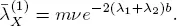
When the real intensity 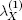 is less than, but close to
is less than, but close to 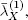 large queues accumulate before the crosswalk.
large queues accumulate before the crosswalk.
Their asymptotic analysis, as well as some results concerning characteristics of the process Q 1in a stationary regime, when ρ (1)< 1 can be found in the papers (Afanasyeva and Rudenko 2012; Afanasyeva and Mihaylova 2015).
Now we will consider model 2, in which the rules for crossing the crosswalk by a car are weakened. We assume that the car can move along the j th lane 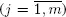 if there are no pedestrians of the first type (going from A to B) on the lanes 1, 2, . . . , j , and there are no pedestrians of the second type on the lanes j, j + 1, ..., 2 m . Denote P 0( j ) as the probability of this event in a steady-state.
if there are no pedestrians of the first type (going from A to B) on the lanes 1, 2, . . . , j , and there are no pedestrians of the second type on the lanes j, j + 1, ..., 2 m . Denote P 0( j ) as the probability of this event in a steady-state.
Since the number of pedestrians of the first type on the lanes (1 ,2,...,j ) is the number of customers in the system M |G|∞ with the intensity λ 2and with an average service time 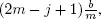 then
then
[1.24] 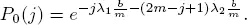
So we have a queueing system with m unreliable servers. All servers break when a pedestrian of the first (second) type appears on lane 1 (the 2 m th).This means that the available time 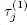 of the j th server is exponentially distributed with the parameter Let
of the j th server is exponentially distributed with the parameter Let 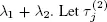 be a block time of the j th server and
be a block time of the j th server and 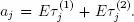 Then
Then 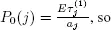
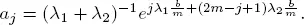
Assuming that 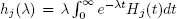 and using the results of section 1.6, we can find the traffic rate ρ 2for model 2.
and using the results of section 1.6, we can find the traffic rate ρ 2for model 2.
[1.25] 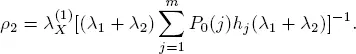
If 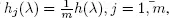 then [1.25]can be written as
then [1.25]can be written as
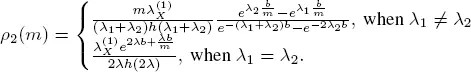
When m = 1, we get
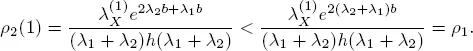
It is easy to show that for all m ≥ 1, the inequality ρ 2( m ) < ρ 1holds. Weakening the rules of crossing the crosswalk increases the capacity of the route. To estimate this effect, we consider the ratio
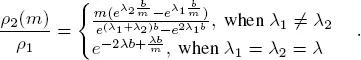
Putting 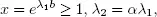 we have
we have
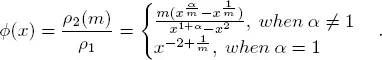
After drawing the graphs for  for α = 0.5; 1.5; 2 (see Figure 1.2), we can see that the effect of the weakened rule (model 2) in comparison with the standard rule (model 1) is stronger, as the number of the lanes increases and the intensity of the number of pedestrians increases.
for α = 0.5; 1.5; 2 (see Figure 1.2), we can see that the effect of the weakened rule (model 2) in comparison with the standard rule (model 1) is stronger, as the number of the lanes increases and the intensity of the number of pedestrians increases.
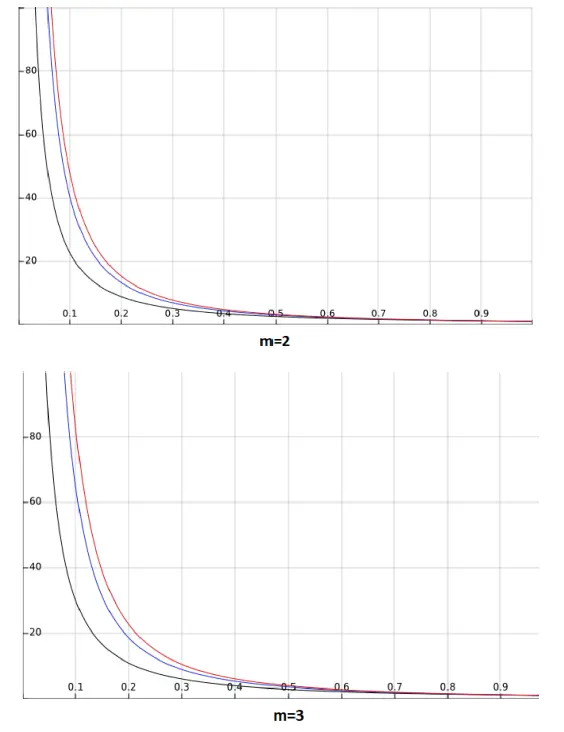
Figure 1.2. Plots for α = 0.5, 1.5, 2
Currently there is no algorithm that estimates the number of cars before the crosswalk in model 2, however we can obtain asymptotic expressions for the average number of expected cars when ρ 2↑ 1. It turns out that 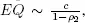 , where c is a constant.
, where c is a constant.
If the length of the queue of cars is unacceptably high, it is necessary to make organizational decisions. One of these decisions is to install a traffic light. Then, in relation to the cars, we again get a one-channel service system with an unreliable server, but now the server will not work if the red light is on (for cars) and will work if the green light is on. This model has been studied in papers (Afanasyeva and Bulinskaya 2013, 2010), in which the algorithms for estimating the queue length were proposed and the number of the asymptotic results were received. It can happen that, with the available traffic intensities of the cars and the pedestrians, the installation of a traffic light, even at the optimum interrelationship between switching intervals, does not provide an acceptable level of queues of pedestrians and cars. This may be used as the basis for the construction of an underground (or overground) pedestrian crossing, its elimination or transfer to another location.
In this chapter, we considered the stability problem for multiserver queues with a regenerative input flow. Let us note that stability analysis is an essential and challenging stage of the investigation of stochastic models. However, stability conditions may be of independent interest. In particular, the stability criterion of the multiserver model can be used for the capacity planning of a model and estimation of the upper bound of potential energy saving. The main contribution of our research is an extension of the stability criterion to the model with a regenerative input flow. The method we use has the following steps. First, we define an auxiliary process Y that is the number of customers that are served up to time t at the auxiliary system S0 in which there are always customers for service. Second, assuming that this process is a regenerative flow not depending on the input flow X under some additional conditions, we construct the common points of regeneration of Y and X . We call this step synchronization of the processes. This approach allows us to use results from the renewal theory for the stability analysis of the systems satisfying additional conditions. These conditions may seem too restrictive to be useful for the analysis of the real models. Therefore, we apply our approach to the stability analysis of two classical systems with service interruptions ( sections 1.6and 1.7) of the queueing system with preemptive priority discipline ( section 1.8) and of the system with simultaneous service of a customer by a random number of servers ( section 1.9). It follows from our results that the structure of the input flow does not affect the stability condition. We only need to know the intensity of this flow to estimate the traffic rate. But for the preemptive repeat different service discipline, the distribution of the service time plays an essential role, since the traffic rate is expressed with the help of the renewal function corresponding to this distribution. We obtain the upper bound for the traffic rate providing the sufficient stability condition. Note that this condition is the same as the condition obtained in Morozov et al . (2011) for a more simple model. Finally, in section 1.9we give applications of our results for the estimation of the capacity of the automobile road, intersected by a crosswalk.
Читать дальше

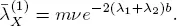
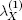 is less than, but close to
is less than, but close to 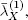 large queues accumulate before the crosswalk.
large queues accumulate before the crosswalk.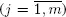 if there are no pedestrians of the first type (going from A to B) on the lanes 1, 2, . . . , j , and there are no pedestrians of the second type on the lanes j, j + 1, ..., 2 m . Denote P 0( j ) as the probability of this event in a steady-state.
if there are no pedestrians of the first type (going from A to B) on the lanes 1, 2, . . . , j , and there are no pedestrians of the second type on the lanes j, j + 1, ..., 2 m . Denote P 0( j ) as the probability of this event in a steady-state.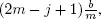 then
then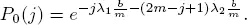
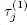 of the j th server is exponentially distributed with the parameter Let
of the j th server is exponentially distributed with the parameter Let 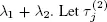 be a block time of the j th server and
be a block time of the j th server and 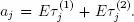 Then
Then 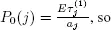
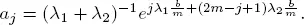
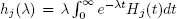 and using the results of section 1.6, we can find the traffic rate ρ 2for model 2.
and using the results of section 1.6, we can find the traffic rate ρ 2for model 2.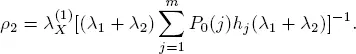
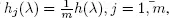 then [1.25]can be written as
then [1.25]can be written as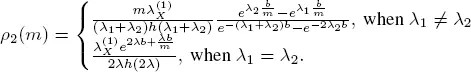
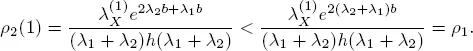
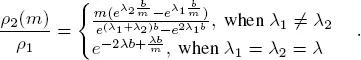
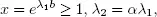 we have
we have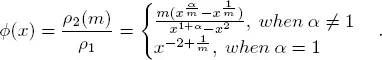
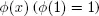 for α = 0.5; 1.5; 2 (see Figure 1.2), we can see that the effect of the weakened rule (model 2) in comparison with the standard rule (model 1) is stronger, as the number of the lanes increases and the intensity of the number of pedestrians increases.
for α = 0.5; 1.5; 2 (see Figure 1.2), we can see that the effect of the weakened rule (model 2) in comparison with the standard rule (model 1) is stronger, as the number of the lanes increases and the intensity of the number of pedestrians increases.
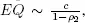 , where c is a constant.
, where c is a constant.










