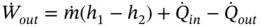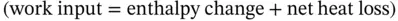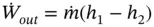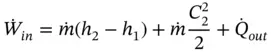Jamil Ghojel - Fundamentals of Heat Engines
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Jamil Ghojel - Fundamentals of Heat Engines» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Fundamentals of Heat Engines
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Fundamentals of Heat Engines: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Fundamentals of Heat Engines»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Fundamentals of Heat Engines: Reciprocating and Gas Turbine Internal-Combustion Engines Covers two main heat engines in one single reference Teaches heat engine fundamentals as well as advanced topics Includes comprehensive thermodynamic and thermochemistry data Offers customizable content to suit beginner or advanced undergraduate courses and entry-level postgraduate studies in automotive, mechanical, and aerospace degrees Provides representative problems at the end of most chapters, along with a detailed example of piston-engine design-point calculations Features case studies of design-point calculations of gas turbine engines in two chapters
can be adopted for mechanical, aerospace, and automotive engineering courses at different levels and will also benefit engineering professionals in those fields and beyond.

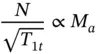
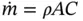 and ρ = p / RT . Combining these equations with the equation for the Mach number, we obtain
and ρ = p / RT . Combining these equations with the equation for the Mach number, we obtain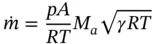
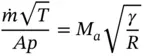
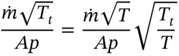
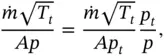
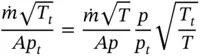
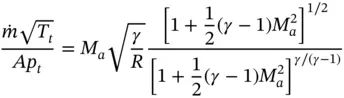
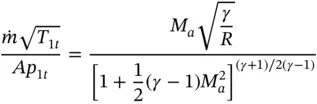
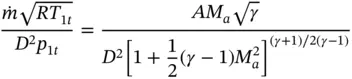
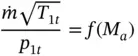
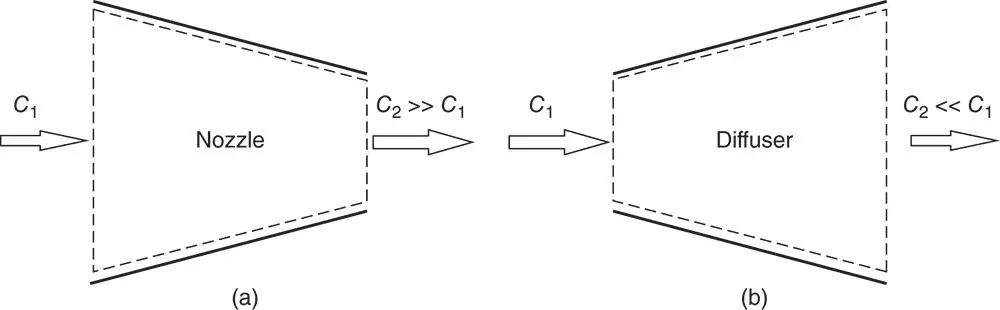
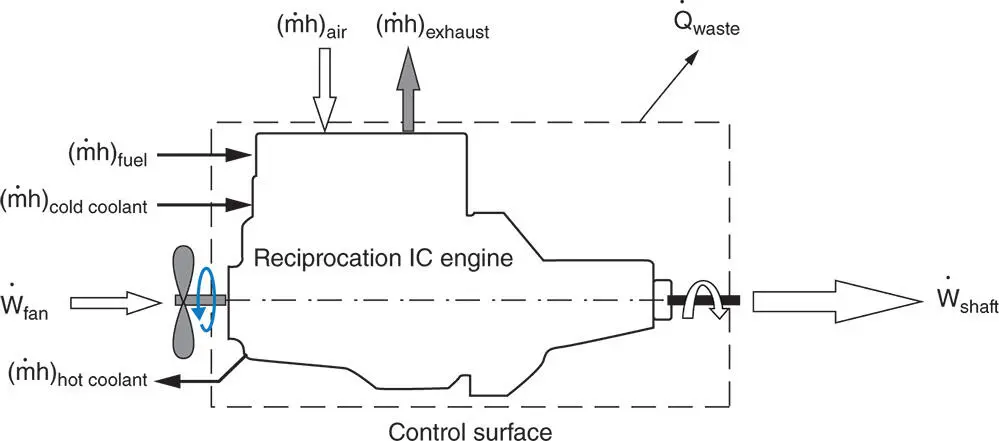
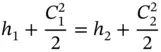
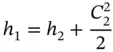
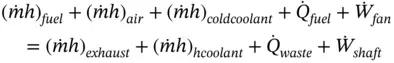
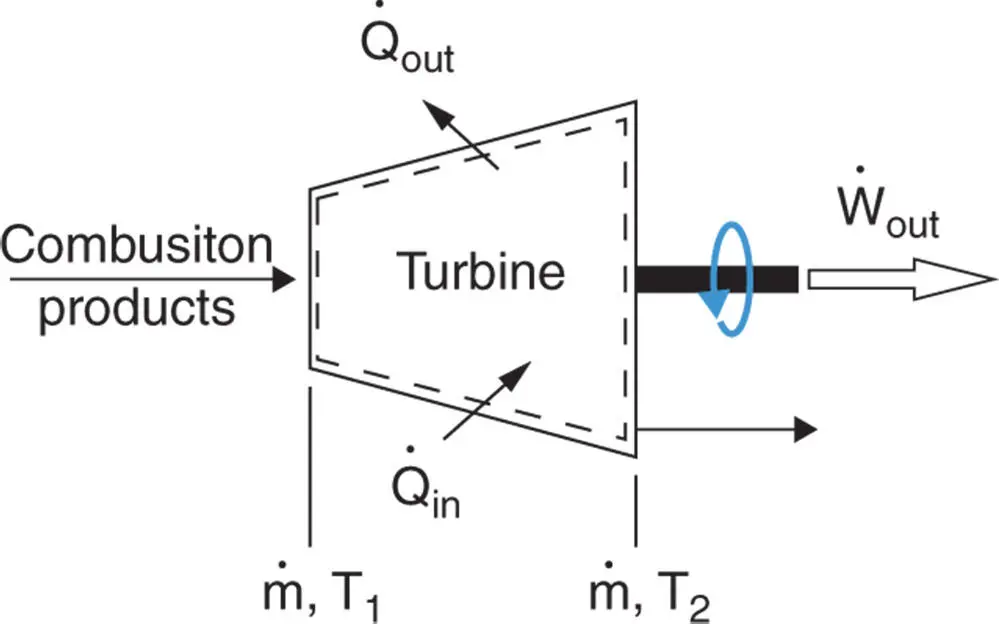
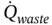 is the total heat wasted as a result of heat transfer from the hot surfaces of the engine to the surroundings.
is the total heat wasted as a result of heat transfer from the hot surfaces of the engine to the surroundings.