In many cases, the transport layer protocol divides large messages into smaller packets that can be sent over the network efficiently. The transport layer protocol reassembles the message on the receiving end, making sure that all the packets that make up a single transmission are received so that no data is lost.
For some applications, speed and efficiency are more important than reliability. In such cases, a connectionless protocol can be used. As you can likely guess, a connectionless protocol doesn’t go to the trouble of establishing a connection before sending a packet: It simply sends the packet. TCP is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol. The connectionless protocol that works alongside TCP is User Datagram Protocol (UDP) .
You can view information about the status of TCP and UDP connections by running the Netstatcommand from a command window, as shown in Figure 1-4. In the figure, you can see that several TCP connections are established.
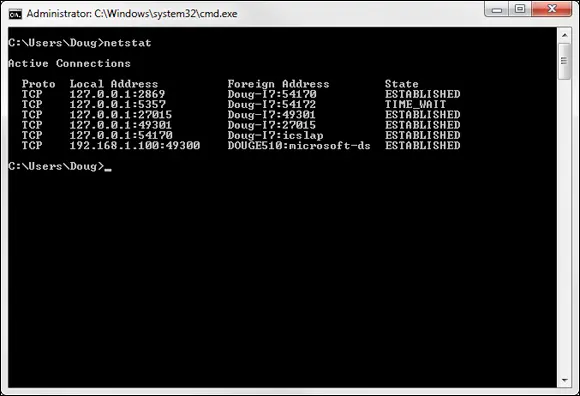
FIGURE 1-4:See TCP and UDP connections.
In fact, you can use the command Netstat /Nto see the numeric network addresses instead of the names. With the /Nswitch, the output in Figure 1-4 would look like this:
Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address StateTCP 127.0.0.1:2869 127.0.0.1:54170 ESTABLISHEDTCP 127.0.0.1:5357 127.0.0.1:54172 TIME_WAITTCP 127.0.0.1:27015 127.0.0.1:49301 ESTABLISHEDTCP 127.0.0.1:49301 127.0.0.1:27015 ESTABLISHEDTCP 127.0.0.1:54170 127.0.0.1:2869 ESTABLISHEDTCP 192.168.1.100:49300 192.168.1.101:445 ESTABLISHED
 TCP is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol. UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol.
TCP is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol. UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol.
The session layer establishes conversations — sessions — between networked devices. A session is an exchange of connection-oriented transmissions between two network devices. Each transmission is handled by the transport layer protocol. The session itself is managed by the session layer protocol.
A single session can include many exchanges of data between the two computers involved in the session. After a session between two computers has been established, it's maintained until the computers agree to terminate the session.
The session layer allows three types of transmission modes:
Simplex: Data flows in only one direction.
Half-duplex: Data flows in both directions, but only in one direction at a time.
Full-duplex: Data flows in both directions at the same time.
 In actual practice, the distinctions in the session, presentation, and application layers are often blurred, and some commonly used protocols actually span all three layers. For example, SMB — the protocol that is the basis of file sharing in Windows networks — functions at all three layers.
In actual practice, the distinctions in the session, presentation, and application layers are often blurred, and some commonly used protocols actually span all three layers. For example, SMB — the protocol that is the basis of file sharing in Windows networks — functions at all three layers.
The presentation layer is responsible for how data is represented to applications. The most common representation for representing character data today is called UTF-8, which uses 8-bit sets to represent most characters found in western alphabets. UTF-8 is compatible with an older standard called ASCII.
 UTF-8 is sometimes called Unicode, which is a standard for representing the characters found in most of the world's writing systems. Technically, UTF-8 is a particular method of implementing Unicode, so although the two terms are related, they are not identical.
UTF-8 is sometimes called Unicode, which is a standard for representing the characters found in most of the world's writing systems. Technically, UTF-8 is a particular method of implementing Unicode, so although the two terms are related, they are not identical.
 Some computers, in particular IBM mainframe computers, use a different code called Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC). ASCII and EBCDIC aren’t compatible. To exchange information between a mainframe computer and a Windows computer, the presentation layer must convert the data from ASCII to EBCDIC, and vice versa.
Some computers, in particular IBM mainframe computers, use a different code called Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC). ASCII and EBCDIC aren’t compatible. To exchange information between a mainframe computer and a Windows computer, the presentation layer must convert the data from ASCII to EBCDIC, and vice versa.
Besides simply converting data from one code to another, the presentation layer can also apply sophisticated compression techniques so that fewer bytes of data are required to represent the information when it’s sent over the network. At the other end of the transmission, the presentation layer then decompresses the data.
The presentation layer can also scramble the data before it’s transmitted and then unscramble it at the other end by using a sophisticated encryption technique that even Sherlock Holmes would have trouble breaking.
The highest layer of the OSI model, the application layer deals with the techniques that application programs use to communicate with the network. The name of this layer is a little confusing. Application programs (such as Microsoft Office or QuickBooks) aren’t a part of the application layer. Rather, the application layer represents the programming interfaces that application programs use to request network services.
Some of the better-known application layer protocols are
Domain Name System (DNS): For resolving Internet domain names
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): For file transfers
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): For email
Server Message Block (SMB): For file sharing in Windows networks
Network File System (NFS): For file sharing in Unix networks
Telnet: For terminal emulation
Following a Packet through the Layers
Figure 1-5 shows how a packet of information flows through the seven layers as it travels from one computer to another on the network. The data begins its journey when an end-user application sends data to another network computer. The data enters the network through an application layer interface, such as SMB. The data then works its way down through the protocol stack. Along the way, the protocol at each layer manipulates the data by adding header information, converting the data into different formats, combining packets to form larger packets, and so on. When the data reaches the physical layer protocol, it’s placed on the network media (in other words, the cable) and sent to the receiving computer.
When the receiving computer receives the data, the data works its way up through the protocol stack. Then, the protocol at each layer reverses the processing that was done by the corresponding layer on the sending computer. Headers are removed, data is converted back to its original format, packets that were split into smaller packets are recombined into larger messages, and so on. When the packet reaches the application layer protocol, it’s delivered to an application that can process the data.
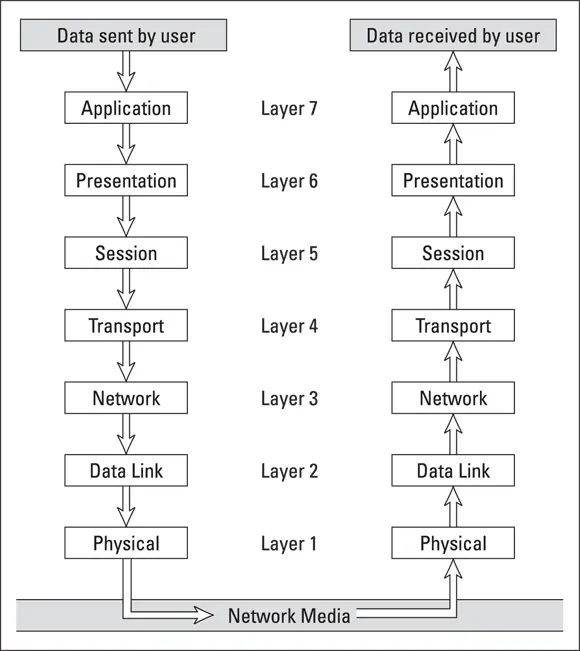
FIGURE 1-5:How data travels through the seven layers.
As I mention earlier, the first two layers of the OSI model deal with the physical structure of the network and the means by which network devices can send information from one device on a network to another. By far, Ethernet is the most popular set of protocols for the physical and data link layers .
Читать дальше


 TCP is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol. UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol.
TCP is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol. UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol. In actual practice, the distinctions in the session, presentation, and application layers are often blurred, and some commonly used protocols actually span all three layers. For example, SMB — the protocol that is the basis of file sharing in Windows networks — functions at all three layers.
In actual practice, the distinctions in the session, presentation, and application layers are often blurred, and some commonly used protocols actually span all three layers. For example, SMB — the protocol that is the basis of file sharing in Windows networks — functions at all three layers. UTF-8 is sometimes called Unicode, which is a standard for representing the characters found in most of the world's writing systems. Technically, UTF-8 is a particular method of implementing Unicode, so although the two terms are related, they are not identical.
UTF-8 is sometimes called Unicode, which is a standard for representing the characters found in most of the world's writing systems. Technically, UTF-8 is a particular method of implementing Unicode, so although the two terms are related, they are not identical.











