1 Cover
2 Table of Contents
3 About the Companion Website
4 Title Page
5 Preface
6 Acknowledgments
7 About the Authors
8 Introduction The Biological Universe What Is Genetics? Bacterial Genetics Phage Genetics A Brief History of Bacterial Molecular Genetics What Is Ahead
9 1 The Bacterial Chromosome: DNA Structure, Replication, and Segregation DNA Structure The Mechanism of DNA Replication Replication Errors Impediments to DNA Replication Replication of the Bacterial Chromosome and Cell Division The Bacterial Nucleoid The Bacterial Genome
10 2 Bacterial Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, Protein Folding, and Localization Overview The Structure and Function of RNA Transcription RNA Degradation The Structure and Function of Proteins Translation Protein Folding and Degradation Protein Localization Protein Secretion and Export Regulation of Gene Expression What You Need To Know
11 3 Bacterial Genetic Analysis: Fundamentals and Current Approaches Definitions Inheritance in Bacteria Mutation Rates Types of Mutations Reversion versus Suppression Genetic Analysis in Bacteria Perspective
12 4 Plasmids What Is a Plasmid? Properties of Plasmids
13 5 Conjugation Overview Mechanism of DNA Transfer during Conjugation in Proteobacteria Chromosome Transfer by Plasmids Diversity in Transfer Systems Integrating Conjugative Elements
14 6 Transformation Natural Transformation Artificially Induced Competence
15 7 Bacteriophages and Transduction Lytic Development Lysogenic Development Genetic Analysis of Phages Phage-Mediated Genetic Transfer Host Defenses Against Phage Infection Phages as Tools
16 8 Transposition, Site-Specific Recombination, and Families of Recombinases Transposition Mechanisms of Transposition General Properties of Transposons Transposon Mutagenesis Site-Specific Recombination Y and S Recombinases Group II Mobile Introns: Elements that Move Using an RNA Intermediate Importance of Transposition and Site-Specific Recombination in Bacterial Adaptation
17 9 Molecular Mechanisms of Homologous Recombination Homologous Recombination and DNA Replication in Bacteria The Molecular Basis for Recombination in E. coli Recombination between Different DNAs in Bacteria Recombineering: Gene Replacements in E. coli with Phage λ Recombination Functions
18 10 DNA Repair and Mutagenesis Evidence for DNA Repair Specific Repair Pathways General Repair Mechanisms DNA Damage Tolerance Mechanisms Summary of Repair Pathways in E. coli Bacteriophage Repair Pathways
19 11 Regulation of Gene Expression: Genes and Operons Transcriptional Regulation in Bacteria Negative Regulation of Transcription Initiation Positive Regulation of Transcription Initiation Regulation by Transcription Attenuation Regulation of mRNA Degradation Regulation of Translation Posttranslational Regulation Why Are There So Many Mechanisms of Gene Regulation?
20 12 Global Regulation: Regulons and Stimulons Carbon Catabolite Regulation Regulation of Nitrogen Assimilation Regulation of Ribosome Components and tRNA Synthesis Ribosomal Protein Gene Regulation Stress Responses in Bacteria Iron Regulation in E. coli Regulation of Virulence Genes in Pathogenic Bacteria Developmental Regulation: Sporulation in B. subtilis
21 13 Genomes and Genomic Analysis The Bacterial Genome DNA Sequencing Barriers to Horizontal Transfer: Genome Gatekeepers and the Molecular Biologist’s Toolkit
22 Glossary
23 End Papers
24 Index
25 End User License Agreement
1 Introduction Figure 1 A molecular tree of life capturing diversity using ribosomal proteins...
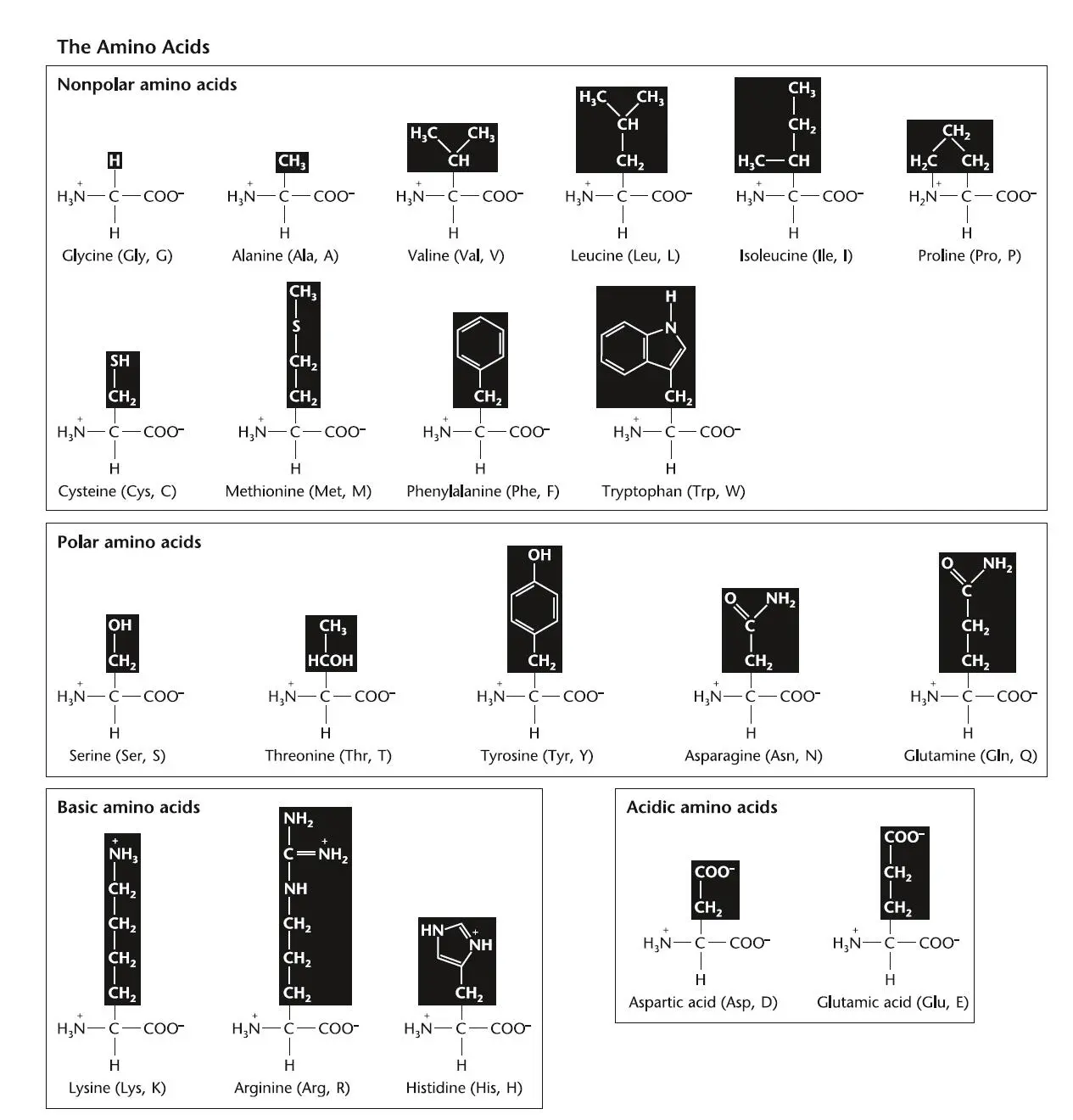
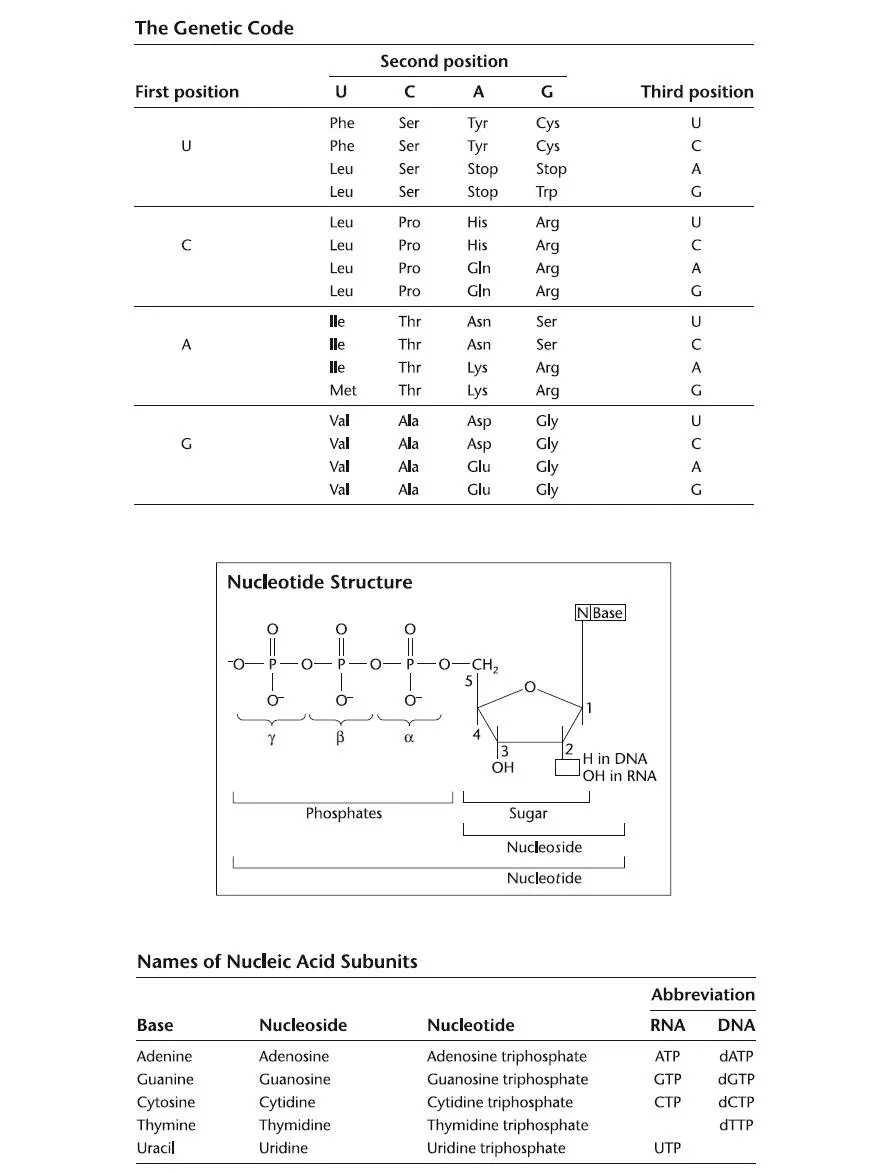
2 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Schematic drawing of the Watson-Crick structure of DNA, showing the... Figure 1.2 Chemical structures of deoxyribonucleotides, showing the bases and ... Figure 1.3 (A)Schematic drawing of a DNA chain, showing the 3′-to-5′ attachme... Figure 1.4 The two complementary base pairs found in DNA. Two hydrogen bonds f... Figure 1.5 The pathways for synthesis of deoxynucleotides from ribonucleotides... Figure 1.6 Features of DNA. (A)Polymerization of the deoxynucleotides during ... Figure 1.7 Functions of the primer and template in DNA replication. (A)The DN... Figure 1.8 Discontinuous synthesis of one of the two strands of DNA during chr... Figure 1.9 DNA polymerase I can remove an RNA primer by using strand displacem... Figure 1.10 “Trombone” model for how both the leading strand and lagging stran... Figure 1.11 Mistakes in base pairing can lead to changes in the DNA sequence c... Figure 1.12 Editing function of DNA polymerase. (A)A G is mistakenly placed o... Figure 1.13 Physical blocks on template DNAs. (A)When DNA polymerase III stal... Figure 1.14 Structure of the origin of chromosomal replication ( oriC ) region o... Figure 1.15 Initiation of replication at the Escherichia coli origin ( oriC ) re... Figure 1.16 Termination of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli . (A)The... Figure 1.17 Model of the way in which chromosome translocation by FtsK coordin... Figure 1.18 Model of the way in which unwinding of the template DNA strands ca... Figure 1.19 Model of the way in which chromosome decatenation by topoisomerase... Figure 1.20 Model of how an origin region containing parS sites bound by the P... Figure 1.21 The E. coli chromosome has four structured regions called macrodom... Figure 1.22 The MinCDE and nucleoid occlusion systems control placement of the... Figure 1.23 Timing of DNA replication during the cell cycle, with two differen... Figure 1.24 Replication creates hemimethylated DNA. (A)The A in the sequence ... Figure 1.25 Model showing the possible functional consequences of SeqA binding... Figure 1.26 (A)Supercoiled DNA. (B)Twisting of the ends in opposite directio... Figure 1.27 Action of the two types of topoisomerases. The type I topoisomeras...
3 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 RNA precursors. (A)A ribonucleoside triphosphate (rNTP) (the form ... Figure 2.2 Secondary structure in an RNA. (A)The RNA folds back on itself to ... Figure 2.3 The structure of bacterial RNA polymerase. The core enzyme is compo... Figure 2.4 Crystal structure of bacterial RNA polymerase and σ interact... Figure 2.5 RNA transcription. (A)The polymerization reaction, in whi... Figure 2.6 (A)Typical structure of a σ 70bacterial... Figure 2.7 Transcription begins at a promoter and ends at a transcription te... Figure 2.8 Overview of transcription. (A)The transcription cycle. Ea... Figure 2.9 Transcription initiation. (A)Binding of σ to RNA p... Figure 2.10 Interactions between RNA polymerase subunits and promoter elements... Figure 2.11 Abortive transcription and RNA polymerase escape from the promoter... Figure 2.12 The transcription elongation complex (TEC). During elongation, nuc... Figure 2.13 Backtracked transcription elongation complex (TEC). Backward movem... Figure 2.14 Transcription termination at a factor-independent termination site... Figure 2.15 Model for factor-dependent transcription termination at a ... Figure 2.16 Precursor of rRNA. The precursor transcript (top) contains ... Figure 2.17 Structure of mature tRNAs.
Читать дальше













