1 Cover
2 Title Page Intelligent IoT for the Digital World Incorporating 5G Communications and Fog/Edge Computing Technologies Yang Yang ShanghaiTech University and Peng Cheng Lab, China Xu Chen Sun Yat‐sen University, China Rui Tan Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Yong Xiao Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
3 Copyright
4 Preface Notes
5 Acknowledgments
6 Acronyms
7 1 IoT Technologies and Applications1.1 Introduction 1.2 Traditional IoT Technologies 1.3 Intelligent IoT Technologies 1.4 Typical Applications 1.5 Requirements and Challenges for Intelligent IoT Services 1.6 Conclusion References
8 2 Computing and Service Architecture for Intelligent IoT 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Multi‐tier Computing Networks and Service Architecture 2.3 Edge‐enabled Intelligence for Industrial IoT 2.4 Fog‐enabled Collaborative SLAM of Robot Swarm 2.5 Conclusion References Notes
9 3 Cross‐Domain Resource Management Frameworks3.1 Introduction 3.2 Joint Computation and Communication Resource Management for Delay‐Sensitive Applications 3.3 Joint Computing, Communication, and Caching Resource Management for Energy‐efficient Applications 3.4 Case Study: Energy‐efficient Resource Management in Tactile Internet 3.5 Conclusion References Notes
10 4 Dynamic Service Provisioning Frameworks4.1 Online Orchestration of Cross‐edge Service Function Chaining 4.2 Dynamic Network Slicing for High‐quality Services 4.3 Collaboration of Multiple Network Operators 4.4 Conclusion References Notes
11 5 Lightweight Privacy‐Preserving Learning Schemes5.1 Introduction 5.2 System Model and Problem Formulation 5.3 Solutions and Results 5.4 Conclusion References Note
12 6 Clock Synchronization for Wide‐area Applications6.1 Introduction 6.2 System Model and Problem Formulation 6.3 Natural Timestamps in Powerline Electromagnetic Radiation 6.4 Wearables Clock Synchronization Using Skin Electric Potentials 6.5 Conclusion References Notes
13 7 Conclusion
14 Index
15 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Comparison of IoT connecting technologies.
2 Chapter 3Table 3.1 Simulation setting.
3 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Configuration of four required SFs.Table 4.2 IoT Solutions in 3GPP Release 13 (Shirvanimoghaddam et al., Septemb...
4 Chapter 5Table 5.1 The overheadof various approaches.Table 5.2 Per‐sample execution time on Coral for 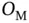 trained for
trained for 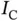 .Table 5.3 Per‐sample execution time on Jetson for
.Table 5.3 Per‐sample execution time on Jetson for 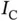 .Table 5.4 Per‐sample execution time of
.Table 5.4 Per‐sample execution time of 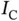 on Coral.
on Coral.
5 Chapter 6Table 6.1 Various sites for performance evaluation.Table 6.2 Decoding error statistics at various sites.Table 6.3 Natural timestamp decoding error statistics in the factory environm...Table 6.4 Measured true positive rate, false positive rate, accuracy, precisi...Table 6.5 Measured true positive rate, false positive rate, accuracy, precisi...Table 6.6 Decoding errors under EMR spoofing attacks.Table 6.7 Storage and compute overhead of TouchSync.Table 6.8 Signal strength and TouchSync accuracy.
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 The architecture of an RFID system. Figure 1.2 NFC system architecture. Figure 1.3 Zigbee system architecture. Figure 1.4 6LoWPAN header layout. Figure 1.5 A BLE network. Figure 1.6 LoRa network architecture. Figure 1.7 Sigfox network architecture. Figure 1.8 NB‐IoT network architecture. Figure 1.9 TS‐UWB telegram splitting. Figure 1.10 OCF core framework. Figure 1.11 The number of connected devices worldwide 2015–2025. Figure 1.12 A traditional cloud‐based IoT architecture. Figure 1.13 A generic and flexible multi‐tier user‐centered IoT network arch... Figure 1.14 Application scenarios of intelligent IoT. Figure 1.15 Network slices existing in 5G architecture. Figure 1.16 The architecture of intelligent IoT multi‐tier computing. Figure 1.17 The network architecture of public safety surveillance. Figure 1.18 Intelligent transportation system scenario overview.Figure 1.19 Description of VANET for autonomous vehicles.
2 Chapter 2Figure 2.1 A multi‐tier computing network architecture. The architecture int...Figure 2.2 An illustration of multi‐tier computing networks (Liu et al., 202...Figure 2.3 The cloud–edge–things system (left), the FA2ST system (right) (Ch...Figure 2.4 The FA2ST framework (Chen et al., 2018a).Figure 2.5 FA2ST application deployment (Chen et al., 2018a).Figure 2.6 Example scenario: edge intelligence enabled product surface inspe...Figure 2.7 Major edge‐centric inference modes: edge‐based, device‐based, edg...Figure 2.8 DNN partitioning and DNN right‐sizing.Figure 2.9 The workflow of Boomerang.Figure 2.10 Point selection algorithm in the Boomerang optimizer.Figure 2.11 The workflow of the DRL model for point selection.Figure 2.12 Evaluation results under different bandwidths and different late...Figure 2.13 The illustration of fog‐enabled robot SLAM system architecture (...Figure 2.14 The workflow of fog‐enabled robot SLAM (Yang et al., 2020b).Figure 2.15 The function view of fog‐enabled robot SLAM (Yang et al., 2020b)...Figure 2.16 The developed demo of fog‐enabled robot SLAM with OpenLTE. (a) m...Figure 2.17 The function view of fog‐enabled robot SLAM (Yang et al., 2020b)...Figure 2.18 The function view of fog‐enabled robot SLAM (Yang et al., 2020b)...Figure 2.19 Challenges and requirements solved and satisfied by the fog‐enab...
3 Chapter 3Figure 3.1 A general heterogeneous MTMH fog network. The FNs have different ...Figure 3.2 System average delay with different number of TNs (non‐splittable...Figure 3.3 System average delay with different number of TNs, under differen...Figure 3.4 System average delay with different number of TNs, under differen...Figure 3.5 Number of beneficial TNs with different number of TNs (non‐splitt...Figure 3.6 Number of beneficial TNs with different number of TNs (splittable...Figure 3.7 Number of decision slots with different number of TNs.Figure 3.8 An illustration of collaborative task execution in fog computing....Figure 3.9 Cooperative F3C task execution.Figure 3.10 1C resource sharing example.Figure 3.11 2C resource sharing example.Figure 3.12 Basic procedures of the F3C algorithm.Figure 3.13 Minimum cost flow network transformation in single task. (a) Coo...Figure 3.14 An auxiliary graph 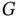 of minimum cost flow for task t .Figure 3.15 Performance gain in energy with different task numbers.Figure 3.16 Performance gain in energy with different device numbers.Figure 3.17 Participated device number under increasing device numbers.Figure 3.18 Average permitted operation number under different task numbers....Figure 3.19 Average permitted operation number under different FN numbers.Figure 3.20 Fog computing‐supported tactile internet architecture.Figure 3.21 (a) Response time under different amounts of workload processed ...Figure 3.22 Response time under different amounts of processed workload and ...Figure 3.23 (a) Distribution of FNs, bus routes, and considered areas, (b) d...Figure 3.24 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN at di...Figure 3.25 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN with ...Figure 3.26 Average response time of users with different power efficiency....
of minimum cost flow for task t .Figure 3.15 Performance gain in energy with different task numbers.Figure 3.16 Performance gain in energy with different device numbers.Figure 3.17 Participated device number under increasing device numbers.Figure 3.18 Average permitted operation number under different task numbers....Figure 3.19 Average permitted operation number under different FN numbers.Figure 3.20 Fog computing‐supported tactile internet architecture.Figure 3.21 (a) Response time under different amounts of workload processed ...Figure 3.22 Response time under different amounts of processed workload and ...Figure 3.23 (a) Distribution of FNs, bus routes, and considered areas, (b) d...Figure 3.24 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN at di...Figure 3.25 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN with ...Figure 3.26 Average response time of users with different power efficiency....
Читать дальше

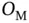 trained for
trained for 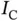 .Table 5.3 Per‐sample execution time on Jetson for
.Table 5.3 Per‐sample execution time on Jetson for 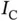 .Table 5.4 Per‐sample execution time of
.Table 5.4 Per‐sample execution time of 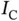 on Coral.
on Coral.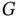 of minimum cost flow for task t .Figure 3.15 Performance gain in energy with different task numbers.Figure 3.16 Performance gain in energy with different device numbers.Figure 3.17 Participated device number under increasing device numbers.Figure 3.18 Average permitted operation number under different task numbers....Figure 3.19 Average permitted operation number under different FN numbers.Figure 3.20 Fog computing‐supported tactile internet architecture.Figure 3.21 (a) Response time under different amounts of workload processed ...Figure 3.22 Response time under different amounts of processed workload and ...Figure 3.23 (a) Distribution of FNs, bus routes, and considered areas, (b) d...Figure 3.24 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN at di...Figure 3.25 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN with ...Figure 3.26 Average response time of users with different power efficiency....
of minimum cost flow for task t .Figure 3.15 Performance gain in energy with different task numbers.Figure 3.16 Performance gain in energy with different device numbers.Figure 3.17 Participated device number under increasing device numbers.Figure 3.18 Average permitted operation number under different task numbers....Figure 3.19 Average permitted operation number under different FN numbers.Figure 3.20 Fog computing‐supported tactile internet architecture.Figure 3.21 (a) Response time under different amounts of workload processed ...Figure 3.22 Response time under different amounts of processed workload and ...Figure 3.23 (a) Distribution of FNs, bus routes, and considered areas, (b) d...Figure 3.24 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN at di...Figure 3.25 Average workload (number of requests) processed by each FN with ...Figure 3.26 Average response time of users with different power efficiency....










