Industrial Manipulators
An industrial manipulator of the type shown in Figure 1.1is essentially a mechanical arm operating under computer control. Such devices, though far from the robots of science fiction, are nevertheless extremely complex electromechanical systems whose analytical description requires advanced methods, presenting many challenging and interesting research problems.
Figure 1.1 A six-axis industrial manipulator, the KUKA 500 FORTEC robot. (Photo courtesy of KUKA Robotics.)
An official definition of such a robot comes from the Robot Institute of America(RIA):
A robot is a reprogrammable, multifunctional manipulator designed to move material, parts, tools, or specialized devices through variable programmed motions for the performance of a variety of tasks .
The key element in the above definition is the reprogrammability, which gives a robot its utility and adaptability. The so-called robotics revolution is, in fact, part of the larger computer revolution.
Even this restricted definition of a robot has several features that make it attractive in an industrial environment. Among the advantages often cited in favor of the introduction of robots are decreased labor costs, increased precision and productivity, increased flexibility compared with specialized machines, and more humane working conditions as dull, repetitive, or hazardous jobs are performed by robots.
The industrial manipulator was born out of the marriage of two earlier technologies: teleoperatorsand numerically controlled milling machines. Teleoperators, or master-slave devices, were developed during the second world war to handle radioactive materials. Computer numerical control (CNC) was developed because of the high precision required in the machining of certain items, such as components of high performance aircraft. The first industrial robots essentially combined the mechanical linkages of the teleoperator with the autonomy and programmability of CNC machines.
The first successful applications of robot manipulators generally involved some sort of material transfer, such as injection molding or stamping, in which the robot merely attended a press to unload and either transfer or stack the finished parts. These first robots could be programmed to execute a sequence of movements, such as moving to a location A, closing a gripper, moving to a location B, etc., but had no external sensor capability. More complex applications, such as welding, grinding, deburring, and assembly, require not only more complex motion but also some form of external sensing such as vision, tactile, or force sensing, due to the increased interaction of the robot with its environment.
Figure 1.2shows the estimated number of industrial robots worldwide between 2014 and 2020. In the future the market for service and medical robots will likely be even greater than the market for industrial robots. Service robots are defined as robots outside the manufacturing sector, such as robot vacuum cleaners, lawn mowers, window cleaners, delivery robots, etc. In 2018 alone, more than 30 million service robots were sold worldwide. The future market for robot assistants for elderly care and other medical robots will also be strong as populations continue to age.
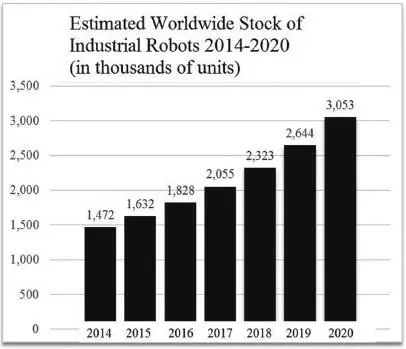
Figure 1.2 Estimated number of industrial robots worldwide 2014–2020. The industrial robot market has been growing around 14% per year. (Source: International Federation of Robotics 2018.)
Mobile Robots
Mobile robots encompass wheel and track driven robots, walking robots, climbing, swimming, crawling and flying robots. A typical wheeled mobile robot is shown in Figure 1.3. Mobile robots are used as household robots for vacuum cleaning and lawn mowing robots, as field robots for surveillance, search and rescue, environmental monitoring, forestry and agriculture, and other applications. Autonomous vehicles, for example self-driving cars and trucks, is an emerging area of robotics with great interest and promise.

Figure 1.3 Example of a typical mobile robot, the Fetch series. The figure on the right shows the mobile robot base with an attached manipulator arm. (Photo courtesy of Fetch Robotics.)
There are many other applications of robotics in areas where the use of humans is impractical or undesirable. Among these are undersea and planetary exploration, satellite retrieval and repair, the defusing of explosive devices, and work in radioactive environments. Finally, prostheses, such as artificial limbs, are themselves robotic devices requiring methods of analysis and design similar to those of industrial manipulators.
The science of robotics has grown tremendously over the past twenty years, fueled by rapid advances in computer and sensor technology as well as theoretical advances in control and computer vision. In addition to the topics listed above, robotics encompasses several areas not covered in this text such as legged robots, flying and swimming robots, grasping, artificial intelligence, computer architectures, programming languages, and computer-aided design. In fact, the new subject of mechatronicshas emerged over the past four decades and, in a sense, includes robotics as a subdiscipline. Mechatronics has been defined as the synergistic integration of mechanics, electronics, computer science, and control, and includes not only robotics, but many other areas such as automotive control systems.
1.1 Mathematical Modeling of Robots
In this text we will be primarily concerned with developing and analyzing mathematical models for robots. In particular, we will develop methods to represent basic geometric aspects of robotic manipulation and locomotion. Equipped with these mathematical models, we will develop methods for planning and controlling robot motions to perform specified tasks. We begin here by describing some of the basic notation and terminology that we will use in later chapters to develop mathematical models for robot manipulators and mobile robots.
1.1.1 Symbolic Representation of Robot Manipulators
Robot manipulators are composed of linksconnected by jointsto form a kinematic chain. Joints are typically rotary (revolute) or linear (prismatic). A revolutejoint is like a hinge and allows relative rotation between two links. A prismaticjoint allows a linear relative motion between two links. We denote revolute joints by R and prismatic joints by P , and draw them as shown in Figure 1.4. For example, a three-link arm with three revolute joints will be referred to as an RRR arm.
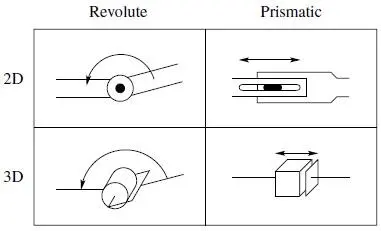
Figure 1.4 Symbolic representation of robot joints. Each joint allows a single degree of freedom of motion between adjacent links of the manipulator. The revolute joint (shown in 2D and 3D on the left) produces a relative rotation between adjacent links. The prismatic joint (shown in 2D and 3D on the right) produces a linear or telescoping motion between adjacent links.
Читать дальше
















