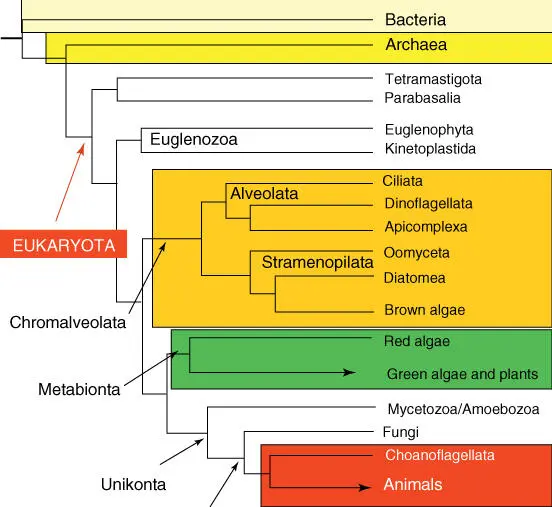
| Major protist clades |
Characteristics |
Example |
| Tetramastigota |
Secondary loss of mitochondria |
|
| Diplomonadida |
Two separate cell nuclei |
Giardia |
| Parabasalia |
|
|
| Trichomonadida |
Undulating membrane |
Trichomonas |
| Euglenozoa |
Flagellates with or without photosynthesis |
|
| Euglenophyta |
Paramylon as storage polysaccharide |
Euglena |
| Kinetoplastida |
With kinetoplast |
Trypanosoma(sleeping sickness) |
| Chromalveolata |
With chloroplasts from secondary endosymbiosis |
|
| Alveolata |
Alveoli under the cell surface |
|
| Dinoflagellata |
Shell from cellulose plates |
Pfiesteria |
| Apicomplexa (Sporozoa) |
Apical complex for penetration of hosts |
Plasmodium(malaria), Toxoplasma |
| Ciliata (ciliates) |
Cilium for movement and nutrient uptake |
Paramecium |
| Stramenopilata or heterokonts |
With trailing and flimmer flagellum |
|
| Oomyceta |
Hypha; cell walls from cellulose |
|
| Bacillariophyceae (diatoms) |
Glassy; walls separated into two |
Pinnularia |
| Chrysophyceae (golden algae) |
Two flagellate cells |
Dinobryon |
| Phaeophyceae (brown algae) |
Brown accessory pigments |
Laminaria |
| Metabionta |
With chloroplasts from primary endosymbiosis |
|
| Rhodobionta (red algae) |
Without flagellate stage; phycoerythrin |
Porphyra |
| Chlorobionta (green algae) |
With chloroplasts (similar to land plants) |
Chlamydomonas |
| Charophyceae |
| → Land plants |
|
|
| Unikonta |
|
|
| Amoebozoa |
With sheet‐like form pseudopods |
Amoeba |
| Mycetozoa (slime mold) |
Saprophyte; amoeboid stages form colonies |
Physarum, Dictyostelium |
| Opisthokonta |
Protruding flagellum |
|
| Fungi (Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes) |
Cell walls from chitin, saprophytic |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae(yeast) |
| Amanita phalloides (deadly agaric) |
| Choanoflagellata |
With microvilli |
|
| → Metazoa (animals) |
|
|
The red, brown, and green algae were previously grouped with the plants; due to new molecular systematics, a new order has been proposed.
Important model organisms are given in bold.
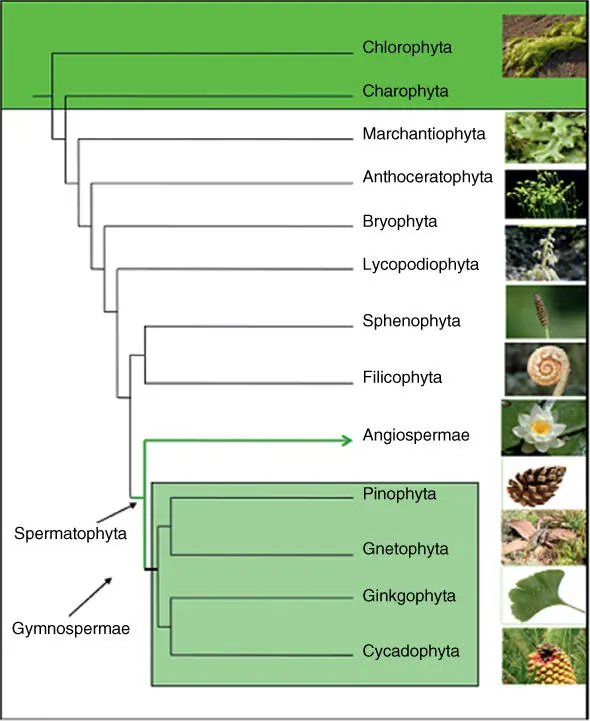
| Subdivision |
Class |
| Sporophyte(spore‐bearing plants) |
|
| Moss plants |
Marchantiophyta (Marchantiopsida, liverwort) |
|
Anthocerotophyta (Anthoceratopsida, hornwort) |
|
Bryophyta (Bryopsida, moss) |
| Lycophytes(club mosses) |
Lycopodiophyta (Lycopodiopsida, lycopod) |
| Pteridophyta(Euphyllophytes; fern and other seedless vascular plants) |
Psilotophyta (Psilotopsida, whisk fern), Sphenophyta (Equisetopsida, horsetail) |
|
Filicophyta (Filicopsida, fern) |
| Spermatophyta(seed‐bearing plants) |
|
| Gymnospermae(naked seed plants) |
Ginkgophyta (Ginkgopsida, Ginkgo plant) |
|
Cycadophyta (Cycadopsida, palm fern) |
|
Gnetophyta (Gnetopsida, joint‐fir family) |
|
Pinophyta (Pinopsida, conifers) |
| Angiospermae(flowering plants) |
Magnoliophyta (Magnoliopsida) |
|
( Arabidopsis thaliana, Nicotiana tabacum) |
Important model organisms are given in bold.
| Category |
Phylum |
Characteristics |
| Parazoa |
Porifera (sponges) |
Simple multicellular animals with choanocytes that can take up bacteria by phagocytosis; cells that are mostly totipotent |
| Radiata |
Cnidaria (anemones and jelly fish) ( Hydra) |
Stinging cells (cnidocytes) with nematocysts; developed gastrovascular system (gastric space with mouth, without anus) |
|
Ctenophora (comb jellies) |
Adhesive cells (colloblasts) to catch prey; eight rows of fused cilia; gastrovascular system |
| Bilateria |
|
|
| Protostomia |
|
|
| Lophotrochozoa(150 000 species) |
|
With lophophore and trochophore larvae |
|
Platyhelminthes (flatworms) |
Dorsoventrally flattened; unsegmented; no coelom |
|
Rotifera (rotifers) |
Pseudocoele with digestive tract; rotary organ; without circulatory system |
|
Ectoprocta/Bryozoa (moss animals) |
With coelom; with ciliated tentacles (lophophore) for uptake of nutrients; colonial |
|
Nemertea (ribbon worms) |
Coelom‐like structure for storing proboscis; closed circulatory system with blood vessels; digestive tract with mouth and anus |
|
Mollusca (mollusks) |
With small coelom; three body parts: foot, visceral mass, mantle; head often reduced |
|
Annelida (segmented worms) |
With small coelom and epitheliomuscular tube; segmented body and segment specialization |
| Ecdysozoa(>1 million species) |
|
|
|
Nematoda (roundworms) ( Caenorhabditis elegans) |
Cylindrical, unsegmented pseudocoelomates; complete digestive tract without circulatory system |
|
Arthropoda |
With coelom and segmented body, jointed appendages; ectodermal exoskeleton |
|
Chelicerata (Arachnida) |
|
|
Myriapoda |
|
|
(millipedes and centipedes) |
|
|
Hexapoda (insects) |
|
|
( Drosophila melanogaster) |
|
|
Crustaceae (crustaceans) |
|
| Deuterostomia (60 000 species) |
|
|
|
Echinodermata (echinoderm) (starfish, sea urchin, sea cucumber) |
With coelom; larvae with bilateral symmetry; adult animals with radial symmetry; ambulacral system; mesodermal endoskeleton |
|
Hemichordata |
With coelom and trimeric abdominal cavity; reduced chorda; branchial gut (pharyngeal gill) |
| Chordata(chordates) |
|
With coelom; chorda dorsalis; dorsal tubular nerve cord branchial gut (pharyngeal gill) |
|
Urochordata |
|
|
(Tunicata, tunicates) |
|
|
Cephalochordata (Acrania, skull‐less) ( Branchiostoma ) |
|
|
Vertebrata (vertebrates) |
Neural crest; cephalization; spinal column; closed circulatory system |
|
Agnatha (lamprey) |
|
|
Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) |
|
|
Osteichthyes (bony fish) |
|
|
( Danio rerio) |
|
|
Lissamphibia (amphibians) ( Xenopus laevis) |
|
|
Reptilia (reptiles) (turtle, lizard, crocodile) |
|
|
Aves (birds) ( Gallus gallus) |
|
|
Mammalia (mammals) ( Mus musculus, Homo sapiens) |
|
Important model organisms are given in bold.



![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)








