
We write down the series of principal minors of the matrix A

Then:
– the matrix A is positive definite, if
– the matrix A is negative definite, if
– the matrix A is non-negative (non-positive) definite, ifand there exists j, such that Δj =0;
– the matrix A is indefinite.
EXAMPLE 1.1.– Find solutions for the optimization problem

Solution . The function is continuous. Obviously, S max= +∞. As a result of the Weierstrass theorem, the minimum is attained. The necessary conditions of the first order

are of the form

Solving these equations, we find the critical points (0, 0), (1, 1), (–1, –1). To use the second-order conditions, we compute matrices composed of the second-order partial derivatives:

The matrix – A 1is non-negative definite. Therefore, the point (0, 0) satisfies the second-order necessary conditions for a maximum. However, a direct verification of the behavior of the function f in a neighborhood of the point (0, 0) shows that (0, 0) ∉ locextr f . The matrix A 2is positive definite. Thus, by theorem 1.13, the local minimum of the problem is attained at the points (1, 1), ( –1, –1).
Answer . (0, 0) ∉ locextr; (1, 1), ( –1, –1) ∈ locmin.
1.4. Constrained optimization problems
1.4.1. Problems with equality constraints
Let fk : ℝ n→ ℝ, k = 0,1, … , m , be differentiable functions of n real variables. The constrained optimization problem ( with equality constraints ) is the problem
[1.2] 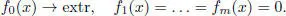
The points x ∈ ℝ n, which satisfy the equation fk ( x ) = 0,  , are called admissible in the problem [1.2]. An admissible point
, are called admissible in the problem [1.2]. An admissible point  gives a local minimum (maximum) of the problem [1.2]if there exists a number δ > 0 such that for all admissible x ∈ ℝ nthat satisfy the conditions fk ( x ) = 0, k = 1, 2, … , m , and the condition
gives a local minimum (maximum) of the problem [1.2]if there exists a number δ > 0 such that for all admissible x ∈ ℝ nthat satisfy the conditions fk ( x ) = 0, k = 1, 2, … , m , and the condition  , the following inequality
, the following inequality

holds true.
The main method of solving constrained optimization problems is the method of indeterminate Lagrange multipliers . It is based on the fact that the solution of the constrained optimization problem [1.2]is attained at points that are critical in the unconstrained optimization problem

where  is the Lagrange function , and λ 0, … , λ mare the Lagrange multipliers .
is the Lagrange function , and λ 0, … , λ mare the Lagrange multipliers .
THEOREM 1.15.– ( Lagrange theorem ) Let  be a point of local extremum of the problem [1.2], and let the functions fi ( x ), i = 0, 1, … , m , be continuously differentiable in a neighborhood U of the point
be a point of local extremum of the problem [1.2], and let the functions fi ( x ), i = 0, 1, … , m , be continuously differentiable in a neighborhood U of the point  . Then there will exist the Lagrange multipliers λ 0, … , λ m, not all equal to zero, such that the stationary condition on x of the Lagrange function is fulfilled
. Then there will exist the Lagrange multipliers λ 0, … , λ m, not all equal to zero, such that the stationary condition on x of the Lagrange function is fulfilled

In order for λ 0≠ 0, it is sufficient that the vectors  be linearly independent.
be linearly independent.
To prove the theorem, we use the inverse function theorem in a finite-dimensional space.
THEOREM 1.16.– ( Inversefunction theorem ) Let F 1( x ,… , xs ), … , Fs ( x 1, ..., xs ) be s continuously differentiable in a neighborhood U of the point  functions of s variables and let the Jacobian
functions of s variables and let the Jacobian

be not equal to zero. Then there exist numbers ε > 0, δ > 0, K > 0 such that for any y = ( y 1, … , ys ), ∥ y ∥ ≤ ε we can find x = ( x 1, … , xs ), which satisfies conditions ∥ x ∥ < δ,  , ∥ x ∥ ≤ K ∥ y ∥.
, ∥ x ∥ ≤ K ∥ y ∥.
PROOF.– We prove the Lagrange theorem by contradiction. Suppose that the stationarity condition

does not hold, and vectors  , i = 0, 1, … , m , are linearly independent, which means that the rank of the matrix
, i = 0, 1, … , m , are linearly independent, which means that the rank of the matrix
Читать дальше







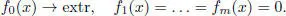
 , are called admissible in the problem [1.2]. An admissible point
, are called admissible in the problem [1.2]. An admissible point  gives a local minimum (maximum) of the problem [1.2]if there exists a number δ > 0 such that for all admissible x ∈ ℝ nthat satisfy the conditions fk ( x ) = 0, k = 1, 2, … , m , and the condition
gives a local minimum (maximum) of the problem [1.2]if there exists a number δ > 0 such that for all admissible x ∈ ℝ nthat satisfy the conditions fk ( x ) = 0, k = 1, 2, … , m , and the condition  , the following inequality
, the following inequality

 is the Lagrange function , and λ 0, … , λ mare the Lagrange multipliers .
is the Lagrange function , and λ 0, … , λ mare the Lagrange multipliers .
 be linearly independent.
be linearly independent. functions of s variables and let the Jacobian
functions of s variables and let the Jacobian
 , ∥ x ∥ ≤ K ∥ y ∥.
, ∥ x ∥ ≤ K ∥ y ∥.
 , i = 0, 1, … , m , are linearly independent, which means that the rank of the matrix
, i = 0, 1, … , m , are linearly independent, which means that the rank of the matrix










