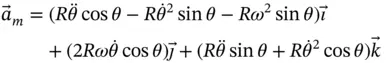Ronald J. Anderson - Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Ronald J. Anderson - Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
is a definitive resource. The text extensively covers foundational knowledge in the field and uses it to lead up to and include: finite elements, the inerter, Discrete Fourier Transforms, flow-induced vibrations, and self-excited oscillations in rail vehicles.
The text aims to accomplish two things in a single, introductory, semester-length, course in vibrations. The primary goal is to present the basics of vibrations in a manner that promotes understanding and interest while building a foundation of knowledge in the field. The secondary goal is to give students a good understanding of two topics that are ubiquitous in today's engineering workplace – finite element analysis (FEA) and Discrete Fourier Transforms (the DFT- most often seen in the form of the Fast Fourier Transform or FFT). FEA and FFT software tools are readily available to both students and practicing engineers and they need to be used with understanding and a degree of caution. While these two subjects fit nicely into vibrations, this book presents them in a way that emphasizes understanding of the underlying principles so that students are aware of both the power and the limitations of the methods.
In addition to covering all the topics that make up an introductory knowledge of vibrations, the book includes:
● End of chapter exercises to help students review key topics and definitions
● Access to sample data files, software, and animations via a dedicated website

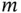 , sliding on a frictionless semicircular wire that rotates about a vertical axis with a constant angular velocity,
, sliding on a frictionless semicircular wire that rotates about a vertical axis with a constant angular velocity, 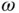 . The wire has radius
. The wire has radius  . Gravity acts to pull the mass to the bottom of the semicircle while centripetal effects try to move it to the top. The single angular degree of freedom,
. Gravity acts to pull the mass to the bottom of the semicircle while centripetal effects try to move it to the top. The single angular degree of freedom, 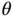 , is sufficient to describe the motion of the bead on the wire.
, is sufficient to describe the motion of the bead on the wire.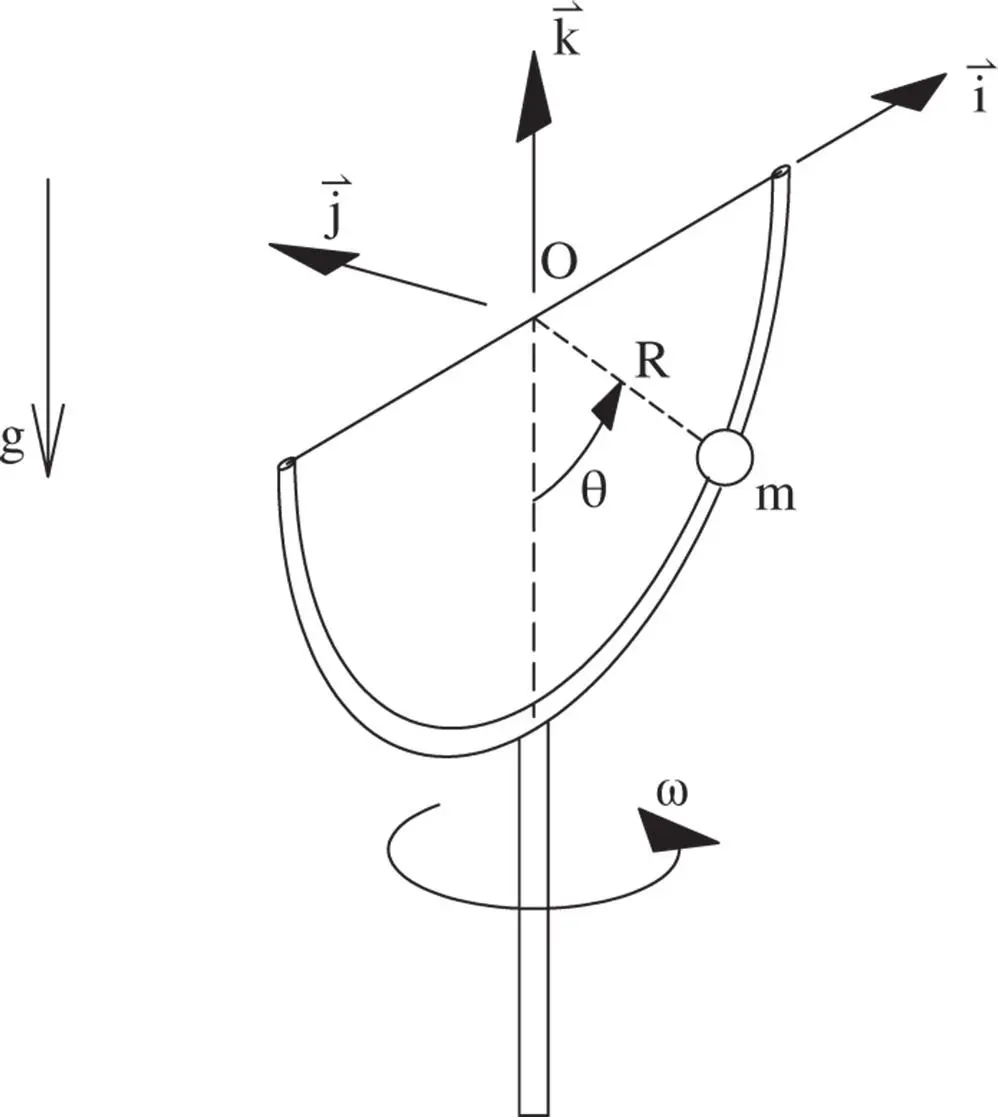
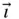 ,
, 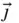 ,
, 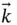 ) system shown in Figure 1.1. This is a rotating system fixed in the wire so that
) system shown in Figure 1.1. This is a rotating system fixed in the wire so that 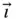 and
and 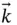 stay in the plane of the wire and
stay in the plane of the wire and 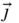 is perpendicular to the plane. Furthermore,
is perpendicular to the plane. Furthermore, 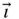 and
and 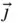 remain horizontal and
remain horizontal and 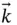 is always vertical. The angular velocity of the coordinate system is
is always vertical. The angular velocity of the coordinate system is 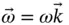 .
.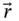 can be a position vector, a velocity vector, an angular momentum vector, or any other vector.
can be a position vector, a velocity vector, an angular momentum vector, or any other vector.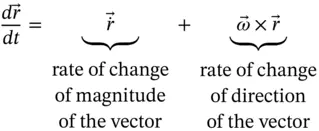
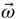 , is the absolute angular velocity of the coordinate system in which the vector,
, is the absolute angular velocity of the coordinate system in which the vector, 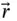 , is expressed. There is a danger that the rate of change of direction terms will be included twice if the angular velocity of the vector relative to the coordinate system in which it is measured is used instead.
, is expressed. There is a danger that the rate of change of direction terms will be included twice if the angular velocity of the vector relative to the coordinate system in which it is measured is used instead.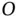 , and writing an expression for the position vector that locates
, and writing an expression for the position vector that locates 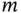 with respect to
with respect to  .
.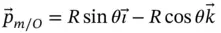
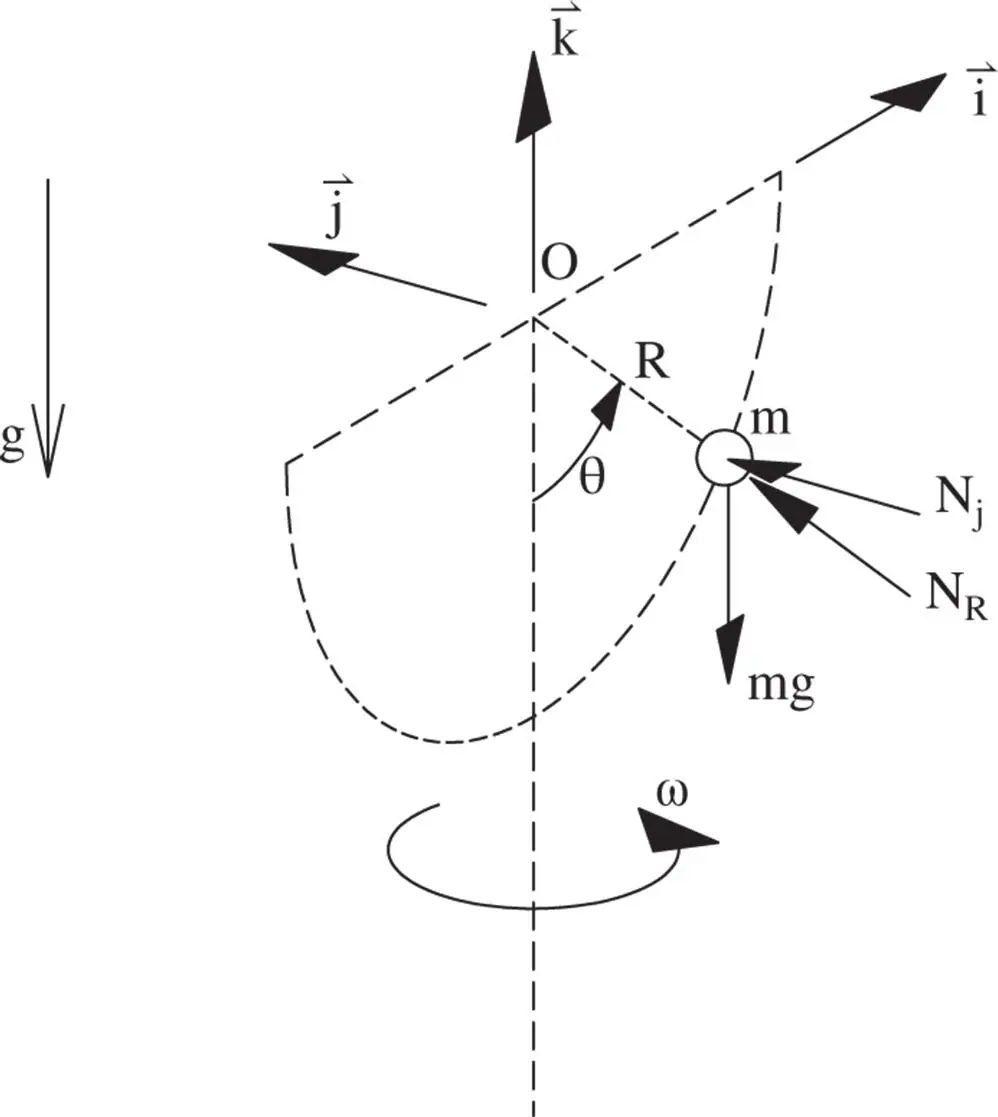
 is
is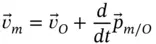
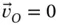 since
since  is a fixed point and that
is a fixed point and that  since the radius of a semicircle is constant,
since the radius of a semicircle is constant,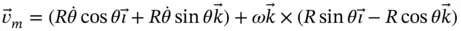
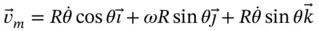
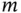 is then
is then