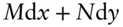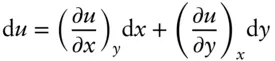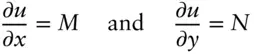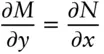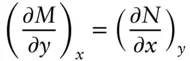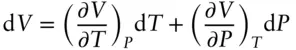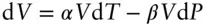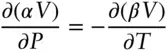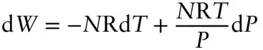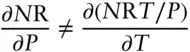(2.24) 
2.5.3 Path independence, exact differentials, state functions, and the first law
We said earlier that state functions are those that depend only on the present state of a system. Another way of expressing this is to say that state functions are path independent. Indeed, path independence may be used as a test of whether a variable is a state function or not. This is to say that if Y is a state function, then for any process that results in a change Y1 → Y2 , the net change in Y , Δ Y , is independent of how one gets from Y1 to Y2 . Furthermore, if Y is a state function, then the differential d Y is said to be mathematically exact .
Let's explore what is meant by an exact differential. An exact differential is the familiar kind, the kind we would obtain by differentiating the function u with respect to x and y , and also the kind we can integrate. But not all differential equations are exact. Let's first consider the mathematical definition of an exact differential, then consider some thermodynamic examples of exact and inexact differentials.
Consider the first order differential expression:
(2.25) 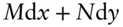
containing variables M and N , which may or may not be functions of x and y . Equation 2.25is said to be an exact differential if there exists some function u of x and y relating them such that the expression:
(2.26) 
is the total differential of u :
(2.27) 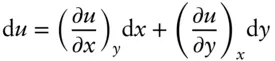
Let's consider what this implies. Comparing 2.26and 2.27, we see that:
(2.28) 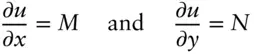
A necessary, but not sufficient, condition for 2.25to be an exact differential is that M and N must be functions of x and y .
A general property of partial differentials is the reciprocity relation or cross-differentiation identity, which states that the order of differentiation does not matter, so that:
(2.29) 
(The reciprocity relation is an important and useful property in thermodynamics, as we shall see at the end of this chapter.) If eqn. 2.26is the total differential of u , it follows that:
(2.30) 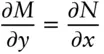
which is equivalent to:
(2.31) 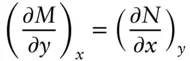
Equation 2.31is a necessary and sufficient condition for 2.25 to be an exact differential; that is, if the cross-differentials are equal, then the differential expression is exact.
Exact differentials have the property that they can be integrated and an exact value obtained. This is true because they depend only on the initial and final values of the independent variables (e.g., x and y in eqn. 2.27).
Now let's consider some thermodynamic examples. Volume is a state function and we can express it as an exact differential in terms of other state functions, as in eqn. 2.17:
(2.17) 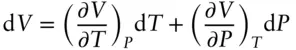
Substituting the coefficient of thermal expansion and compressibility for ∂V/∂T and ∂V/∂P respectively, equation 2.30becomes equal to eqn. 2.18:
(2.18) 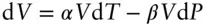
According to eqn. 2.31, if V is a state function, then:
(2.32) 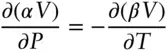
You should satisfy yourself that eqn. 2.32indeed holds for ideal gases and therefore that V is a state variable.
Work is not a state function, that is, the work done does not depend only on the initial and final states of a system. We would expect then that d W is not an exact differential, and indeed, this is easily shown for an ideal gas.
For PV work, d W = – P d V . Substituting eqn. 2.17for d V and rearranging, we have:
(2.33) 
Evaluating ∂V/∂T and ∂V/∂P for the ideal gas equation and multiplying through by P, this becomes:
(2.34) 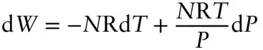
but
(2.35) 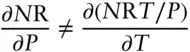
We cannot integrate eqn. 2.34and obtain a value for the work done without additional knowledge of the variation of T and P because the amount of work done does not depend only on the initial and final values of T and P ; it depends on the path taken. Heat is also not a state function, not an exact differential, and is also path dependent. Path dependent functions always have inexact differentials; path independent functions always have exact differentials.
On a less mathematical level, let's consider how the work and heat will vary in a transformation of a system, say from state 1 to state 2. Imagine that we burn gasoline in an open container. In this case, in the transformation from state 1 (gasoline) to state 2 (combustion products of gasoline), energy is given up by the system only as heat. Alternatively, we could burn the gasoline in an engine and recover some of the energy as work (expansion of the volume of the cylinder resulting in motion of the piston). The end states of these two transformations are the same, but the amount of heat released and work done varies, depending on the path we took. Thus, neither work nor heat can be state functions. Energy is a state function, is path independent, and is an exact differential. Whether we burn the gasoline in an open container or an engine, the energy released will be the same. Herein lies the significance for thermodynamics of Joule's discovery: that the sum of heat and work is independent of the path taken even though, independently, work and heat are not .
Читать дальше