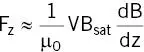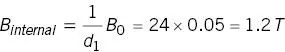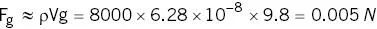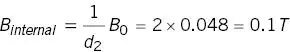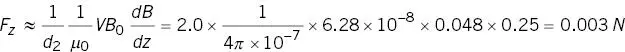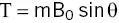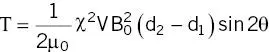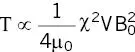For strongly ferromagnetic objects, the translational force does not depend upon its magnetic susceptibility, but upon its shape, the external field B 0(or B sat), and the spatial gradient dB/dz.
Soft saturated ferromagnetic material
For a saturated metal the magnetization within the material is at a maximum so once saturation occurs B 0becomes irrelevant, and the maximum force is
(2.13) 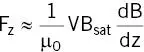
Here, for a given object, the only variable is the gradient of the B 0fringe field, which itself changes over distance from the magnet. The shape of the object is no longer a significant factor as it has been completely magnetized. Figure 2.19a shows the relative forces from a 1.5 and 3 T shielded magnet on 0.1 kg ferromagnetic objects which saturate at 1.6 T. State of saturation is more significant than field strength. The object’s shape is a key factor. You will get closer to the magnet holding a sphere without it being wrenched from your grasp than you would with an elongated object of the same mass. Figure 2.19b, plotted on a logarithmic scale, shows the force on each object at greater distances from the iso‐centre, compared to the gravitational force of around 1N. A length‐diameter ratio of 50 corresponds to the geometry of a Birmingham gauge 21 hypodermic needle. The force on the needle exceeds that of gravity around two meters from iso‐centre, half a meter further than for a spherical object of the same material and mass. Needles and scissors constitute two of the most hazardous objects around MRI scanners.
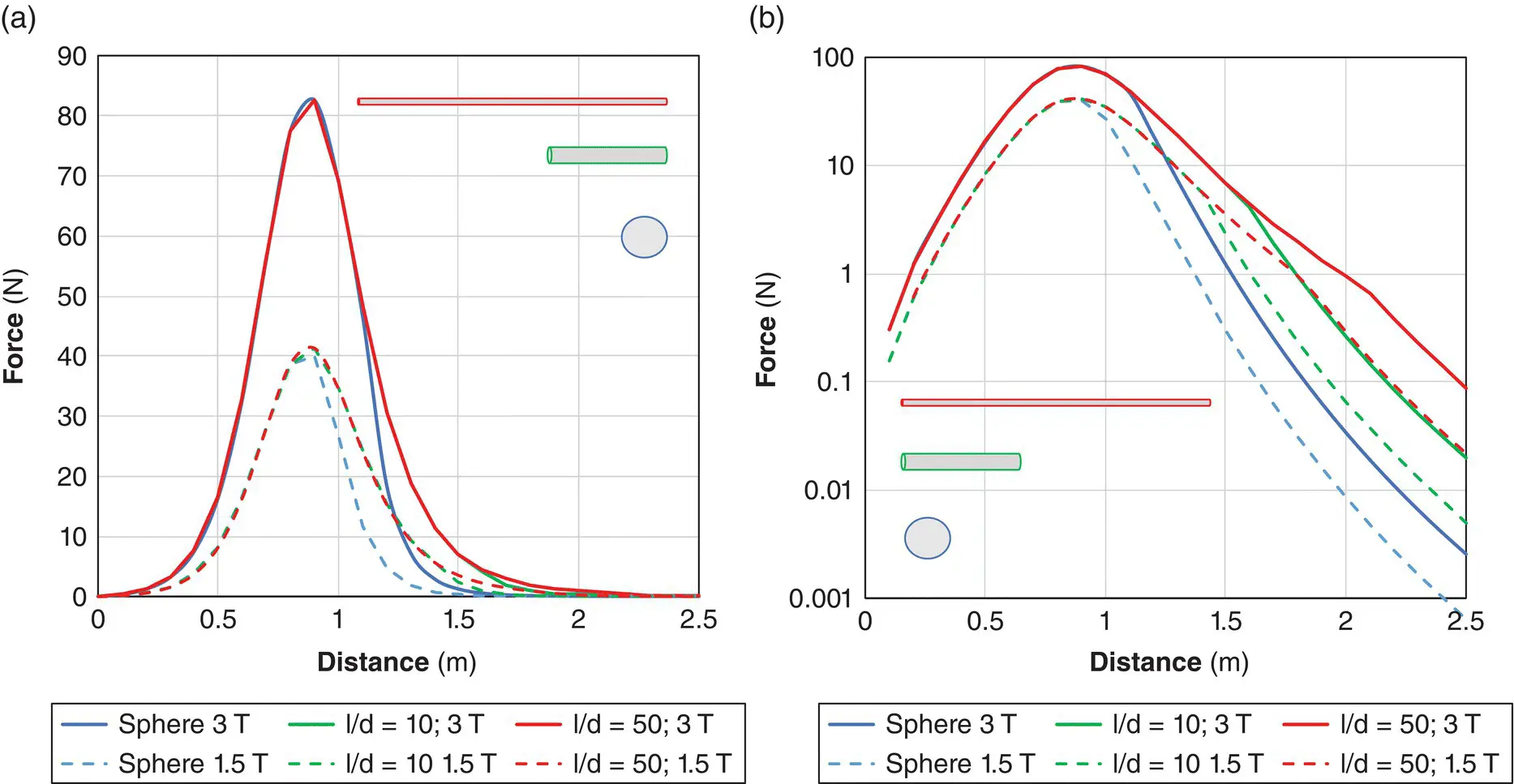
Figure 2.19 Predicted translational force on spherical and cylindrical 0.1 kg objects along the z‐axis: (a) linear plot; (b) logarithmic scale. The bore entrance is at 0.8 m. The objects have density of 8000 kg m −3and χ = 1000 with B sat= 1.6 T.
What if the object is already magnetized, i.e. is a permanent magnet? Such a situation may arise in MR if it is your institution’s policy to scan patients with cochlear implants. To start, we are not reliant on the external B 0to magnetize the object. Whether an increase occurs close to the magnet will depend upon the hysteresis properties of the object – it may even become demagnetized‐ so it is virtually impossible to predict. We can say, however, that the initial translational (attractive or repulsive depending upon orientation) and twisting forces are likely to exceed those of a soft ferromagnetic object. Cochlear implants are discussed in Chapter 10.
Example 2.5Force on a ferromagnetic object aligned with B 0
What is the maximum force on a ferromagnetic steel cylinder of length 2 cm, diameter 2 mm in the fringe field of a MRI magnet with B = 50 mT and dB/dz = 0.25 Tm −1? The material saturates at 1 T.
The maximum force occurs when the object’s long axis is aligned with B0. Firstly determine if the object is saturated. From Figure 2.14 or Equations A1.31 and 2.9a
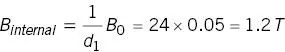
This exceeds Bsat so use Equation 2.13

By contrast the gravitational force is
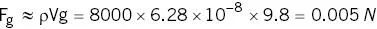
The magnetic force is 2.5 times the force due to gravity at this point .
Example 2.6 Force on a ferromagnetic object side on to B 0
If the object in Example 2.5has its long axis perpendicular to B 0. What is the attractive force on it?
Firstly determine if the object is saturated. From Figure 2.14 or Equations A1.31 and 2.9b
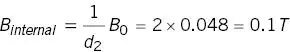
In this orientation the object is not saturated so use Equation 2.11 with θ = 90°
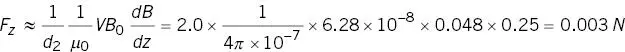
(We could also have used Equation 2.13 using B = 0.1 T in place of Bsat) .
This is one quarter of the gravitational force. The orientation of the object matters! Twisting it towards the magnet is potentially dangerous .
We can estimate the velocity of ferromagnetic projectiles from the basic laws of mechanics ( Figure 2.20). One non‐intuitive feature of projectile velocities is that they are broadly independent of the mass of the object. For example, if the densities of two objects are equal, then the translational force will scale with the mass, but acceleration scales with its inverse. Provided objects are the same shape (rather than size) and made of the same material, they will fly in equally fast with velocities of tens of meters per second‐ in under half a second for a given magnet!
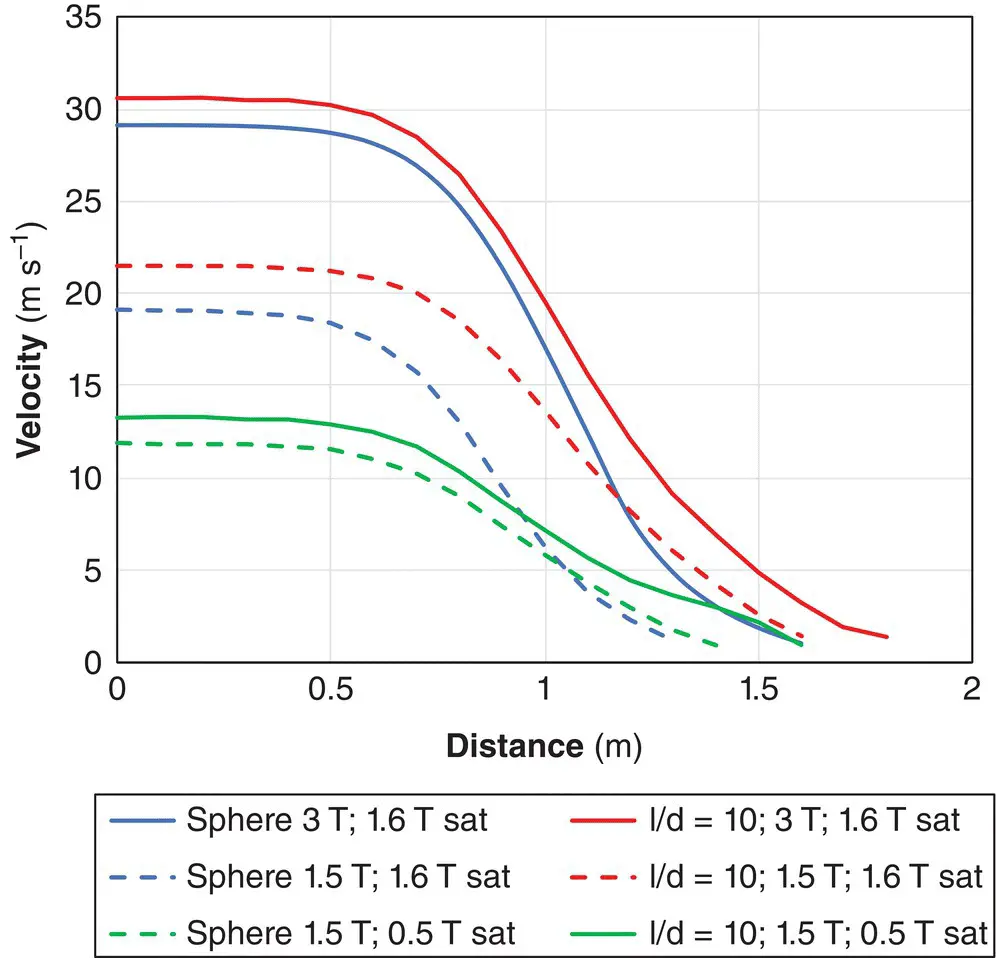
Figure 2.20 Predicted projectile velocity for the objects and magnets in Figure 2.19saturating at 1.6 and 0.5 T.
If the object is non‐spherical and has an axis at an angle θ with respect to B, there will be a twisting force or torque acting to align the object with the field. Torque, T, is a vector ( Figure 2.21) with a magnitude
(2.14) 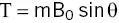
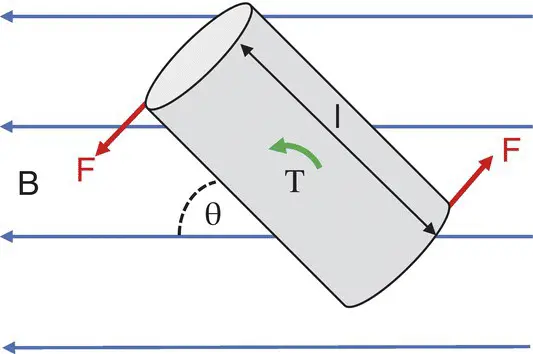
Figure 2.21 Torque Τ on a ferromagnetic object of length l. The force on either end is F = Τ/(0.5l) assuming a central axis of rotation.
Torque is measured in newton‐metres (N m). mis the object’s magnetic moment (= MV).
Torque on diamagnetic and paramagnetic objects
For |χ m| << 1 the torque is [1]:
(2.15) 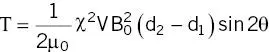
Perhaps at odds with “common sense” is the observation that the maximum torque is exerted at 45° ( Figure 2.22a), but at this angle there is the greatest product of magnetization and interaction with B. The maximum torque for a long object becomes
(2.16) 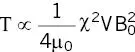
Читать дальше