Readers are encouraged and sincerely welcome to contact me at ozgoren@metu.edu.tr with regard to feedback, suggestions, and questions.
Ankara, March 2019
M. Kemal Ozgoren
This book is based on the graduate courses “Advanced Dynamics” and “Principles of Robotics” that I have been teaching for a long time. Therefore, many students of these courses and several colleagues involved with related subjects have so far indicated their valuable opinions and encouraged me to write such a book. I would like to express my thanks to all of them and also to the Mechanical Engineering Department of Middle East Technical University that has provided the excellent academic medium and all the conveniences for me in developing and teaching the mentioned courses.
I would also like to express my thanks to the reviewers for their constructive comments and to all the related personnel of Wiley for their highly appreciated efforts during all the time from the initiation to the finalization of this book.
List of Commonly Used Symbols, Abbreviations, and Acronyms
Symbols Based on the Latin Alphabet
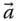 Acceleration of an implied point (in a general use)
Acceleration of an implied point (in a general use) 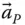 Acceleration of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame
Acceleration of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame 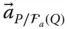 Acceleration of a point P with respect to a reference frame
Acceleration of a point P with respect to a reference frame 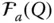 ;
; 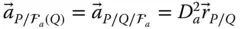 b kEffective length of
b kEffective length of 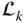 between
between 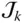 and
and 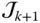 along
along 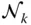
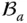 A rigid body denoted by the index a and represented by the frame
A rigid body denoted by the index a and represented by the frame 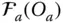
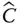 Orientation matrix of an implied body or frame (in a general use)
Orientation matrix of an implied body or frame (in a general use) 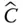 Orientation matrix of the end‐effector (
Orientation matrix of the end‐effector ( 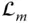 ) with respect to the base frame;
) with respect to the base frame; 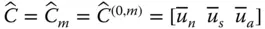
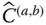 CTM that transforms components from
CTM that transforms components from 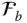 to
to 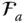 ;
; 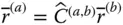
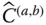 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 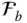 with respect to
with respect to 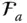 ;
; 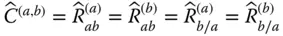
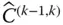 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 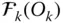 with respect to
with respect to 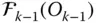
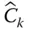 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 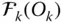 with respect to
with respect to 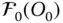 ;
; 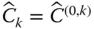
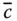 A general column matrix;
A general column matrix; 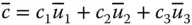
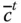 A general row matrix, i.e. the transpose of
A general row matrix, i.e. the transpose of 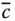
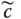 Skew symmetric matrix generated from
Skew symmetric matrix generated from 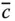 ;
; 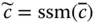 D aVector differentiator with respect to
D aVector differentiator with respect to 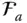 ;
; 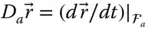 d kConstant offset of
d kConstant offset of 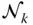 with respect to
with respect to 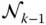 if
if 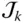 is revolute d mTip point offset; d m= RP = O m − 1 O m E Elbow point of a manipulator
is revolute d mTip point offset; d m= RP = O m − 1 O m E Elbow point of a manipulator 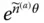 Exponential form of
Exponential form of 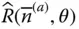
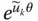 Exponential form of
Exponential form of 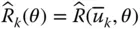
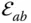 Kinematic element of
Kinematic element of 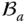 that mates with
that mates with 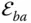 of
of 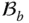 f ab( x , y , z )Surface function that describes the surface
f ab( x , y , z )Surface function that describes the surface 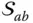 in the link frame
in the link frame 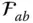
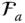 A reference frame with an orientation index a , whose origin is implied
A reference frame with an orientation index a , whose origin is implied 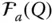 A reference frame
A reference frame 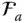 with a specific origin Q
with a specific origin Q 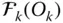 Reference frame attached to
Reference frame attached to 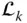
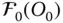 Base frame, i.e. the reference frame attached to the base link
Base frame, i.e. the reference frame attached to the base link 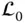
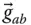 Gradient vector of the surface
Gradient vector of the surface 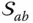
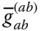 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 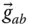 in the link frame
in the link frame 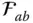
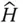 Abbreviation for
Abbreviation for 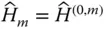 of the last link
of the last link 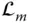
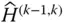 HTM that represents the displacement from
HTM that represents the displacement from 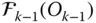 to
to 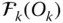
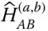 HTM that transforms coordinates from
HTM that transforms coordinates from 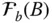 to
to 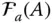 ;
; 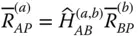
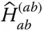 Hessian matrix of the surface
Hessian matrix of the surface 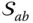 expressed in the link frame
expressed in the link frame 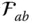
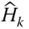 Abbreviation for
Abbreviation for 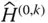 of the link
of the link 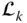
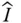 Identity matrix;
Identity matrix; 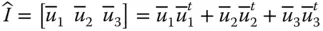 j kNumber of joints with k degrees of relative freedom
j kNumber of joints with k degrees of relative freedom 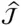 A general Jacobian matrix
A general Jacobian matrix 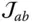 The joint (i.e. kinematic pair) between
The joint (i.e. kinematic pair) between 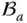 and
and 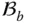 ;
; 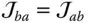
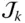 Joint between
Joint between 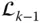 and
and 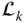
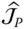 Tip point Jacobian matrix
Tip point Jacobian matrix 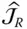 Wrist point Jacobian matrix L k k th leg (or limb) of a parallel manipulator
Wrist point Jacobian matrix L k k th leg (or limb) of a parallel manipulator 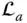 A link denoted by the index a
A link denoted by the index a 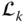 k th link of a manipulator
k th link of a manipulator 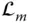 The last link (i.e. end‐effector) of a serial manipulator with m links
The last link (i.e. end‐effector) of a serial manipulator with m links 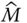 A general square matrix m Number of links and joints of a serial manipulator
A general square matrix m Number of links and joints of a serial manipulator 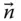 A general unit vector
A general unit vector 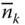 Unit column matrix that represents the twisted axis of
Unit column matrix that represents the twisted axis of 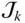 ;
; 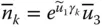 n LNumber of legs (or limbs) of a parallel manipulator n iklNumber of independent kinematic loops n kpmNumber of distinct posture modes of the leg L k n mNumber of moving or movable bodies n pvNumber of primary variables; n pv= μ n pmNumber of distinct posture modes of a manipulator n svNumber of secondary variables; n sv= λn ikl n vNumber of variables needed to describe the pose of a mechanical system
n LNumber of legs (or limbs) of a parallel manipulator n iklNumber of independent kinematic loops n kpmNumber of distinct posture modes of the leg L k n mNumber of moving or movable bodies n pvNumber of primary variables; n pv= μ n pmNumber of distinct posture modes of a manipulator n svNumber of secondary variables; n sv= λn ikl n vNumber of variables needed to describe the pose of a mechanical system 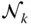 Common normal between the axes of
Common normal between the axes of 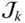 and
and 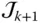 O Origin of the base frame
O Origin of the base frame 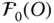 ; O = O 0 O kOrigin of the reference frame
; O = O 0 O kOrigin of the reference frame 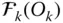 P An arbitrary point (in a general use) P Tip point of a manipulator; P = O mfor a serial manipulator
P An arbitrary point (in a general use) P Tip point of a manipulator; P = O mfor a serial manipulator 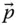 Tip point position vector with respect to the base frame;
Tip point position vector with respect to the base frame; 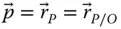
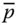 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 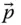 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 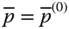 Q abContact point on the surface
Q abContact point on the surface 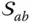
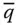 Column matrix of the joint variables q kGeneralized joint variable of
Column matrix of the joint variables q kGeneralized joint variable of 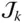 ; q k= θ kor q k= s k R Wrist point of a manipulator; R = O m − 1for a serial manipulator
; q k= θ kor q k= s k R Wrist point of a manipulator; R = O m − 1for a serial manipulator 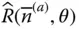 Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot(
Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( 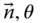 ) in a frame
) in a frame 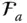
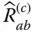 Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( a , b ) in a frame
Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( a , b ) in a frame 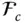
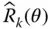 k th basic rotation matrix;
k th basic rotation matrix; 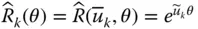
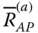 Augmented position matrix of a point P with respect to a frame
Augmented position matrix of a point P with respect to a frame 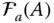
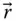 Position vector of an implied point (in a general use)
Position vector of an implied point (in a general use) 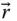 Wrist point position vector with respect to the base frame;
Wrist point position vector with respect to the base frame; 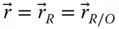
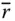 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 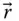 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 
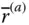 Column matrix representation of a vector
Column matrix representation of a vector 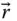 in a frame
in a frame 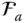 ;
; 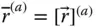
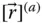 Column matrix representation of a vector
Column matrix representation of a vector 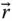 in a frame
in a frame 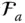 ;
; 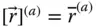
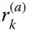 k th component of a vector
k th component of a vector 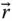 in a frame
in a frame 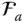 ;
; 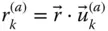
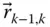 Displacement vector from the origin O k − 1to the origin O k
Displacement vector from the origin O k − 1to the origin O k 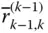 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 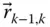 in the link frame
in the link frame 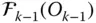
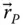 Position vector of a point P with respect to an implied point
Position vector of a point P with respect to an implied point 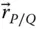 Position vector of a point P with respect to a point Q ;
Position vector of a point P with respect to a point Q ; 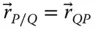
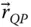 Displacement vector from a point Q to a point P ;
Displacement vector from a point Q to a point P ; 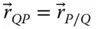 s kJoint variable (sliding displacement) of the prismatic joint
s kJoint variable (sliding displacement) of the prismatic joint 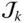 s kVariable offset of
s kVariable offset of 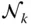 with respect to
with respect to 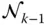 if
if 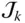 is prismatic S Shoulder point of a manipulator
is prismatic S Shoulder point of a manipulator 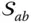 Surface of the kinematic element
Surface of the kinematic element 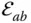
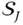 Joint space of a manipulator
Joint space of a manipulator 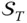 Task space of a manipulator
Task space of a manipulator 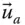 Approach vector of the end‐effector;
Approach vector of the end‐effector; 
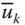 k th basic column matrix;
k th basic column matrix; 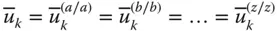
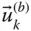 k th unit basis vector of a frame
k th unit basis vector of a frame 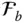
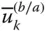 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 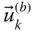 in a frame
in a frame 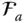 ;
; 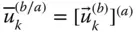
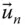 Normal vector of the end‐effector;
Normal vector of the end‐effector; 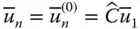
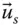 Side vector of the end‐effector;
Side vector of the end‐effector; 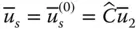
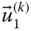 Unit vector along the common normal
Unit vector along the common normal 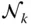
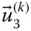 Unit vector along the axis of
Unit vector along the axis of 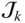
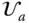 Basis vector triad of a reference frame
Basis vector triad of a reference frame 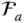 ;
; 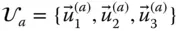
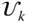 Basis vector triad of the link frame
Basis vector triad of the link frame 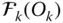 ;
; 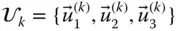
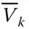 Tip point velocity influence coefficient due to
Tip point velocity influence coefficient due to 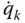 ;
; 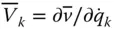
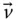 Velocity of an implied point (in a general use)
Velocity of an implied point (in a general use) 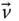 Tip point velocity with respect to the base frame;
Tip point velocity with respect to the base frame; 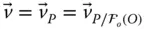
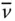 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 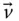 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 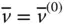
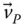 Velocity of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame
Velocity of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame 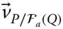 Velocity of a point P with respect to a reference frame
Velocity of a point P with respect to a reference frame 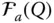 ;
; 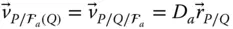
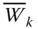 Wrist point velocity influence coefficient due to
Wrist point velocity influence coefficient due to 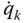 ;
; 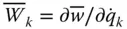
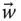 Wrist point velocity with respect to the base frame;
Wrist point velocity with respect to the base frame; 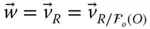
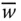 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 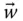 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 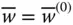
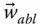 Generatrix line vector of a conical surface
Generatrix line vector of a conical surface 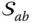
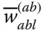 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 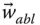 in the link frame
in the link frame 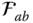
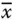 Column matrix of the primary variables
Column matrix of the primary variables 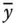 Column matrix of the secondary variables
Column matrix of the secondary variables 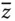 Column matrix of the primary and secondary variables
Column matrix of the primary and secondary variables
Читать дальше

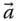 Acceleration of an implied point (in a general use)
Acceleration of an implied point (in a general use) 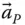 Acceleration of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame
Acceleration of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame 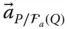 Acceleration of a point P with respect to a reference frame
Acceleration of a point P with respect to a reference frame 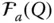 ;
; 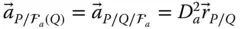 b kEffective length of
b kEffective length of 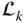 between
between 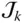 and
and 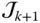 along
along 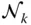
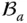 A rigid body denoted by the index a and represented by the frame
A rigid body denoted by the index a and represented by the frame 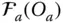
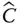 Orientation matrix of an implied body or frame (in a general use)
Orientation matrix of an implied body or frame (in a general use) 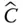 Orientation matrix of the end‐effector (
Orientation matrix of the end‐effector ( 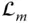 ) with respect to the base frame;
) with respect to the base frame; 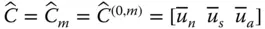
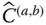 CTM that transforms components from
CTM that transforms components from 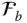 to
to 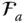 ;
; 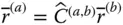
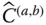 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 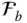 with respect to
with respect to 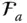 ;
; 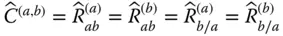
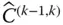 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 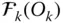 with respect to
with respect to 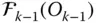
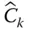 Orientation matrix of
Orientation matrix of 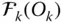 with respect to
with respect to 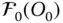 ;
; 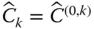
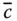 A general column matrix;
A general column matrix; 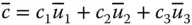
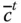 A general row matrix, i.e. the transpose of
A general row matrix, i.e. the transpose of 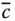
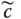 Skew symmetric matrix generated from
Skew symmetric matrix generated from 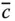 ;
; 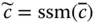 D aVector differentiator with respect to
D aVector differentiator with respect to 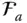 ;
; 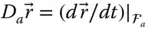 d kConstant offset of
d kConstant offset of 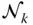 with respect to
with respect to 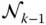 if
if 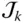 is revolute d mTip point offset; d m= RP = O m − 1 O m E Elbow point of a manipulator
is revolute d mTip point offset; d m= RP = O m − 1 O m E Elbow point of a manipulator 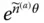 Exponential form of
Exponential form of 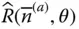
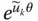 Exponential form of
Exponential form of 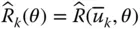
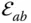 Kinematic element of
Kinematic element of 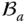 that mates with
that mates with 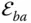 of
of 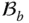 f ab( x , y , z )Surface function that describes the surface
f ab( x , y , z )Surface function that describes the surface 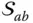 in the link frame
in the link frame 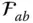
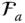 A reference frame with an orientation index a , whose origin is implied
A reference frame with an orientation index a , whose origin is implied 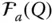 A reference frame
A reference frame 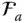 with a specific origin Q
with a specific origin Q 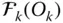 Reference frame attached to
Reference frame attached to 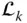
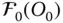 Base frame, i.e. the reference frame attached to the base link
Base frame, i.e. the reference frame attached to the base link 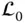
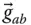 Gradient vector of the surface
Gradient vector of the surface 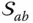
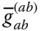 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 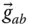 in the link frame
in the link frame 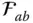
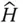 Abbreviation for
Abbreviation for 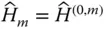 of the last link
of the last link 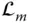
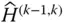 HTM that represents the displacement from
HTM that represents the displacement from 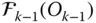 to
to 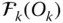
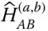 HTM that transforms coordinates from
HTM that transforms coordinates from 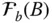 to
to 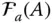 ;
; 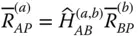
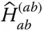 Hessian matrix of the surface
Hessian matrix of the surface 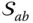 expressed in the link frame
expressed in the link frame 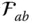
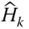 Abbreviation for
Abbreviation for 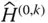 of the link
of the link 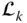
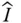 Identity matrix;
Identity matrix; 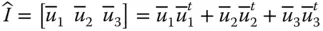 j kNumber of joints with k degrees of relative freedom
j kNumber of joints with k degrees of relative freedom 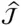 A general Jacobian matrix
A general Jacobian matrix 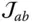 The joint (i.e. kinematic pair) between
The joint (i.e. kinematic pair) between 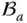 and
and 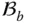 ;
; 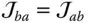
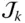 Joint between
Joint between 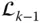 and
and 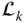
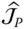 Tip point Jacobian matrix
Tip point Jacobian matrix 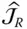 Wrist point Jacobian matrix L k k th leg (or limb) of a parallel manipulator
Wrist point Jacobian matrix L k k th leg (or limb) of a parallel manipulator 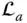 A link denoted by the index a
A link denoted by the index a 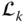 k th link of a manipulator
k th link of a manipulator 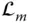 The last link (i.e. end‐effector) of a serial manipulator with m links
The last link (i.e. end‐effector) of a serial manipulator with m links 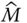 A general square matrix m Number of links and joints of a serial manipulator
A general square matrix m Number of links and joints of a serial manipulator 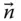 A general unit vector
A general unit vector 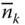 Unit column matrix that represents the twisted axis of
Unit column matrix that represents the twisted axis of 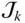 ;
; 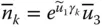 n LNumber of legs (or limbs) of a parallel manipulator n iklNumber of independent kinematic loops n kpmNumber of distinct posture modes of the leg L k n mNumber of moving or movable bodies n pvNumber of primary variables; n pv= μ n pmNumber of distinct posture modes of a manipulator n svNumber of secondary variables; n sv= λn ikl n vNumber of variables needed to describe the pose of a mechanical system
n LNumber of legs (or limbs) of a parallel manipulator n iklNumber of independent kinematic loops n kpmNumber of distinct posture modes of the leg L k n mNumber of moving or movable bodies n pvNumber of primary variables; n pv= μ n pmNumber of distinct posture modes of a manipulator n svNumber of secondary variables; n sv= λn ikl n vNumber of variables needed to describe the pose of a mechanical system 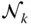 Common normal between the axes of
Common normal between the axes of 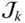 and
and 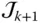 O Origin of the base frame
O Origin of the base frame 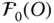 ; O = O 0 O kOrigin of the reference frame
; O = O 0 O kOrigin of the reference frame 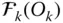 P An arbitrary point (in a general use) P Tip point of a manipulator; P = O mfor a serial manipulator
P An arbitrary point (in a general use) P Tip point of a manipulator; P = O mfor a serial manipulator 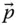 Tip point position vector with respect to the base frame;
Tip point position vector with respect to the base frame; 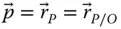
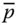 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 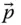 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 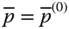 Q abContact point on the surface
Q abContact point on the surface 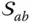
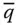 Column matrix of the joint variables q kGeneralized joint variable of
Column matrix of the joint variables q kGeneralized joint variable of 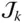 ; q k= θ kor q k= s k R Wrist point of a manipulator; R = O m − 1for a serial manipulator
; q k= θ kor q k= s k R Wrist point of a manipulator; R = O m − 1for a serial manipulator 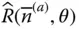 Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot(
Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( 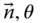 ) in a frame
) in a frame 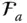
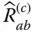 Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( a , b ) in a frame
Matrix representation of the rotation operator rot( a , b ) in a frame 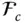
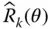 k th basic rotation matrix;
k th basic rotation matrix; 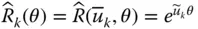
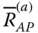 Augmented position matrix of a point P with respect to a frame
Augmented position matrix of a point P with respect to a frame 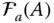
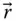 Position vector of an implied point (in a general use)
Position vector of an implied point (in a general use) 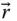 Wrist point position vector with respect to the base frame;
Wrist point position vector with respect to the base frame; 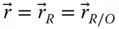
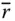 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 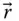 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 
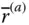 Column matrix representation of a vector
Column matrix representation of a vector 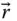 in a frame
in a frame 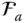 ;
; 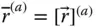
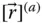 Column matrix representation of a vector
Column matrix representation of a vector 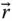 in a frame
in a frame 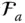 ;
; 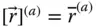
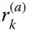 k th component of a vector
k th component of a vector 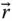 in a frame
in a frame 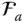 ;
; 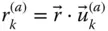
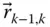 Displacement vector from the origin O k − 1to the origin O k
Displacement vector from the origin O k − 1to the origin O k 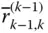 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 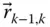 in the link frame
in the link frame 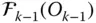
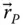 Position vector of a point P with respect to an implied point
Position vector of a point P with respect to an implied point 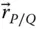 Position vector of a point P with respect to a point Q ;
Position vector of a point P with respect to a point Q ; 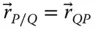
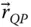 Displacement vector from a point Q to a point P ;
Displacement vector from a point Q to a point P ; 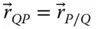 s kJoint variable (sliding displacement) of the prismatic joint
s kJoint variable (sliding displacement) of the prismatic joint 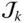 s kVariable offset of
s kVariable offset of 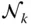 with respect to
with respect to 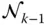 if
if 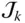 is prismatic S Shoulder point of a manipulator
is prismatic S Shoulder point of a manipulator 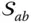 Surface of the kinematic element
Surface of the kinematic element 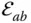
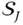 Joint space of a manipulator
Joint space of a manipulator 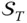 Task space of a manipulator
Task space of a manipulator 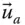 Approach vector of the end‐effector;
Approach vector of the end‐effector; 
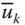 k th basic column matrix;
k th basic column matrix; 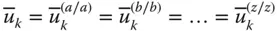
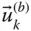 k th unit basis vector of a frame
k th unit basis vector of a frame 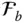
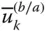 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 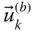 in a frame
in a frame 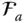 ;
; 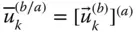
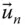 Normal vector of the end‐effector;
Normal vector of the end‐effector; 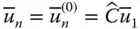
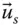 Side vector of the end‐effector;
Side vector of the end‐effector; 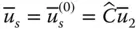
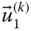 Unit vector along the common normal
Unit vector along the common normal 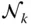
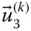 Unit vector along the axis of
Unit vector along the axis of 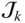
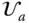 Basis vector triad of a reference frame
Basis vector triad of a reference frame 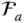 ;
; 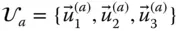
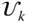 Basis vector triad of the link frame
Basis vector triad of the link frame 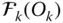 ;
; 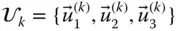
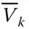 Tip point velocity influence coefficient due to
Tip point velocity influence coefficient due to 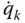 ;
; 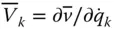
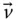 Velocity of an implied point (in a general use)
Velocity of an implied point (in a general use) 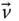 Tip point velocity with respect to the base frame;
Tip point velocity with respect to the base frame; 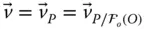
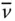 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 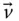 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 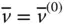
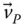 Velocity of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame
Velocity of a point P with respect to an implied reference frame 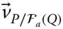 Velocity of a point P with respect to a reference frame
Velocity of a point P with respect to a reference frame 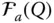 ;
; 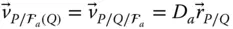
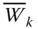 Wrist point velocity influence coefficient due to
Wrist point velocity influence coefficient due to 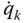 ;
; 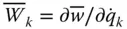
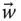 Wrist point velocity with respect to the base frame;
Wrist point velocity with respect to the base frame; 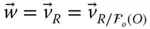
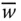 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 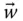 in the base frame;
in the base frame; 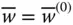
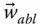 Generatrix line vector of a conical surface
Generatrix line vector of a conical surface 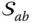
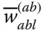 Column matrix representation of
Column matrix representation of 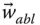 in the link frame
in the link frame 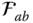
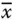 Column matrix of the primary variables
Column matrix of the primary variables 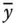 Column matrix of the secondary variables
Column matrix of the secondary variables 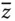 Column matrix of the primary and secondary variables
Column matrix of the primary and secondary variables










