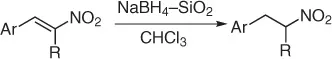Conjugated nitroalkenes are a very important class of molecules easily prepared by nitroaldol condensation or direct nitration of the corresponding olefins. Their reduction provides a convenient route to a variety of different functionalities including oximes, carbonyl compounds, hydoxylamines, alkylamines, and nitroalkanes [27,28].
1.4.1 Reduction of Nitroalkenes into Nitroalkanes
The reduction of conjugate nitroalkenes into nitroalkanes ( Scheme 1.16) has been achieved under several distinct protocols; however, often there is a loss of product due to dimerization caused by the competitive Michael addition of the formed nitronate to another molecule of nitroalkene.
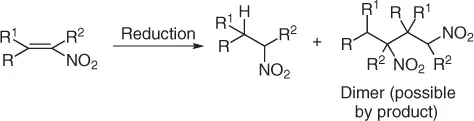
Scheme 1.16 Reduction of nitroalkenes.
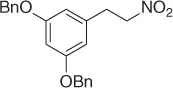
However, because this by-product may be suppressed at reduced pH, the main theme of several reports is the selective reduction of the double bond avoiding the formation of the Michael by-product. Thus, a plethora of reductive methods have been reported. A modified reduction with sodium borohydride in the presence of both silica gel and a mixture of chloroform-propanol as solvent system achieves good results of nitroalkanes ( Table 1.1) [29].
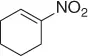
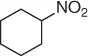
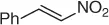
Successively, Kabalka et al. [28] proposed three different reductive agents ( Table 1.2): (i) trialkylborohydride, (ii) NaBH 4in a mixed MeOH-THF solvents, and (iii) NaBH 4supported on an ion exchange resin, for an effective conversion of nitroalkenes to nitroalkanes.
Table 1.1 NaBH 4/SiO 2reduction of nitroalkenes (selected examples).
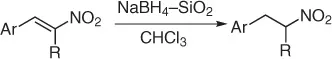 |
| Nitroalkene |
Nitroalkane |
Yield (%) |
 |
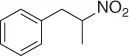 |
93 |
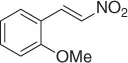 |
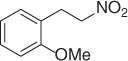 |
92 |
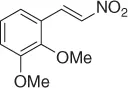 |
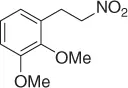 |
94 |
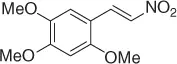 |
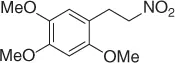 |
94 |
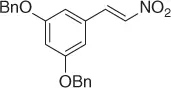 |
 |
98 |
Table 1.2 Comparative reduction of nitroalkenes with methods (i)–(iii) (selected examples).
 |
| Nitroalkene |
Nitroalkane |
Yield (%) |
|
|
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
 |
 |
69 |
62 |
80 |
 |
 |
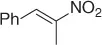
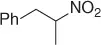
78 |
64 |
— |
 |
 |
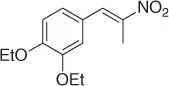
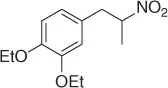
81 |
82 |
80 |
 |
 |
69 |
75 |
83 |
Later, Vankar and coworkers [30] developed an efficient, chemoselective procedure for the reduction of conjugated nitroalkenes with the use of NaCNBH 3(1 equiv) in methanol ( Table 1.3), by the help of Zeolite (H-ZSM-5, [Si:Al = 35 : 1], 0.5 equiv), and a careful control of the pH.
1.4.2 Stereoselective Reduction of Conjugated Nitroalkenes
The stereoselective reduction of conjugated nitroalkenes is an important goal and a variety of efficient procedures have been reported [31–36]; however, they seem to be restricted to the reduction of nitrostyrene derivatives. Thus, a survey of the most representative examples is reported in Table 1.4.
1.4.3 Aldehyde Reductive Nitromethylation
Several decades ago, Wollemberg and Miller developed a useful procedure for the preparation of primary nitroalkanes with an extra atom beginning from aldehydes [37]. The starting point is the nitroaldol (Henry) reaction ( Scheme 1.17) of an aldehyde with nitromethane, catalyzed with KF and in the presence of i -PrOH as solvent. The formed nitroalkanol is acetylated (acetic anhydride in the presence of 4-dimethylaminopridine as catalyst) and treated with sodium borohydride affording the desired nitroalkane via “one-pot” acetic acid-elimination and C=C double bond reduction.
So, this procedure offers the opportunity to increase the chain length of the starting aldehyde.
Table 1.3 Reduction of nitroalkenes with NaCNBH 3(selected examples).
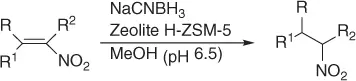 |
| Nitroalkene |
Nitroalkane |
Yield (%) |
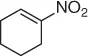 |
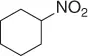 |
79 |
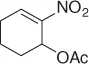 |
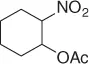 |
74 |
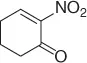 |
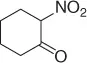 |
70 |
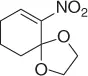 |
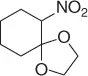 |
78 |
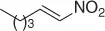 |
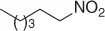 |
78 |
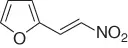 |
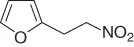 |
69 |
Читать дальше