Ethernet has been around in various forms since the early 1970s. (For a brief history of Ethernet, see the sidebar, “Ethernet folklore and mythology.”) The current incarnation of Ethernet is defined by the 802.3 IEEE standard. Various flavors of Ethernet operate at different speeds and use different types of media. However, all the versions of Ethernet are compatible with each other, so you can mix and match them on the same network by using devices such as bridges, hubs, and switches to link network segments that use different types of media.
 The actual transmission speed of Ethernet is measured in millions of bits per second (Mbps) or billions of bits per second (Gbps). Ethernet comes in several different speed versions:
The actual transmission speed of Ethernet is measured in millions of bits per second (Mbps) or billions of bits per second (Gbps). Ethernet comes in several different speed versions:
Standard Ethernet: 10 Mbps; rarely (if ever) used today.
Fast Ethernet: 100 Mbps; still used for devices where speed is not particularly important, such as printers or fax machines.
Gigabit Ethernet and beyond: 1,000 Mbps; the most common speed used to connect user computers to a network. Faster speeds, such as 10 Gbps, 100 Gbps, and even faster, are sometimes used in high-speed networks to connect servers and other critical devices to the network.
 Network transmission speed refers to the maximum speed that can be achieved over the network under ideal conditions. In reality, the actual throughput of an Ethernet network rarely reaches this maximum speed.
Network transmission speed refers to the maximum speed that can be achieved over the network under ideal conditions. In reality, the actual throughput of an Ethernet network rarely reaches this maximum speed.
Ethernet operates at the first two layers of the OSI model — the physical and the data link layers. However, Ethernet divides the data link layer into two separate layers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer and the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer. Figure 1-6 shows how the various elements of Ethernet match up to the OSI model.
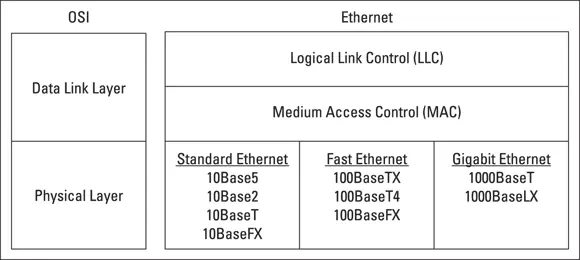
FIGURE 1-6:Ethernet and the OSI model.
The following sections describe Standard Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet in more detail.
Standard Ethernet is the original Ethernet. It runs at 10 Mbps, which was considered fast in the 1970s but is excruciatingly slow by today’s standards. Although plenty of existing Standard Ethernet is still in use, it’s considered obsolete and should be replaced by Gigabit Ethernet as soon as possible.
Standard Ethernet came in three incarnations, depending on the type of cable used to string the network together:
10Base5: This original Ethernet cable was thick (about as thick as your thumb), heavy, and difficult to work with. It’s seen today only in museum exhibits.
10Base2: This thinner type of coaxial cable (it resembles television cable) became popular in the 1980s and lingered into the early 1990s. Plenty of 10Base2 cable is still in use, but it’s rarely installed in new networks. 10Base2 (like 10Base5) uses a bus topology, so wiring a 10Base2 network involves running cable from one computer to the next until all the computers are connected in a segment.ETHERNET FOLKLORE AND MYTHOLOGYHere’s how Ethernet came to be so popular. The original idea for the Ethernet was hatched in the mind of Robert Metcalfe, a graduate computer science student at Harvard University. Looking for a thesis idea in 1970, he refined a networking technique used in Hawaii — the AlohaNet (actually a wireless network) — and developed a technique that would enable a network to efficiently use as much as 90 percent of its capacity. By 1973, he had his first Ethernet network up and running at the famous Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). Bob dubbed his network “Ethernet” in honor of the thick network cable, which he called “the ether.” (Xerox PARC was busy in 1973. In addition to Ethernet, PARC developed the first personal computer that used a graphical user interface (GUI) complete with icons, windows, and menus, and the world’s first laser printer.)In 1979, Xerox began working with Intel and DEC (a once-popular computer company) to make Ethernet an industry standard networking product. Along the way, they enlisted the help of the IEEE, which formed committee number 802.3 and began the process of standardizing Ethernet in 1981. The 802.3 committee released the first official Ethernet standard in 1983.Meanwhile, Bob Metcalfe left Xerox, turned down a job offer from Steve Jobs to work at Apple computers, and started a company called the Computer, Communication, and Compatibility Corporation — now known as 3Com. 3Com has since become one of the largest manufacturers of Ethernet equipment in the world.
10BaseT: Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable became popular in the 1990s because it’s easier to install, lighter, and more reliable, and also it offers more flexibility in how networks are designed. 10BaseT networks use a star topology with hubs at the center of each star. Although the maximum length of 10BaseT cable is only 100 meters, hubs can be chained to extend networks well beyond the 100-meter limit.10BaseT cable has four pairs of wires twisted together throughout the entire span of the cable. However, 10BaseT uses only two of these wire pairs, so the unused pairs are spares.
 If you find yourself working with 10 Mbps Ethernet, spend a few moments enjoying your historical find. Then, as quickly as you can, update the entire network to Gigabit Ethernet.
If you find yourself working with 10 Mbps Ethernet, spend a few moments enjoying your historical find. Then, as quickly as you can, update the entire network to Gigabit Ethernet.
Fast Ethernet refers to Ethernet that runs at 100 Mbps, which is ten times the speed of Standard Ethernet. Although there are several varieties of Fast Ethernet, the most common is 100BaseTX, which transmits at 100 Mbps over just two pairs of a UTP cable. 100 Mbps Ethernet requires at least Cat-5 cable, but most networks are now wired with Cat-5e or Cat-6 cable, both of which are capable of gigabit speeds.
Gigabit Ethernet is Ethernet running at a 1,000 Mbps, or 1 Gbps. Gigabit Ethernet was once considerably more expensive than Fast Ethernet, so it was used only when the improved performance justified the extra cost. However, today Gigabit Ethernet is the standard for nearly all desktop and laptop PCs. Two grades of cable are commonly used: Cat-5e and Cat-6; Cat-6 is preferred because it can be used for even faster networks.
Several varieties of Ethernet faster than 1 Gbps on copper cable are available:
2.5GBase-T: 2.5 Gbps speed that can operate on Cat-5e cable.
5GBase-T: 5 Gbps speed that requires Cat-6 cable.
10GBase-T: 10 Gbps speed that requires Cat-6A cable.
25GBase-T: 25 Gbps speed that requires Cat-8 cable.
40GBase-T: 40 Gbps speed that also requires Cat-8 cable.
There are also many varieties of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, 100 Gbps, 200 Gbps, and even 400 Gbps Ethernet that run on fiber-optic cable. In the near future, terabit (1,000 Gbps) Ethernet may be possible.
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite
TCP/IP, the protocol on which the Internet is built, is not a single protocol but rather an entire suite of related protocols. TCP is even older than Ethernet. It was first conceived in 1969 by the Department of Defense. For more on the history of TCP/IP, see the sidebar, “The fascinating story of TCP/IP,” later in this chapter. Currently, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) manages the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Читать дальше

 The actual transmission speed of Ethernet is measured in millions of bits per second (Mbps) or billions of bits per second (Gbps). Ethernet comes in several different speed versions:
The actual transmission speed of Ethernet is measured in millions of bits per second (Mbps) or billions of bits per second (Gbps). Ethernet comes in several different speed versions: Network transmission speed refers to the maximum speed that can be achieved over the network under ideal conditions. In reality, the actual throughput of an Ethernet network rarely reaches this maximum speed.
Network transmission speed refers to the maximum speed that can be achieved over the network under ideal conditions. In reality, the actual throughput of an Ethernet network rarely reaches this maximum speed.











