides, this equation must be solved iteratively for
appears on both sides, this equation must be solved iteratively for 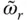 . Hydrodynamic effects always reduce the natural vibration frequency because Re[ B 1( ω )] > 0 for all excitation frequencies. Does Eq. (2.6.11), determined from the properties of the equivalent SDF system, give the correct reduction in frequency of the dam due to dam–water interaction? The fundamental resonant frequency of the dam–water system is approximately given by the excitation frequency that makes the real‐valued component of the denominator in the exact fundamental mode response, Eq. (2.6.1), equal to zero. This argument also leads to Eq. (2.6.11), which demonstrates that the mass of the equivalent SDF system defined in Eqs. (2.6.5)and (2.6.6)reduces the fundamental resonant frequency of the dam due to hydrodynamic effects by the exact amount.
. Hydrodynamic effects always reduce the natural vibration frequency because Re[ B 1( ω )] > 0 for all excitation frequencies. Does Eq. (2.6.11), determined from the properties of the equivalent SDF system, give the correct reduction in frequency of the dam due to dam–water interaction? The fundamental resonant frequency of the dam–water system is approximately given by the excitation frequency that makes the real‐valued component of the denominator in the exact fundamental mode response, Eq. (2.6.1), equal to zero. This argument also leads to Eq. (2.6.11), which demonstrates that the mass of the equivalent SDF system defined in Eqs. (2.6.5)and (2.6.6)reduces the fundamental resonant frequency of the dam due to hydrodynamic effects by the exact amount.
The damping ratio of the equivalent SDF system 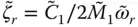 is determined by substituting Eqs. (2.6.10b)and (2.6.10a)and utilizing Eq. (2.6.11):
is determined by substituting Eqs. (2.6.10b)and (2.6.10a)and utilizing Eq. (2.6.11):
(2.6.12) 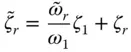
in which the added damping due to upstream propagation of hydrodynamic waves and their absorption at the reservoir bottom is represented by the frequency‐independent damping ratio, ζ r, defined as
(2.6.13) 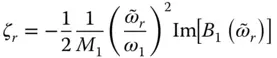
The damping ratio ζ ris non‐negative because Im[ B 1( ω )] ≤ 0 for all excitation frequencies.
For dam–water systems with non‐absorptive reservoir bottom ( α = 1), 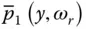 is real‐valued ( Section 2.3). Thus, m a( y ) is real‐valued and Eq. (2.6.11)reduces to the earlier result (Chopra 1978) for the natural vibration frequency of the equivalent SDF system; and the added damping ratio, ζ r, is zero, so Eq. (2.6.13)reduces to the earlier expression (Chopra 1978) for the damping ratio of the equivalent SDF system. An absorptive reservoir bottom ( α < 1) results in complex‐valued m a( y ), which modifies the resonant frequency and increases the damping because now hydrodynamic pressure waves propagate upstream and refract into the absorptive reservoir bottom at the excitation frequency,
is real‐valued ( Section 2.3). Thus, m a( y ) is real‐valued and Eq. (2.6.11)reduces to the earlier result (Chopra 1978) for the natural vibration frequency of the equivalent SDF system; and the added damping ratio, ζ r, is zero, so Eq. (2.6.13)reduces to the earlier expression (Chopra 1978) for the damping ratio of the equivalent SDF system. An absorptive reservoir bottom ( α < 1) results in complex‐valued m a( y ), which modifies the resonant frequency and increases the damping because now hydrodynamic pressure waves propagate upstream and refract into the absorptive reservoir bottom at the excitation frequency, 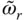 .
.
2.6.2 Evaluation of Equivalent SDF System
The effectiveness of the equivalent SDF system in representing the fundamental mode response of dams with impounded water is demonstrated in Figure 2.6.1. The exact and equivalent‐SDF‐system responses of an idealized concrete gravity dam monolith with the triangular cross section (described in Section 2.5.2) to harmonic horizontal ground motion were computed by numerically evaluating Eqs. (2.6.1)and (2.6.7), respectively. The absolute value of the complex‐valued frequency response function for horizontal acceleration at the dam crest is plotted against the normalized excitation frequency parameter, ω / ω 1, so the results are valid for dams of any height, H s. Figure 2.6.1demonstrates that the equivalent SDF system provides a good approximation of the fundamental mode response of the dam with impounded water for a wide range of values of the frequency ratio Ω r– hence of the concrete modulus, E s– and of the wave reflection coefficient, α , at the reservoir bottom. The approximation of the frequency bandwidth of the resonant peak is more accurate if the reservoir bottom is absorptive because additional energy is lost at this boundary, which eliminates the sharp peaks in the response curves.
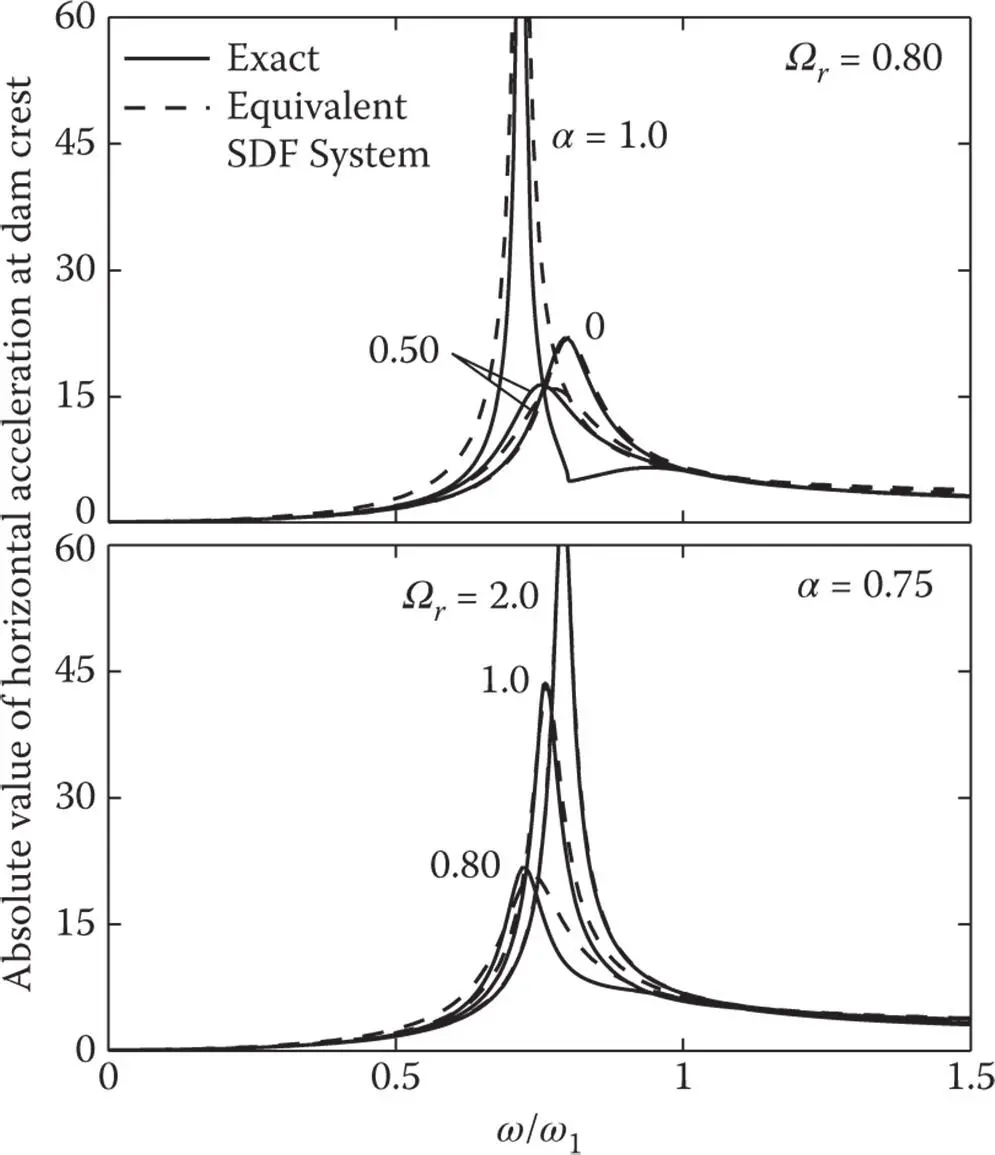
Figure 2.6.1Comparison of exact and equivalent SDF system response of dams on rigid foundation with impounded water due to harmonic horizontal ground motion; ζ 1= 2%.
The exact value of the fundamental resonant period, obtained from the resonant peak of 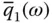 , computed from Eq. (2.6.1), is compared in Figure 2.6.2with the natural vibration period,
, computed from Eq. (2.6.1), is compared in Figure 2.6.2with the natural vibration period, 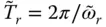 , of the equivalent SDF system in which
, of the equivalent SDF system in which 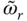 is computed from Eq. (2.6.11). It is apparent that the natural vibration period of the equivalent SDF system provides a very accurate approximation of the fundamental resonant period of the dam with impounded water if the reservoir bottom is non‐absorptive, but it is slightly less accurate if the reservoir bottom is absorptive.
is computed from Eq. (2.6.11). It is apparent that the natural vibration period of the equivalent SDF system provides a very accurate approximation of the fundamental resonant period of the dam with impounded water if the reservoir bottom is non‐absorptive, but it is slightly less accurate if the reservoir bottom is absorptive.
2.6.3 Hydrodynamic Effects on Natural Frequency and Damping Ratio
Figure 2.6.2demonstrates that dam–water interaction lengthens the vibration period, with this effect being especially small for H / H s, less than 0.5, but increasing rapidly with water depth (Chakrabarti and Chopra 1974). Furthermore, the vibration period ratio, 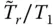 , increases as the frequency ratio, Ω r, decreases (i.e. the modulus of elasticity, E s, of the concrete increases) because of interaction between the closely‐spaced fundamental vibration frequencies of the dam and water ( Section 2.5.3); these observations first appeared in Chopra (1968). As the reservoir bottom becomes more absorptive, i.e. as the wave reflection coefficient α decreases, the fundamental resonant period is reduced from its value for a non‐absorptive reservoir bottom. This occurs because reservoir bottom absorption reduces the hydrodynamic terms ( Section 2.3.3), thus reducing the value of the added mass. The wave reflection coefficient, α , has little influence on the fundamental resonant period for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s. However, the
, increases as the frequency ratio, Ω r, decreases (i.e. the modulus of elasticity, E s, of the concrete increases) because of interaction between the closely‐spaced fundamental vibration frequencies of the dam and water ( Section 2.5.3); these observations first appeared in Chopra (1968). As the reservoir bottom becomes more absorptive, i.e. as the wave reflection coefficient α decreases, the fundamental resonant period is reduced from its value for a non‐absorptive reservoir bottom. This occurs because reservoir bottom absorption reduces the hydrodynamic terms ( Section 2.3.3), thus reducing the value of the added mass. The wave reflection coefficient, α , has little influence on the fundamental resonant period for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s. However, the  ratio is relatively insensitive to E sif the reservoir bottom is absorptive with α ≤ 0.5.
ratio is relatively insensitive to E sif the reservoir bottom is absorptive with α ≤ 0.5.
Читать дальше

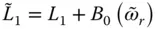
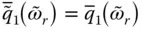 , i.e. the equivalent SDF system gives the exact value for the fundamental resonant response of the dam–water system.
, i.e. the equivalent SDF system gives the exact value for the fundamental resonant response of the dam–water system.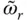 , of the equivalent SDF system is
, of the equivalent SDF system is 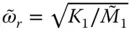 ; substituting
; substituting 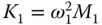 and Eq. (2.6.10a)for
and Eq. (2.6.10a)for 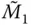 , gives
, gives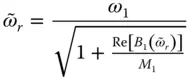
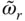 appears on both sides, this equation must be solved iteratively for
appears on both sides, this equation must be solved iteratively for 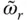 . Hydrodynamic effects always reduce the natural vibration frequency because Re[ B 1( ω )] > 0 for all excitation frequencies. Does Eq. (2.6.11), determined from the properties of the equivalent SDF system, give the correct reduction in frequency of the dam due to dam–water interaction? The fundamental resonant frequency of the dam–water system is approximately given by the excitation frequency that makes the real‐valued component of the denominator in the exact fundamental mode response, Eq. (2.6.1), equal to zero. This argument also leads to Eq. (2.6.11), which demonstrates that the mass of the equivalent SDF system defined in Eqs. (2.6.5)and (2.6.6)reduces the fundamental resonant frequency of the dam due to hydrodynamic effects by the exact amount.
. Hydrodynamic effects always reduce the natural vibration frequency because Re[ B 1( ω )] > 0 for all excitation frequencies. Does Eq. (2.6.11), determined from the properties of the equivalent SDF system, give the correct reduction in frequency of the dam due to dam–water interaction? The fundamental resonant frequency of the dam–water system is approximately given by the excitation frequency that makes the real‐valued component of the denominator in the exact fundamental mode response, Eq. (2.6.1), equal to zero. This argument also leads to Eq. (2.6.11), which demonstrates that the mass of the equivalent SDF system defined in Eqs. (2.6.5)and (2.6.6)reduces the fundamental resonant frequency of the dam due to hydrodynamic effects by the exact amount.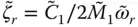 is determined by substituting Eqs. (2.6.10b)and (2.6.10a)and utilizing Eq. (2.6.11):
is determined by substituting Eqs. (2.6.10b)and (2.6.10a)and utilizing Eq. (2.6.11):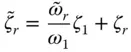
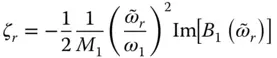
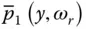 is real‐valued ( Section 2.3). Thus, m a( y ) is real‐valued and Eq. (2.6.11)reduces to the earlier result (Chopra 1978) for the natural vibration frequency of the equivalent SDF system; and the added damping ratio, ζ r, is zero, so Eq. (2.6.13)reduces to the earlier expression (Chopra 1978) for the damping ratio of the equivalent SDF system. An absorptive reservoir bottom ( α < 1) results in complex‐valued m a( y ), which modifies the resonant frequency and increases the damping because now hydrodynamic pressure waves propagate upstream and refract into the absorptive reservoir bottom at the excitation frequency,
is real‐valued ( Section 2.3). Thus, m a( y ) is real‐valued and Eq. (2.6.11)reduces to the earlier result (Chopra 1978) for the natural vibration frequency of the equivalent SDF system; and the added damping ratio, ζ r, is zero, so Eq. (2.6.13)reduces to the earlier expression (Chopra 1978) for the damping ratio of the equivalent SDF system. An absorptive reservoir bottom ( α < 1) results in complex‐valued m a( y ), which modifies the resonant frequency and increases the damping because now hydrodynamic pressure waves propagate upstream and refract into the absorptive reservoir bottom at the excitation frequency, 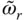 .
.
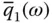 , computed from Eq. (2.6.1), is compared in Figure 2.6.2with the natural vibration period,
, computed from Eq. (2.6.1), is compared in Figure 2.6.2with the natural vibration period, 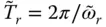 , of the equivalent SDF system in which
, of the equivalent SDF system in which 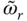 is computed from Eq. (2.6.11). It is apparent that the natural vibration period of the equivalent SDF system provides a very accurate approximation of the fundamental resonant period of the dam with impounded water if the reservoir bottom is non‐absorptive, but it is slightly less accurate if the reservoir bottom is absorptive.
is computed from Eq. (2.6.11). It is apparent that the natural vibration period of the equivalent SDF system provides a very accurate approximation of the fundamental resonant period of the dam with impounded water if the reservoir bottom is non‐absorptive, but it is slightly less accurate if the reservoir bottom is absorptive.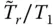 , increases as the frequency ratio, Ω r, decreases (i.e. the modulus of elasticity, E s, of the concrete increases) because of interaction between the closely‐spaced fundamental vibration frequencies of the dam and water ( Section 2.5.3); these observations first appeared in Chopra (1968). As the reservoir bottom becomes more absorptive, i.e. as the wave reflection coefficient α decreases, the fundamental resonant period is reduced from its value for a non‐absorptive reservoir bottom. This occurs because reservoir bottom absorption reduces the hydrodynamic terms ( Section 2.3.3), thus reducing the value of the added mass. The wave reflection coefficient, α , has little influence on the fundamental resonant period for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s. However, the
, increases as the frequency ratio, Ω r, decreases (i.e. the modulus of elasticity, E s, of the concrete increases) because of interaction between the closely‐spaced fundamental vibration frequencies of the dam and water ( Section 2.5.3); these observations first appeared in Chopra (1968). As the reservoir bottom becomes more absorptive, i.e. as the wave reflection coefficient α decreases, the fundamental resonant period is reduced from its value for a non‐absorptive reservoir bottom. This occurs because reservoir bottom absorption reduces the hydrodynamic terms ( Section 2.3.3), thus reducing the value of the added mass. The wave reflection coefficient, α , has little influence on the fundamental resonant period for larger values of Ω r, i.e. smaller values of E s. However, the  ratio is relatively insensitive to E sif the reservoir bottom is absorptive with α ≤ 0.5.
ratio is relatively insensitive to E sif the reservoir bottom is absorptive with α ≤ 0.5.










