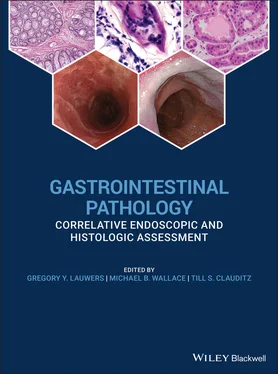
Figure 2.17 Endoscopic appearance of necrotizing esophagitis with appearance of “black esophagus.”
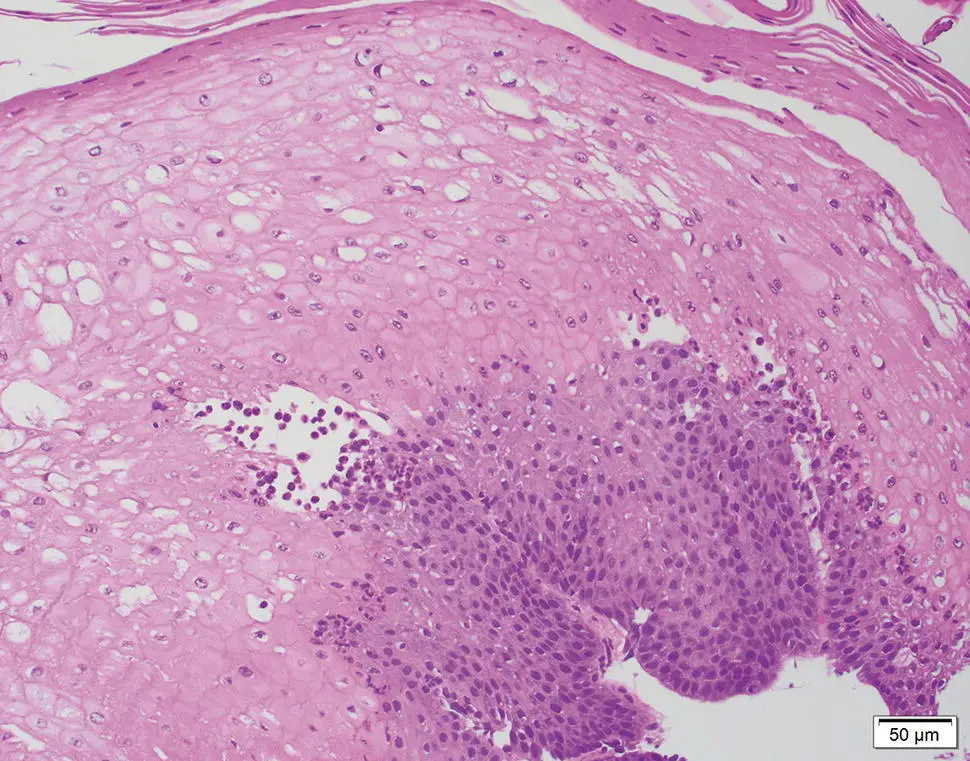
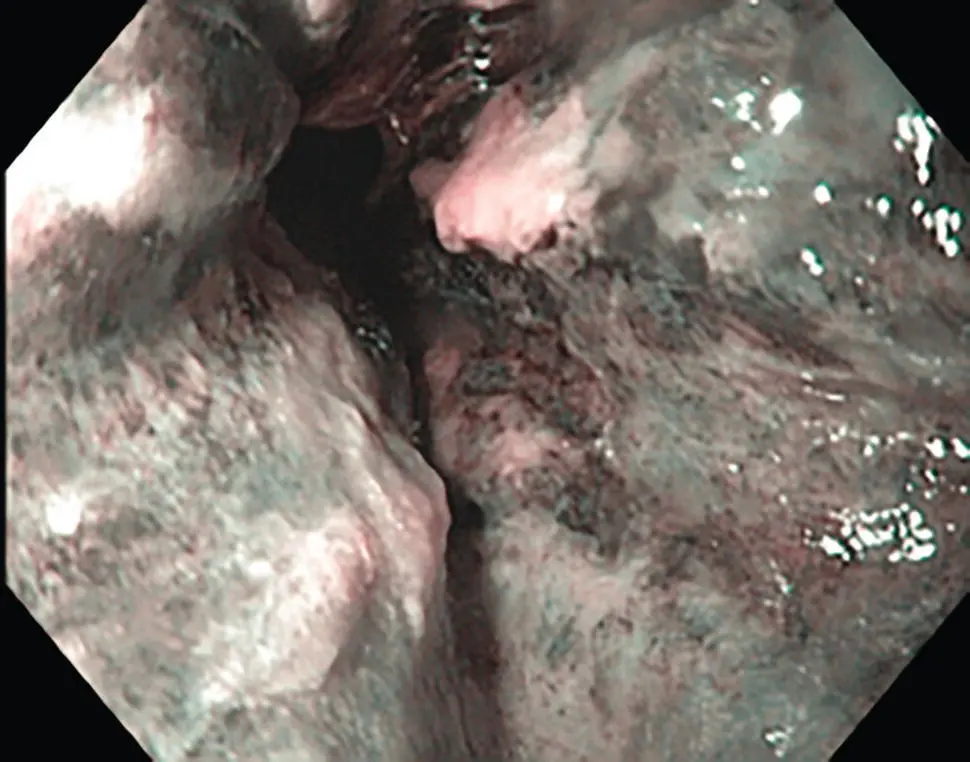
Figure 2.18 Characteristic appearance of sloughing esophagitis with two‐tone appearance of the esophageal mucosa.
Biopsies show a two‐toned appearance, with a superficial zone of necrotic, eosinophilic squamous epithelium and underlying intact squamous mucosa that appears normal or reactive. The necrotic epithelial layer may be partially or completely detached and exhibits pyknotic, parakeratosis‐like or faded, ghost‐like nuclei. In some cases a neutrophilic infiltrate is seen between the epithelial layers, ranging from mild to severe ( Figure 2.18). In black esophagus, biopsies show necrotic squamous epithelium and mucosa, with possible involvement of submucosa. Pill fragments and surface colonization by bacteria or fungal yeasts have also been described.
Immunohistochemical Studies and Molecular Features
Ancillary studies may be necessary to exclude differential diagnostic considerations including special stains for fungal organisms, viruses or direct immunofluorescence for skin disease‐associated esophagitis (see below).
The differential diagnosis includes disorders that may exhibit histologic epithelial necrosis and/or endoscopic plaques. Candida esophagitis may exhibit similar white plaques endoscopically. Histologically, the plaques appear flaky and less compact, and special stains (GMS, PAS) are diagnostic. Pill‐induced esophagitis is more often associated with nonspecific mucosal ulcers. Corrosive or caustic injury, such as alkali (lye) or acid ingestion, typically shows extensive edema, erythema, and hemorrhage in addition to necrotic exudates. Clinical history is key and the mucosa is seldom biopsied. Esophageal involvement by cutaneous bullous disorders may need to be excluded by immunofluorescence studies for IgG and C3. Severe eosinophilic esophagitis may also exhibit sloughing membranes, but is recognized by the marked intraepithelial eosinophilic infiltration. Black esophagus (i.e. acute esophageal necrosis) is a rare condition that arises in debilitated patients with multiple comorbidities such as hypoperfusion, sepsis, diabetic ketoacidosis, and malignancy. It results from the combining effect of ischemia and corrosive injury of gastric contents. The clinical presentation is distinctive with bleeding and a characteristic diffuse circumferential black mucosal discoloration of the distal esophagus with an abrupt transition at the gastroesophageal junction.
Prognosis, Evolution and Management
The clinical course and outcome in patients with sloughing esophagitis is primarily related to the presence of significant underlying diseases. In the few patients with follow‐up biopsies documented, most have shown endoscopic and histologic resolution.
Graft Versus Host Disease of the Esophagus
Definition, General Features, Predisposing Factors
Graft versus host disease (GVHD) is an important complication of allogeneic stem cell transplantation, leading to considerable morbidity and mortality. Gastrointestinal tract involvement is frequent, and endoscopy with biopsy plays a central role in the diagnosis and management of patients with suspected GVHD. Although the pathologic features of GVHD are well described in glandular mucosa, they are less so for the esophagus. Manifestations of esophageal injury may occur in the acute or chronic phases of GVHD. Diagnosis requires correlation of the clinical and pathologic features.
Clinical and Endoscopic Characteristics
Symptoms of esophageal GVHD include dysphagia and odynophagia. Endoscopically, acute presentations of GVHD have been described as showing bullous disease or a desquamative process with mucosal cast formation ( Figure 2.19). In the chronic phase, the presence of webs, strictures, or concentric rings involving the mid‐upper esophagus on EGD or barium contrast imaging are considered diagnostic features ( Figure 2.20).
The histologic features of esophageal GVHD are similar to those of other sites in the GI tract. The squamous epithelium exhibits apoptosis, intraepithelial lymphocytosis, basal vacuolization, and necrosis in severe cases ( Figure 2.21). Apoptotic keratinocytes are prominent in the basal and suprabasal region and the associated lymphocytosis can have a lichenoid interface appearance. The extent of the findings can be graded as mild, moderate, or severe. Severe GVHD is characterized by erosion and/or ulceration. Involvement of deeper layers with submucosal fibrosis has been described in chronic GVHD, but this layer is seldom represented in biopsy samples. Due to potential discordance among the observed clinical severity, endoscopic abnormalities, and histologic findings, it is recommended that a minimum of 8–10 serial H&E stained sections be cut to detect minimal histologic changes of GVHD. Finally, comparison to prior biopsies should be noted in order to assess treatment effects.
Figure 2.19 Endoscopic appearance of acute GVHD of esophagus with diffuse mucosal desquamation.
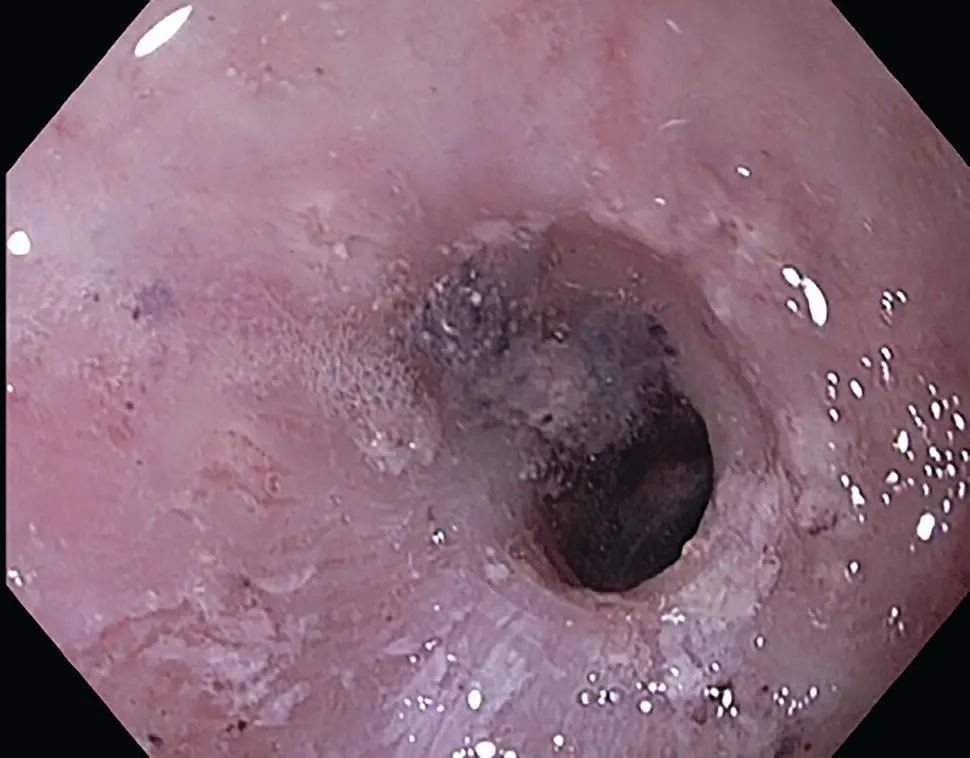
Figure 2.20 Endoscopic appearance of inflammatory stricture with persistent desquamation in chronic esophageal GVHD.
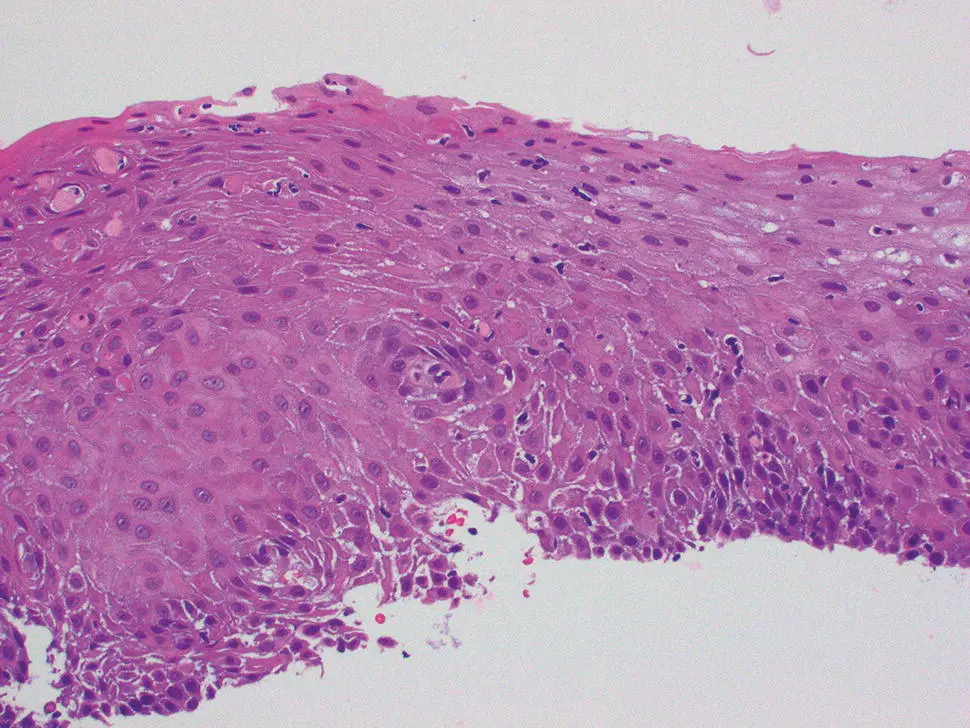
Figure 2.21 Microscopic appearance of acute GVHD of esophagus with basal apoptosis, lymphocytic infiltration, and dyskeratotic epithelial elements.
The major differential diagnostic considerations include other types of esophageal mucosal injury that may lead to increased apoptosis, such as drug or infection. Knowledge of the clinical context is important, as epithelial apoptosis in the setting of stem cell transplantation likely represents GVHD, whereas mycophenolate‐associated injury occurs in solid organ transplant recipients. Cytomegalovirus infection also causes apoptosis, and may coexist with GVHD, necessitating immunohistochemical staining for exclusion. In cases where bullae or desquamation is observed endoscopically, the differential diagnosis may also include other vesiculobullous dermatologic disorders involving the esophagus.
Prognosis, Evolution, and Clinical Management
Systemic immunomodulatory therapy is indicated for patients with moderate to severe GHVD. Corticosteroids are used as first‐line therapy, and other agents considered as options in an algorithmic approach.
Radiation Esophagitis
Definition, General Features, Predisposing Factors
Radiation injury to the esophagus is a dose‐limiting toxicity occurring as either an acute or late complication of radiation therapy of thoracic neoplasms. The risk of radiation esophagitis is increased by concurrent chemotherapy and radiation dose–volumetric parameters, which may be related to underlying vascular changes and ischemic injury. Overall, symptomatic radiation esophagitis is rare, affecting <1% of treated patients.
Читать дальше