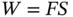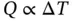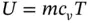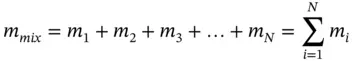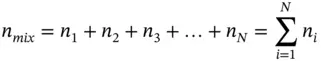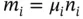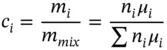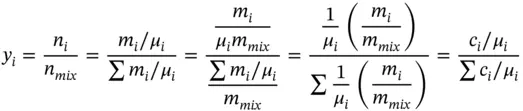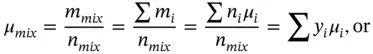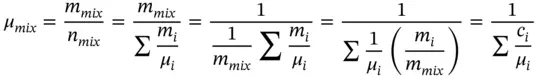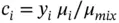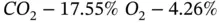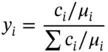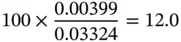| Machine |
Working substance |
| Air compressor |
Air |
| Reciprocating and gas turbine engines |
Combustion products |
| Steam turbines |
Water vapour (steam) |
| Refrigerators |
Ammonia, CFCs, HCFCs |
1.3.1 Work and Heat as Different Forms of Energy
Energy is the capacity a body or substance possesses that can result in the performance of mechanical work. The presence of energy can only be observed by its effects, which can appear in different forms such as work and heat. Other forms of energy include potential, kinetic, and internal. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Mechanical work is the product of force and distance:
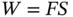
If F and S are at right angles to each other, no work can be done.
Heat is a manifestation of the degree of agitation of atoms and molecules making up a body as its temperature changes. It is also the effect of one system on another as a result of temperature inequality. Alternately, it can be said that heat is interaction that is not work.
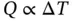
A system is a region in space with boundaries across which matter, work, and heat can cross, as shown schematically in Figure 1.7. An example of a real system is a mass of gas or vapour contained in an engine cylinder, the boundary of which is comprised of the cylinder walls, cylinder head, and piston crown when the valves are closed.
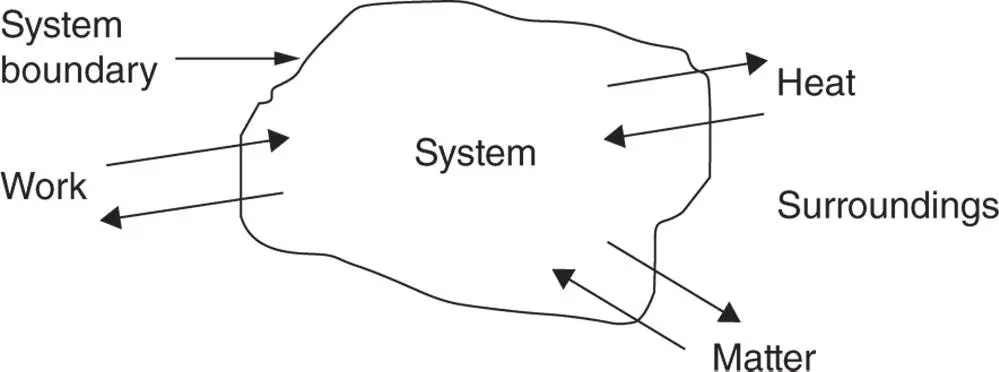
Figure 1.7Schematic diagram of a thermodynamic system.
There are two types of systems:
Open system in which matter, heat, and work can pass through the system boundary
Closed system in which neither matter, heat, nor work pass through the system boundary
The state of the working fluid (matter) in a system is fully defined by two independent properties.
A property is a measurable characteristic of a system such as pressure, volume, temperature, energy, density, or a combination of the former such as internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy. Some measured properties were defined in Section 1.2, and temperature will be discussed in detail later, so we will define the derived (or combination) properties here.
Specific internal energy u is the intrinsic energy per unit mass of a fluid that is not in motion. Its value depends on its pressure and temperature unless the fluid is a perfect gas, in which case the specific internal energy will be dependent on temperature only. For a perfect gas, u = c v T
and for a mass m of the fluid,
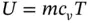
Enthalpy is defined as H = U + pV kJ . Specific enthalpy is h = u + pv kJ / kg .
Entropy can be defined from the equation dQ = Tds , where T is the absolute thermodynamic temperature and s is the property entropy in units of J / mole . K .
A process is a change in a system from one state to another. Hence, the change in the pressure and temperature of a mass of gas from ( p 1, T 1) to ( p 2, T 2) is a process. The state defined by ( p 1, T 1) is the initial state of the system, and the state defined by ( p 2, T 2) is the final state of the system. Processes can be reversible or irreversible. In a reversible process, both the system and the surroundings are returned to their original conditions after the process and the reverse process had been carried out. In an irreversible process, reversal cannot be effected without leaving some change in the system or surroundings. Any process with friction (dry friction or viscous friction) is irreversible because some energy of the system is expended in overcoming friction and dissipated in the surroundings.
For a mixture of N gaseous components, the total mass and total moles are, respectively,
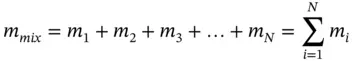
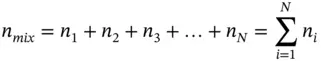
where
m i: mass of the i th component
n i: amount of substance in moles of the i th component
If the molecular mass of i th component is μ i, then
(1.40) 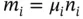
The mass fraction (or mass concentration) is
(1.41) 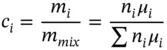
Similarly, the mole fraction (or mole concentration) can be found as follows:
(1.42) 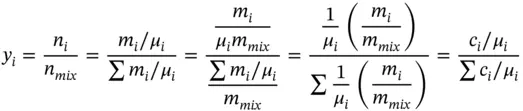
The molar mass of the total mixture is
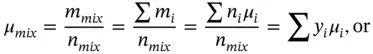
(1.43) 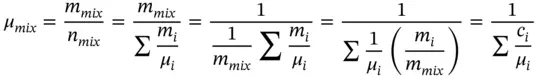
From Eqs. (1.40), ( 1.41), and 1.42,
(1.44) 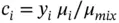
A gas mixture has the following mass composition:
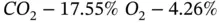
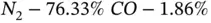
Determine the molar composition of the mixture.
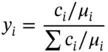
| Gas |
% Mass fraction |
Mass fraction, c i |
Molecular mass, μ i |
Mole fraction, c i/ μ i |
% Mole fraction |
| CO 2 |
17.55 |
0.175 5 |
44 |
0.003 99 |
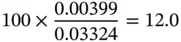 |
| O 2 |
4.26 |
0.042 6 |
32 |
0.001 33 |
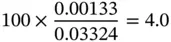 |
| N 2 |
76.33 |
0.763 3 |
28 |
0.027 26 |
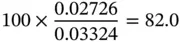 |
| CO |
1.86 |
0.018 6 |
28 |
0.000 66 |
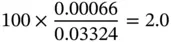 |
|
100 |
∑ c i= 1.0 |
|
∑ c i/ μ i= 0.03324 |
Total = 100 |
1.3.2.1 Dalton Model of Gas Mixtures
Читать дальше