A particle is defined to have a finite mass but infinitesimal dimensions, and is therefore regarded to be a point mass. Since a particle has negligible dimensions, its position in space is completely determined by the radius vector,  , measured from a fixed point, o , at any instant of time ,
, measured from a fixed point, o , at any instant of time ,  . The components of
. The components of  are resolved in a right‐handed reference frame with origin at o , having three mutually perpendicular axes denoted by the unit vectors
are resolved in a right‐handed reference frame with origin at o , having three mutually perpendicular axes denoted by the unit vectors  , and
, and  , and are defined to be the Cartesian position coordinates,
, and are defined to be the Cartesian position coordinates,  , of the particle along the respective axes,
, of the particle along the respective axes,  , as shown in Fig. 2.1. The velocity ,
, as shown in Fig. 2.1. The velocity ,  , of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the radius vector, and given by
, of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the radius vector, and given by
(2.18) 

Figure 2.1The position vector, 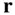 , of a particle resolved in an inertial reference frame using Cartesian coordinates, (
, of a particle resolved in an inertial reference frame using Cartesian coordinates, (  ).
).
If the reference frame,  , used to measure the velocity of the particle is at rest, then the components of the velocity,
, used to measure the velocity of the particle is at rest, then the components of the velocity, 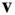 , resolved along the axes of the frame,
, resolved along the axes of the frame,  , and
, and  , are simply the time derivatives of the position coordinates,
, are simply the time derivatives of the position coordinates,  , and
, and 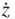 , respectively. However, if the origin,
, respectively. However, if the origin,  , of the reference frame itself is moving with a velocity,
, of the reference frame itself is moving with a velocity,  , and the frame,
, and the frame,  , is rotating with an angular velocity,
, is rotating with an angular velocity,  , with respect to an inertial frame 3, then the velocity of the moving reference frame must be vectorially added to that of the particle in order to derive the net velocity of the particle in the stationary frame as follows:
, with respect to an inertial frame 3, then the velocity of the moving reference frame must be vectorially added to that of the particle in order to derive the net velocity of the particle in the stationary frame as follows:
(2.19) 
The last term on the right‐hand side of Eq. (2.19)is the change caused by rotating axes,  , each of which have the same angular velocity,
, each of which have the same angular velocity,  . The relationship between the position and velocity described by a vector differential equation, either Eq. (2.18)or Eq. (2.19), is termed the kinematics of the particle.
. The relationship between the position and velocity described by a vector differential equation, either Eq. (2.18)or Eq. (2.19), is termed the kinematics of the particle.
Since the velocity of the particle could be varying with time, the acceleration ,  , of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the velocity vector, and is given by
, of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the velocity vector, and is given by
(2.20) 
with the understanding that the derivatives are taken with respect to a stationary reference frame. If the reference frame in which the position and velocity of the particle are resolved is itself moving such that its origin, 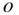 , has an instantaneous velocity,
, has an instantaneous velocity,  and an instantaneous acceleration,
and an instantaneous acceleration,  , and its axes are rotating with an instantaneous angular velocity,
, and its axes are rotating with an instantaneous angular velocity,  , all measured in a stationary frame, then the net acceleration of the particle is given by
, all measured in a stationary frame, then the net acceleration of the particle is given by
(2.21) 
Equation ( 2.21) is an alternative kinematical description of the particle's motion, and can be regarded as being equivalent to that given by Eq. (2.19), which has been differentiated in time according to the chain rule. Equation ( 2.21) is useful in finding the acceleration of the particle from the position and velocity measured in a moving reference frame. The first two terms on the right‐hand side of Eq. (2.21)represent the net acceleration due to the origin of the moving frame. The term  is the Coriolis acceleration , and
is the Coriolis acceleration , and 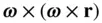 the centripetal acceleration of the particle in the moving reference frame. The term
the centripetal acceleration of the particle in the moving reference frame. The term  is the effect of the angular acceleration of the reference frame, whereas
is the effect of the angular acceleration of the reference frame, whereas  is the acceleration due to a changing magnitude of
is the acceleration due to a changing magnitude of  , and would be the only acceleration had the reference frame been stationary.
, and would be the only acceleration had the reference frame been stationary.
Читать дальше

 , measured from a fixed point, o , at any instant of time ,
, measured from a fixed point, o , at any instant of time ,  . The components of
. The components of  are resolved in a right‐handed reference frame with origin at o , having three mutually perpendicular axes denoted by the unit vectors
are resolved in a right‐handed reference frame with origin at o , having three mutually perpendicular axes denoted by the unit vectors  , and
, and  , and are defined to be the Cartesian position coordinates,
, and are defined to be the Cartesian position coordinates,  , of the particle along the respective axes,
, of the particle along the respective axes,  , as shown in Fig. 2.1. The velocity ,
, as shown in Fig. 2.1. The velocity ,  , of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the radius vector, and given by
, of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the radius vector, and given by

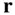 , of a particle resolved in an inertial reference frame using Cartesian coordinates, (
, of a particle resolved in an inertial reference frame using Cartesian coordinates, (  ).
). , used to measure the velocity of the particle is at rest, then the components of the velocity,
, used to measure the velocity of the particle is at rest, then the components of the velocity, 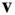 , resolved along the axes of the frame,
, resolved along the axes of the frame,  , and
, and  , are simply the time derivatives of the position coordinates,
, are simply the time derivatives of the position coordinates,  , and
, and 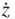 , respectively. However, if the origin,
, respectively. However, if the origin,  , of the reference frame itself is moving with a velocity,
, of the reference frame itself is moving with a velocity,  , and the frame,
, and the frame,  , is rotating with an angular velocity,
, is rotating with an angular velocity,  , with respect to an inertial frame 3, then the velocity of the moving reference frame must be vectorially added to that of the particle in order to derive the net velocity of the particle in the stationary frame as follows:
, with respect to an inertial frame 3, then the velocity of the moving reference frame must be vectorially added to that of the particle in order to derive the net velocity of the particle in the stationary frame as follows:
 , each of which have the same angular velocity,
, each of which have the same angular velocity,  . The relationship between the position and velocity described by a vector differential equation, either Eq. (2.18)or Eq. (2.19), is termed the kinematics of the particle.
. The relationship between the position and velocity described by a vector differential equation, either Eq. (2.18)or Eq. (2.19), is termed the kinematics of the particle. , of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the velocity vector, and is given by
, of the particle is defined to be the time derivative of the velocity vector, and is given by
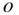 , has an instantaneous velocity,
, has an instantaneous velocity,  and an instantaneous acceleration,
and an instantaneous acceleration,  , and its axes are rotating with an instantaneous angular velocity,
, and its axes are rotating with an instantaneous angular velocity,  , all measured in a stationary frame, then the net acceleration of the particle is given by
, all measured in a stationary frame, then the net acceleration of the particle is given by
 is the Coriolis acceleration , and
is the Coriolis acceleration , and 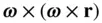 the centripetal acceleration of the particle in the moving reference frame. The term
the centripetal acceleration of the particle in the moving reference frame. The term  is the effect of the angular acceleration of the reference frame, whereas
is the effect of the angular acceleration of the reference frame, whereas  is the acceleration due to a changing magnitude of
is the acceleration due to a changing magnitude of  , and would be the only acceleration had the reference frame been stationary.
, and would be the only acceleration had the reference frame been stationary.










