In case the decision process can be described in a standardized way, automated solution finding and decision making can be possible. Based on predefined checking and decision finding processes, the “application” (App) in use executes automatically the predefined solution process or gives a proposal to a human decider. Logistics management has to think about which kind of decision situations (e.g. data given by a Thing) can occur in which process and how the decision processes can be defined in a standardized way, including standardized answers. This is also discussed in Chapter 5.
The next level of decision making is currently in development using AI. Such AI systems can autonomously find solutions and come to decisions. Using big data and a self‐learning mode, the “machine” or application itself is smart enough to decide what to do next at a much higher speed and accuracy than humans. Logistics management has to determine which type of decision making is appropriate for which process based on which data from which Thing. Regardless of which type of decision making is applied, the analytics of the data as an input for the decision making can be done in mainly four different ways: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, or prescriptive Figure 3.3(Porter and Heppelmann 2015).
In a descriptive way, all selected information is gathered, and the monitored situation is described (e.g. condition, environment, process). Using the diagnostic way, the root causes of deviations between the set target value and the actual monitored value are analyzed. Hence, both the descriptive and diagnostic ways of analytics look back and explain what happened in the past. In a predictive way, the analyzed data is used to detect indications that signal impending events in the future. For example, if the system shows a certain number of Things in the inbound area of a warehouse while in parallel the internal data indicates that several workers are ill, it will most likely result in a delay or congestion in the goods receiving process – if no actions are taken. Lastly, the p rescriptive form of data analytics strives for identifying measures to improve results or correct errors.
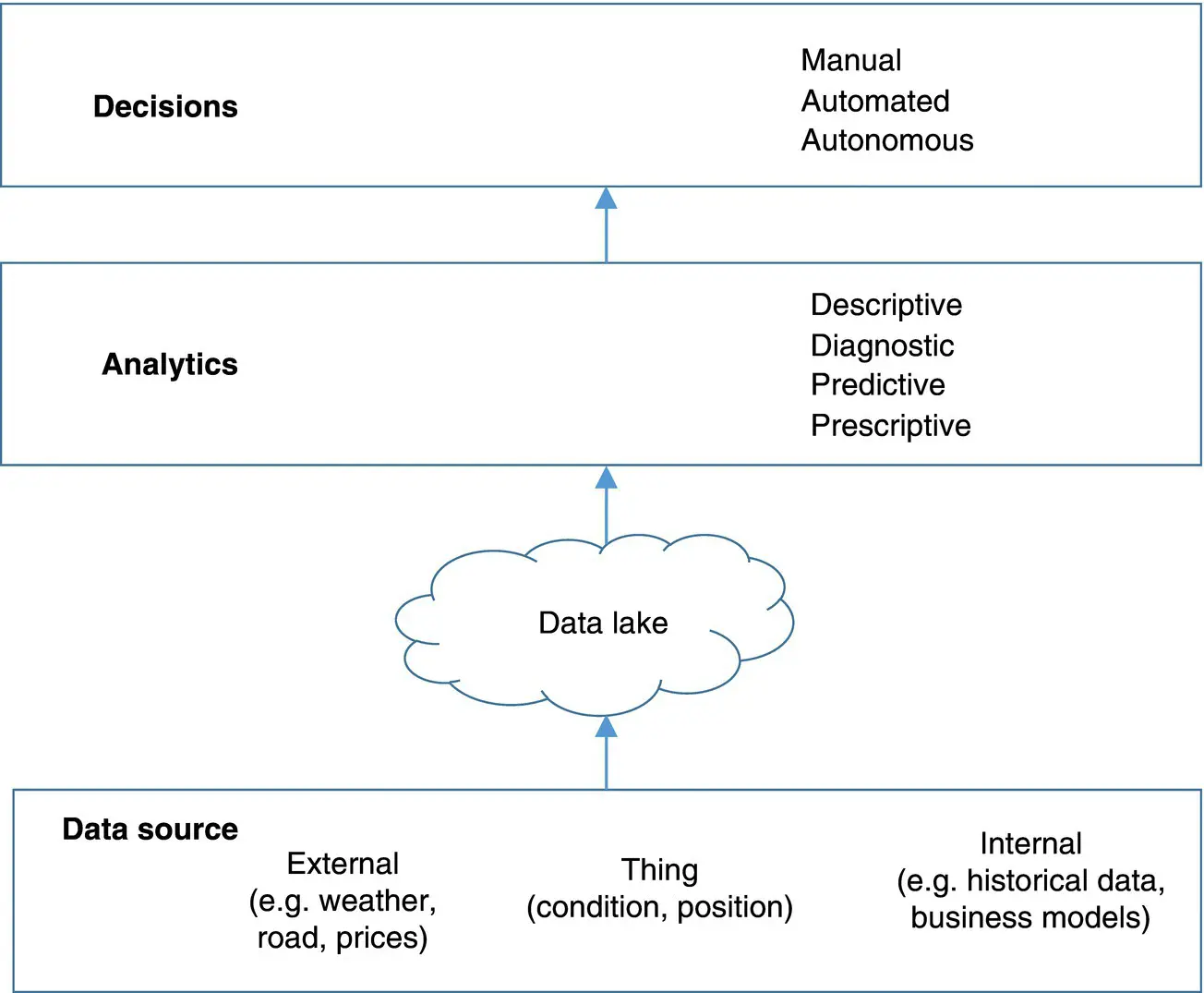
Figure 3.3 Get decisions.
Different applications need different ways of conducting data analytics. What they all have in common is that they get the data out of the pooled data location. In the first part of this chapter, we have discussed how the data get into the data lake and how to get improved decisions out of it. In the section that follows, we will discuss what needs to be considered to get prepared for logistics management in an IoT world.
In logistics management in an IoT world, the management of material and information flows in supply chains still has the same overall goals as before: to provide the right Thing, in the right quantity, at the right time, to the right place (Pfohl 2016, 2018). As outlined above, the IoT world provides new tools to realize these targets more effectively and efficiently. But this new IoT approach also demands new skills and a new way of thinking in logistics management. Aside from the new IoT‐related technologies, the prevailing characteristics of IoT and its management are the data.
Logistics management has always had to handle a lot of data to manage supply chains effectively, but with IoT, a new level of big data is reached. In current daily operations, we still see a lot of inefficiencies due to bad data quality. Material master data (e.g. weight, dimension, country of origin, packaging information, etc.) are missing or often incorrect that can lead to wrong decisions or interruption of operations. As disturbing as such problems of data quality are already today, data quality will be the crucial prerequisite for logistics management in an IoT world. In summary, getting more bad data in a faster way will not improve the process but instead have the opposite effect.
Most international companies still have a functional supply chain organizational structure. However, operating in an IoT world requires close cross‐functional collaboration. Research and development (R&D), information technology (IT), engineering, logistics, purchasing, marketing, and sales will need to be aligned on how the “Thing” will be used and how to use the data lake. Especially the integration of and collaboration with the IT team have shown to be particularly important. A functional setup of data storage, data analytics, and data security might not be the most effective and efficient way of dealing with an increasing data volume. For this reason, some companies are already building up some dedicated “data groups” who only deal with these increased requests of data storage, analytics, and security in a cross‐functional way.
People working in IoT logistics need to have the right skills to get Things connected and get the best out of big data (Heckel 2017). This involves know‐how of IoT technology, logistics process understanding, data analysis, and systems. Companies who want to make full use of IoT have to develop such multiskilled logistics employees. 6 On a management level, this requires skills to “see” supply chains from an IoT point of view. This contains the abilities to handle the above‐shown topics: “get connected,” “get decisions,” and “get prepared.” On an operational level the following skills are needed:
Data analytics – skills to handle and analyze big data and discover new insights/patterns of the IoT logistics processes.
Process mapping and description of reaction processes – understand the actual processes and define/describe (for automated execution) potential reaction processes on detected deviations.
Ability to react faster – to get full advantage of online data, fast reactions are necessary: Is the associate prepared for this? Does he have the authorization to do so?
Check reliability of IT/AI decisions – Is the data correct? Do the automated/autonomous decision‐making processes make the right decisions and show the expected results?
Human–machine interaction – with more automation and robotics, especially in handling areas like goods receiving, warehousing, and loading/unloading, the interaction between robots and machines will only increase (Klumpp 2018). Is your staff prepared and trained how to work with a robot? In the case of small technical errors, can your staff troubleshoot the issue in terms of working with the software program of the robot, or can they do maintenance on the machine, such as exchanging batteries or conducting simple repairs?
To set up and run an operation in an IoT world, new players are necessary. Besides the logistics service providers, producers of embedded systems and sensors, telecommunication companies, IoT platform providers and operators, application developers, certification companies, data analytics providers, and a lot more have to be coordinated and managed to put IoT solutions into practice. A whole IoT ecosystem (Papert and Pflaum 2017) needs to be managed (see Figure 3.4).
This stresses once more the strong need for close coordination with IT‐related players and the “classical” material flow‐related players. Today, the different players in a supply chain often use their own proprietary systems to handle their data and to manage the material flow (Vial 2019). In an IoT world, the sensors of the Thing will provide all data needed for the business. In the collaboration with internal and external partners, this brings up several questions:
Читать дальше













