Identification and sensor technologyTo connect Things, the first step is to know about the Thing (what, where). So, one crucial aspect of IoT is the identification and sensor technology enabling the automated identification of an object (Thing) and collection of “sensed” real‐time data (e.g. temperature, acceleration, humidity, vibration, and location).
Networking technology (e.g. 5G, Wi‐Fi 6)Enabling to connect the Things in a fast and reliable way to interact (network) with each other. With more Things to be connected and thus more data to be transmitted, new powerful networking technologies are required to provide the capability of transmitting big data volume of many Things in parallel with a short latency.
Big dataAs a result (or intention) of connecting everything with everything, a lot of data are created. New technologies provide the possibility to transmit (see networking technology), store, and analyze a huge amount of data – big data. Especially the topic of big data analytics and decisions based on a huge amount of data is seen as one big lever to improve speed and quality of management and pave the way for artificial intelligence (AI).
Artificial intelligenceEnabling automated and autonomous decision making and operations, based on self‐learning systems without the intervention of humans.
Autonomous robots and vehicles (e.g. drones, automated guided vehicle [AGV])Material handling and transportation are done by robots or AGVs that execute the defined tasks in an automated or autonomous way in interaction with other Things.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)Devices supporting decisions and processes by providing instructions via augmented and virtual reality technologies (e.g. headsets or smart glasses showing the worker on a small display in the glasses what to do next).
Logistics managers not only have to understand these new technologies, but also the overall concept of IoT and its implications for managing material and information flows in global supply chains.
One prevailing “new” quality of IoT is “connection.” Therefore, the first new topic in logistics management is to think about how to “ get connected”. Acknowledging that the overall approach of IoT is to connect everything with everything, it is important to reflect what this will mean for logistics. What are the “Things” in the supply chain we want to connect to be able to operate faster and more efficiently?
One of the major goals of having connected Things is to gather big data. Logistics management must define which data is needed, e.g. data about the on‐time delivery of products, quality of the product in transit, or security of facilities and vehicles, and how to make the best use of the data for their business customers. Hence, the second new topic in logistics management is to define how IoT is used to “get decisions ” in a better way than before.
To connect Things in supply chains and to come to better decisions in logistics management, new management strategies, new mindsets, and new skills must be developed. Similar to other disruptive changes in the previous industrial revolutions, like mechanization, mass production, and computerization, IoT not only is a new way of using technology but also very much requires a change of thinking. The third topic for logistics in an IoT world is therefore to “get prepared” for this new way of logistics management. Besides just ensuring high data quality, the industry needs to reconsider organization, skills, and the whole ecosystem of logistics in an IoT world.

Figure 3.1 IoT logistics.
What follows is a discussion about how to get connected, how to get decisions, and how to get prepared. Regarding getting connected, relevant topics are sensors, identification, standards, and security. In the section about getting decisions, descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive ways of data analytics are introduced, and manual, automated, and autonomous decision making contrasted. Finally, key topics to get prepared such as data quality, organization, skills, and ecosystems are addressed. This is also summarized in Figure 3.1. The conclusion in the end highlights that logistics management in an IoT world will require managing new IoT ecosystem setups with new actors and new skill requirements.
Logistics Management in an IoT World
Get Connected
The defining element of IoT is connectivity. Therefore, the first aspects of setting up the supply chain and its management in an IoT style are to define what are the relevant Things that need to be connected, in what way data should be collected, and finally, which data needs to be collected. Simply collecting more and more data might just increase the amount of available data exponentially, but not necessarily lead to improved patterns of doing business.
When is a thing a Thing in the sense of logistics in an IoT world? Is a small component a Thing that needs to be monitored by sensors and always be online? Or does the Thing start with complex finished goods that are themselves composed of multiple components? Here, we need to distinguish between the user perspective and the logistics perspective. From the logistics perspective, i.e. the material and information flow point of view, everything is a Thing. From the classical user IoT point of view, the Thing is more related to machines and devices, such as finished products, components in a production line, transport vehicles, or whole warehouses. This chapter will examine Things from the logistics perspective.
Criteria for Defining the Right Things
Some examples of criteria based on which a Thing may be included in an IoT system or application would be as follows:
Requests from customers (e.g. to stay informed about the placed order).
The criticality of the Things to influence the supply chain performance (e.g. keeping a certain temperature or avoiding shocks during transport).
Requirements from the business model (e.g. provide services).
Depending on the needed information, the appropriate sensor and identification technology has to be selected. For instance, to keep customers informed about their delivery, it might be sufficient to collect information once the Thing is passing certain checkpoints, like a warehouse, cross‐dock, or the truck for the last mile, through simple scanning. Meanwhile, in case the Thing needs to be cooled or is sensitive to shocks, information on temperature or acceleration provided by sensors might always be necessary. Otherwise, the business model might require a continuous condition monitoring of a forklift or AGV through embedded sensors. In case deviations are detected, an alert can be triggered and then, for example, spare parts ordered.
Sensors and Identification
The level of monitoring and identification, thus the Thing itself, e.g. product, box, container, or transport device (see Figure 3.2), can vary according to the requirements. Although in a narrow sense the Thing is equal to the product, for example, for tracking a shipment from Europe to Asia by an ocean carrier, tracking the vessel itself during its way might be enough – knowing and trusting that the product was loaded onboard the ship. Thus, tracking information does not have to be sent from every single of the millions of products on a containership, but only from the ship itself. If the sensor data from individual products are requested, other solutions are required.
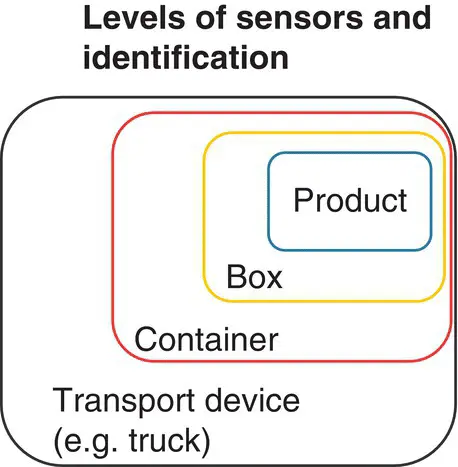
Figure 3.2 Levels of sensors and identification.
Читать дальше














