Kanti V. Mardia - Spatial Analysis
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Kanti V. Mardia - Spatial Analysis» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Spatial Analysis
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Spatial Analysis: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Spatial Analysis»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Explore the foundations and latest developments in spatial statistical analysis Spatial Analysis,
Spatial Analysis
Spatial Analysis — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Spatial Analysis», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Table of Contents
1 Cover
2 Title Page Spatial Analysis John T. Kent University of Leeds, UK Kanti V. Mardia University of Leeds, UK University of Oxford, UK
3 Copyright
4 Dedication
5 Dedication
6 List of Figures
7 List of Tables
8 Preface
9 List of Notation and Terminology
10 1 Introduction1.1 Spatial Analysis 1.2 Presentation of the Data 1.3 Objectives 1.4 The Covariance Function and Semivariogram 1.5 Behavior of the Sample Semivariogram 1.6 Some Special Features of Spatial Analysis Exercises
11 2 Stationary Random Fields2.1 Introduction 2.2 Second Moment Properties 2.3 Positive Definiteness and the Spectral Representation 2.4 Isotropic Stationary Random Fields 2.5 Construction of Stationary Covariance Functions 2.6 Matérn Scheme 2.7 Other Examples of Isotropic Stationary Covariance Functions 2.8 Construction of Nonstationary Random Fields 2.9 Smoothness 2.10 Regularization 2.11 Lattice Random Fields 2.12 Torus Models 2.13 Long‐range Correlation 2.14 Simulation Exercises
12 3 Intrinsic and Generalized Random Fields3.1 Introduction 3.2 Intrinsic Random Fields of Order 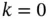 3.3 Characterizations of Semivariograms 3.4 Higher Order Intrinsic Random Fields 3.5 Registration of Higher Order Intrinsic Random Fields 3.6 Generalized Random Fields 3.7 Generalized Intrinsic Random Fields of Intrinsic Order
3.3 Characterizations of Semivariograms 3.4 Higher Order Intrinsic Random Fields 3.5 Registration of Higher Order Intrinsic Random Fields 3.6 Generalized Random Fields 3.7 Generalized Intrinsic Random Fields of Intrinsic Order 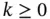 3.8 Spectral Theory for Intrinsic and Generalized Processes 3.9 Regularization for Intrinsic and Generalized Processes 3.10 Self‐Similarity 3.11 Simulation 3.12 Dispersion Variance Exercises
3.8 Spectral Theory for Intrinsic and Generalized Processes 3.9 Regularization for Intrinsic and Generalized Processes 3.10 Self‐Similarity 3.11 Simulation 3.12 Dispersion Variance Exercises
13 4 Autoregression and Related Models4.1 Introduction 4.2 Background 4.3 Moving Averages 4.4 Finite Symmetric Neighborhoods of the Origin in 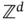 4.5 Simultaneous Autoregressions (SARs) 4.6 Conditional Autoregressions (CARs) 4.7 Limits of CAR Models Under Fine Lattice Spacing 4.8 Unilateral Autoregressions for Lattice Random Fields 4.9 Markov Random Fields (MRFs) 4.10 Markov Mesh Models Exercises
4.5 Simultaneous Autoregressions (SARs) 4.6 Conditional Autoregressions (CARs) 4.7 Limits of CAR Models Under Fine Lattice Spacing 4.8 Unilateral Autoregressions for Lattice Random Fields 4.9 Markov Random Fields (MRFs) 4.10 Markov Mesh Models Exercises
14 5 Estimation of Spatial Structure5.1 Introduction 5.2 Patterns of Behavior 5.3 Preliminaries 5.4 Exploratory and Graphical Methods 5.5 Maximum Likelihood for Stationary Models 5.6 Parameterization Issues for the Matérn Scheme 5.7 Maximum Likelihood Examples for Stationary Models 5.8 Restricted Maximum Likelihood (REML) 5.9 Vecchia's Composite Likelihood 5.10 REML Revisited with Composite Likelihood 5.11 Spatial Linear Model 5.12 REML for the Spatial Linear Model 5.13 Intrinsic Random Fields 5.14 Infill Asymptotics and Fractal Dimension Exercises
15 6 Estimation for Lattice Models 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Sample Moments 6.3 The AR(1) Process on 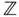 6.4 Moment Methods for Lattice Data 6.5 Approximate Likelihoods for Lattice Data 6.6 Accuracy of the Maximum Likelihood Estimator 6.7 The Moment Estimator for a CAR Model Exercises
6.4 Moment Methods for Lattice Data 6.5 Approximate Likelihoods for Lattice Data 6.6 Accuracy of the Maximum Likelihood Estimator 6.7 The Moment Estimator for a CAR Model Exercises
16 7 Kriging7.1 Introduction 7.2 The Prediction Problem 7.3 Simple Kriging 7.4 Ordinary Kriging 7.5 Universal Kriging 7.6 Further Details for the Universal Kriging Predictor 7.7 Stationary Examples 7.8 Intrinsic Random Fields 7.9 Intrinsic Examples 7.10 Square Example 7.11 Kriging with Derivative Information 7.12 Bayesian Kriging 7.13 Kriging and Machine Learning 7.14 The Link Between Kriging and Splines 7.15 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces 7.16 Deformations Exercises
17 8 Additional Topics8.1 Introduction 8.2 Log‐normal Random Fields 8.3 Generalized Linear Spatial Mixed Models (GLSMMs) 8.4 Bayesian Hierarchical Modeling and Inference 8.5 Co‐kriging 8.6 Spatial–temporal Models 8.7 Clamped Plate Splines 8.8 Gaussian Markov Random Field Approximations 8.9 Designing a Monitoring Network Exercises
18 Appendix A Mathematical Background A.1 Domains for Sequences and Functions A.2 Classes of Sequences and Functions A.3 Matrix Algebra A.4 Fourier Transforms A.5 Properties of the Fourier Transform A.6 Generalizations of the Fourier Transform A.7 Discrete Fourier Transform and Matrix Algebra A.8 Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) A.9 Periodic Approximations to Sequences A.10 Structured Matrices in 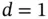 Dimension A.11 Matrix Approximations for an Inverse Covariance Matrix A.12 Maximum Likelihood Estimation A.13 Bias in Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Dimension A.11 Matrix Approximations for an Inverse Covariance Matrix A.12 Maximum Likelihood Estimation A.13 Bias in Maximum Likelihood Estimation
19 Appendix B A Brief History of the Spatial Linear Model and the Gaussian Process Approach B.1 Introduction B.2 Matheron and Watson B.3 Geostatistics at Leeds 1977–1987 B.4 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Inference
20 References and Author Index
21 Index
22 Wiley End User License Agreement
List of Tables
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Illustrative data 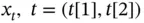 , on a
, on a 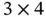 regular grid, represented in various ... Table 1.2 Elevation data: elevation
regular grid, represented in various ... Table 1.2 Elevation data: elevation 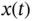 in feet above the sea level, where
in feet above the sea level, where 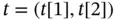 ,... Table 1.3 Bauxite data: percentage ore grade for bauxite at
,... Table 1.3 Bauxite data: percentage ore grade for bauxite at 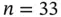 locations. Table 1.4 Gravimetric data: local gravity measurements in Quebec, Canada. Table 1.5 Semivariograms in each direction for the gravimetric data. Table 1.6 Soil data: surface pH in
locations. Table 1.4 Gravimetric data: local gravity measurements in Quebec, Canada. Table 1.5 Semivariograms in each direction for the gravimetric data. Table 1.6 Soil data: surface pH in 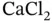 on an
on an 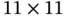 grid. Table 1.7 Mercer–Hall wheat yield (in lbs.) for 20 (rows)
grid. Table 1.7 Mercer–Hall wheat yield (in lbs.) for 20 (rows)  25 (columns) ag... Table 1.8 Aggregated Mercer–Hall wheat data for plots aggregated into block...
25 (columns) ag... Table 1.8 Aggregated Mercer–Hall wheat data for plots aggregated into block...
2 Chapter 2Table 2.1 Some radial covariance functions.Table 2.2 Special cases of the Matérn covariance function in 2.34 for half‐...Table 2.3 Some examples of stationary covariance functions 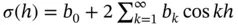 on the circle,...
on the circle,...
3 Chapter 3Table 3.1 Self‐similar random fields with spectral density 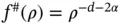 : some particul...
: some particul...
4 Chapter 5Table 5.1 Parameter estimates (and standard errors) for the bauxite data us...Table 5.2 Parameter estimates (and standard errors) for the elevation data ...Table 5.3 Parameter estimates (with standard errors in parentheses) for Vec...
5 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Notation used for kriging at the data sites  , and at the predict...Table 7.2 Various methods of determining the kriging predictor
, and at the predict...Table 7.2 Various methods of determining the kriging predictor 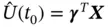 , where
, where 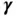 c...Table 7.3 Comparison between the terminology and notation of this book for ...
c...Table 7.3 Comparison between the terminology and notation of this book for ...
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Spatial Analysis»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Spatial Analysis» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Spatial Analysis» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












