Yang Yang - Intelligent IoT for the Digital World
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Yang Yang - Intelligent IoT for the Digital World» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Intelligent IoT for the Digital World
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Intelligent IoT for the Digital World: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Intelligent IoT for the Digital World»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Provides information on what IoT/WoT is, when to use it, how to provide IoT services with certain technologies, and more Discusses restful architecture, main protocols (ZigBee, 6lowpan, CoAP, HTML5) Explores key technologies on different layers (sensing, gathering, application) Examines how IoT will change the information and communication technology industry Written for professionals working in IoT development, management and big data analytics,
offers an overview of IoT architecture, key technology, current applications and future development of the technology.

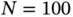 ).Figure 5.9 Impact of differential privacy loss on learning performance (MNIS...Figure 5.10 Impact of the number of participants (spambase). The error bars ...Figure 5.11 Overview of our proposed privacy‐preserving collaborative learni...Figure 5.12 CNN structure.Figure 5.13 Impact of privacy loss level ε on the test accuracy of the ...Figure 5.14 Impact of batch size on the test accuracy of the collaboratively...Figure 5.15 Impact of privacy loss level ε on the test accuracy of the ...Figure 5.16 ObfNet for remote inference. The fog node i desires privacy prot...Figure 5.17 The procedure to generate ObfNets.Figure 5.18 Structure of
).Figure 5.9 Impact of differential privacy loss on learning performance (MNIS...Figure 5.10 Impact of the number of participants (spambase). The error bars ...Figure 5.11 Overview of our proposed privacy‐preserving collaborative learni...Figure 5.12 CNN structure.Figure 5.13 Impact of privacy loss level ε on the test accuracy of the ...Figure 5.14 Impact of batch size on the test accuracy of the collaboratively...Figure 5.15 Impact of privacy loss level ε on the test accuracy of the ...Figure 5.16 ObfNet for remote inference. The fog node i desires privacy prot...Figure 5.17 The procedure to generate ObfNets.Figure 5.18 Structure of 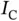 for FSD recognition.Figure 5.19 Structure of
for FSD recognition.Figure 5.19 Structure of 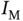 for FSD recognition.Figure 5.20 Test accuracy of different ObfNet–InfNet concatenations in 10 te...Figure 5.21 Structure of
for FSD recognition.Figure 5.20 Test accuracy of different ObfNet–InfNet concatenations in 10 te...Figure 5.21 Structure of 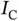 for MNIST recognition.Figure 5.22 Structure of
for MNIST recognition.Figure 5.22 Structure of 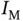 for MNIST recognition.Figure 5.23 Test accuracy of InfNets and ObfNet–InfNet concatenations for MN...Figure 5.24 Obfuscation results of ObfNet
for MNIST recognition.Figure 5.23 Test accuracy of InfNets and ObfNet–InfNet concatenations for MN...Figure 5.24 Obfuscation results of ObfNet 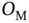 on MNIST.Figure 5.25 Structure of
on MNIST.Figure 5.25 Structure of 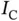 for the ASL dataset.Figure 5.26 Test accuracy of InfNet and ObfNet–InfNet concatenations for ASL...Figure 5.27 Obfuscation results of ObfNet on ASL.Figure 5.28 InfNet's per‐sample execution time on Jetson versus batch size. ...Figure 5.29 Data sample transmission time versus network connection data rat...
for the ASL dataset.Figure 5.26 Test accuracy of InfNet and ObfNet–InfNet concatenations for ASL...Figure 5.27 Obfuscation results of ObfNet on ASL.Figure 5.28 InfNet's per‐sample execution time on Jetson versus batch size. ...Figure 5.29 Data sample transmission time versus network connection data rat...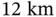 apart in a city. Mean ...Figure 6.2 Ac voltage and EMR data.Figure 6.3 Illustration of an EMR natural timestamping system.Figure 6.4 EMR capture devices.Figure 6.5 Challenges of zero crossing detection in a noisy EMR signal, and ...Figure 6.6 Comparison between the dead‐zone approach and our BPF‐based appro...Figure 6.7 Mean decoding error versus natural timestamp length under differe...Figure 6.8 Impact of sampling rate and timestamp length on the RPi‐based EMR...Figure 6.9 ENF trace computed based on EMR measurements captured by the Z1 m...Figure 6.10 Impact of sampling rate and timestamp length on the timestamping...Figure 6.11 ENF trace estimated by the Z1 mote based on EMR signals sampled ...Figure 6.12 Distribution of decoding errors of RPi‐based EMR sensor at sites...Figure 6.13 Decoding errors in one month. Each error bar is computed based o...Figure 6.14 Deployment spots at site B. An RPi‐based EMR sensor is deployed ...Figure 6.15 Z1 decoding error versus EMR signal strength.Figure 6.16 Decoding errors of Z1 under the sliding and neighboring approach...Figure 6.17 Factory floor plan and EMR sensors' locations.Figure 6.18 ENFs sensed by the RPi‐based EMR sensor and the Z1 on the factor...Figure 6.19 Natural timestamp decoding errors in the factory environment. Th...Figure 6.20 Dividing a natural timestamp to sub‐natural timestamps to verify...Figure 6.21 PDF of decoding offsets when the decoding condition is respectiv...Figure 6.22 A schematic of the EMR spoofer.Figure 6.23 EMR spoofer (left) and spoofing experiment (middle and right).Figure 6.24 The ENF sensed by the victim EMR sensor when the EMR spoofer is ...Figure 6.25 Packet delay attack and secure clock synchronization.Figure 6.26 NTP principle and packet timestamping.Figure 6.27 Performance of NTP over a BLE connection.Figure 6.28 Flora.Figure 6.29 TouchSync prototypes.Figure 6.30 No human body contact.Figure 6.31 iSEPs on the same wearer (shared ground).Figure 6.32 iSEPs on different wearers (shared ground).Figure 6.33 Absolute time displacement
apart in a city. Mean ...Figure 6.2 Ac voltage and EMR data.Figure 6.3 Illustration of an EMR natural timestamping system.Figure 6.4 EMR capture devices.Figure 6.5 Challenges of zero crossing detection in a noisy EMR signal, and ...Figure 6.6 Comparison between the dead‐zone approach and our BPF‐based appro...Figure 6.7 Mean decoding error versus natural timestamp length under differe...Figure 6.8 Impact of sampling rate and timestamp length on the RPi‐based EMR...Figure 6.9 ENF trace computed based on EMR measurements captured by the Z1 m...Figure 6.10 Impact of sampling rate and timestamp length on the timestamping...Figure 6.11 ENF trace estimated by the Z1 mote based on EMR signals sampled ...Figure 6.12 Distribution of decoding errors of RPi‐based EMR sensor at sites...Figure 6.13 Decoding errors in one month. Each error bar is computed based o...Figure 6.14 Deployment spots at site B. An RPi‐based EMR sensor is deployed ...Figure 6.15 Z1 decoding error versus EMR signal strength.Figure 6.16 Decoding errors of Z1 under the sliding and neighboring approach...Figure 6.17 Factory floor plan and EMR sensors' locations.Figure 6.18 ENFs sensed by the RPi‐based EMR sensor and the Z1 on the factor...Figure 6.19 Natural timestamp decoding errors in the factory environment. Th...Figure 6.20 Dividing a natural timestamp to sub‐natural timestamps to verify...Figure 6.21 PDF of decoding offsets when the decoding condition is respectiv...Figure 6.22 A schematic of the EMR spoofer.Figure 6.23 EMR spoofer (left) and spoofing experiment (middle and right).Figure 6.24 The ENF sensed by the victim EMR sensor when the EMR spoofer is ...Figure 6.25 Packet delay attack and secure clock synchronization.Figure 6.26 NTP principle and packet timestamping.Figure 6.27 Performance of NTP over a BLE connection.Figure 6.28 Flora.Figure 6.29 TouchSync prototypes.Figure 6.30 No human body contact.Figure 6.31 iSEPs on the same wearer (shared ground).Figure 6.32 iSEPs on different wearers (shared ground).Figure 6.33 Absolute time displacement 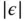 between the EMR signals captured by...Figure 6.34 iSEPs on the same wearer (independent grounds).Figure 6.35 iSEPs on different wearers (independent grounds).Figure 6.36 Normalized range and time displacement
between the EMR signals captured by...Figure 6.34 iSEPs on the same wearer (independent grounds).Figure 6.35 iSEPs on different wearers (independent grounds).Figure 6.36 Normalized range and time displacement  of iSEPs under differen...Figure 6.37 A synchronization process of TouchSync.Figure 6.38 iSEP signal processing pipeline.Figure 6.39 A synchronization session of TouchSync. The vertical arrows repr...Figure 6.40 An example of solving the integer ambiguity. The transmissions o...Figure 6.41 Convergence speed of IAS.Figure 6.42 Distribution of absolute clock offset estimation errors.Figure 6.43 An example of IPS‐based TouchSync (unit: ms).Figure 6.44 Convergence speed under various settings of IPS period.Figure 6.45 Impact of signal strength.Figure 6.46 Wearing position.Figure 6.47 EMR signals near an electric oven and a microwave oven.Figure 6.48 Errors introduced into time displacements of the EMR signals.Figure 6.49 Laboratory floor plan with test points marked.Figure 6.50 Home floor plan with test points marked.Figure 6.51 One‐way delays over a ngrok tunnel.Figure 6.52 Accuracy of TouchSync‐over‐Internet.
of iSEPs under differen...Figure 6.37 A synchronization process of TouchSync.Figure 6.38 iSEP signal processing pipeline.Figure 6.39 A synchronization session of TouchSync. The vertical arrows repr...Figure 6.40 An example of solving the integer ambiguity. The transmissions o...Figure 6.41 Convergence speed of IAS.Figure 6.42 Distribution of absolute clock offset estimation errors.Figure 6.43 An example of IPS‐based TouchSync (unit: ms).Figure 6.44 Convergence speed under various settings of IPS period.Figure 6.45 Impact of signal strength.Figure 6.46 Wearing position.Figure 6.47 EMR signals near an electric oven and a microwave oven.Figure 6.48 Errors introduced into time displacements of the EMR signals.Figure 6.49 Laboratory floor plan with test points marked.Figure 6.50 Home floor plan with test points marked.Figure 6.51 One‐way delays over a ngrok tunnel.Figure 6.52 Accuracy of TouchSync‐over‐Internet.










