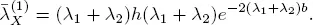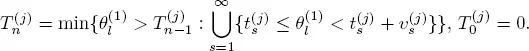
Let
[1.20] 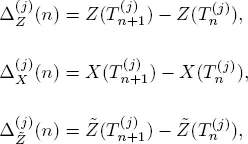
where 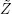 is the process Z for the system S that is the number of service completions by all m servers up to time t . Now we formulate the main result of this section.
is the process Z for the system S that is the number of service completions by all m servers up to time t . Now we formulate the main result of this section.
COROLLARY 1.4.– For the system S , the process Q is a stable process if and only if ρ < 1.
PROOF.– Consider the case ρ ≥ 1 and take m instead of j in [1.20]. It is evident that the stochastic inequality
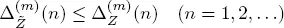
takes place. Therefore condition 1.3 is fulfilled. Based on theorem 1.1, we obtain the convergence
[1.21] 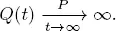
For the case ρ < 1, we take j0 instead of j in [1.20]. Then if convergence [1.21]takes place for any ϵ > 0, there is n ϵsuch that
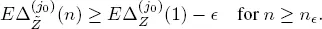
The proof is based on the approach described in Afanasyeva and Tkachenko (2014). Thus, conditions 1.1, 1.4 and 1.5 of theorem 1.2 are fulfilled and Q is a stochastically bounded process when ρ < 1. Since Q is a regenerative process, this means that it is stable.
We see that for the model under consideration, the stability condition does not depend on the structure of the input flow. ■
1.10. Applications to transport systems analysis
The study of traffic flows has a long history (Gideon and Pyke 1999; Grinbeerg 1959; Greenshields 1935; Inose and Hamada 1975; and references therein). Various methods such as cellular automate (Maerivoet and de Moor 2005), statistical mechanics and mathematical physics (Blank 2003; Chowdhury 1999; Fuks and Boccara 2001; Helbing 2001; Schadschneider 2000) or queueing theory (Afanasyeva and Bulinskaya 2009, 2010, 2011, 2013; Afanasyeva and Mihaylova 2015; Afanasyeva and Rudenko 2012; Baycal-Gursoy and Xiao 2004; Baycal-Gursoy et al . 2009; Caceres and Ferrari 2007) were used.
The purpose of the proposed study is an estimation of the carrying capacity of the automobile road, intersected by a crosswalk. Under the capacity, we mean the upper bound of the intensity of the flow of cars, when the queue of cars does not tend to infinity. This means that the stability condition for the process determining the number of these cars is satisfied, so our analysis will be based on the results obtained in section 1.6.
Let us move to the description of the models.
We consider an automobile road with two directions of traffic and m traffic lanes in each. The flow of cars Xi in the i th direction is a regenerative flow with intensity  The road is intersected by a two-directional pedestrian crossing ( Figure 1.1). We denote that pedestrians following from A to B have the first type, and from B to A have the second type. The flow of pedestrians of the i th type is a Poisson flow with intensity λi ( i = 1, 2). Pedestrians cross the road independently of each other with a random (but constant during the entire time of being at the crosswalk) speed.
The road is intersected by a two-directional pedestrian crossing ( Figure 1.1). We denote that pedestrians following from A to B have the first type, and from B to A have the second type. The flow of pedestrians of the i th type is a Poisson flow with intensity λi ( i = 1, 2). Pedestrians cross the road independently of each other with a random (but constant during the entire time of being at the crosswalk) speed.
First, we assume that there is no traffic light at the crossing and pedestrians have an absolute priority over cars. In this case the number of pedestrians at the crosswalk is the number of customers in the infinite-channel service system of M |G|∞ type.

Figure 1.1. A road intersected by a pedestrian crossing
Let us assume that 2 b is an average time of crossing the road by a pedestrian. Then the probability P 0that there is no pedestrian at the crosswalk in a stationary regime is defined by the expression
[1.22] 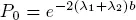
Saaty (1961).
First assume that a car can cross a pedestrian crossing only if there are no pedestrians on it. Let us assume that the cars in the lanes 1, 2, ..., m are going in one direction and the cars in the lanes m + 1,..., 2 m – in another. We consider the process Q 1( t ) – the number of cars in the lanes 1,2,..., m at time t (the consideration of lanes m + 1,m + 2,..., 2 m is analogous).
Denote Hj ( t ) the mathematical expectation of the number of cars that pass through the crosswalk at the lane j during time t under the condition that there are always cars at this lane and the crosswalk is free. Also denote 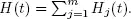 In relation to the process Q 1( t ), we have a single-channel service system with an unreliable server. The operating time u 1has an exponential distribution with the parameter λ 1+ λ 2, and the unavailable time u 2is the period of the system M |G|∞ being busy.
In relation to the process Q 1( t ), we have a single-channel service system with an unreliable server. The operating time u 1has an exponential distribution with the parameter λ 1+ λ 2, and the unavailable time u 2is the period of the system M |G|∞ being busy.
Since
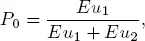
then
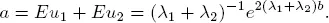
It is not difficult to show that under the assumptions made, the results of section 1.6are correct and the traffic rate ρ 1is determined by the expression
[1.23] 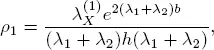
where 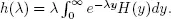
The necessary and sufficient condition for the stability of the process Q 1is the fulfillment of the inequality ρ 1< 1, and the capacity 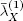 is defined as
is defined as
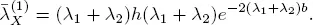
If, for example H ( t ) = mνt , which corresponds to the assumption that each car crosses the pedestrian crossing during an exponentially distributed time with a parameter ν , then
Читать дальше

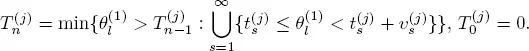
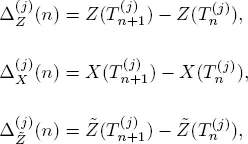
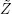 is the process Z for the system S that is the number of service completions by all m servers up to time t . Now we formulate the main result of this section.
is the process Z for the system S that is the number of service completions by all m servers up to time t . Now we formulate the main result of this section.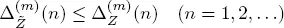
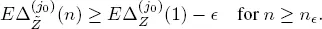
 The road is intersected by a two-directional pedestrian crossing ( Figure 1.1). We denote that pedestrians following from A to B have the first type, and from B to A have the second type. The flow of pedestrians of the i th type is a Poisson flow with intensity λi ( i = 1, 2). Pedestrians cross the road independently of each other with a random (but constant during the entire time of being at the crosswalk) speed.
The road is intersected by a two-directional pedestrian crossing ( Figure 1.1). We denote that pedestrians following from A to B have the first type, and from B to A have the second type. The flow of pedestrians of the i th type is a Poisson flow with intensity λi ( i = 1, 2). Pedestrians cross the road independently of each other with a random (but constant during the entire time of being at the crosswalk) speed.
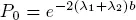
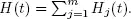 In relation to the process Q 1( t ), we have a single-channel service system with an unreliable server. The operating time u 1has an exponential distribution with the parameter λ 1+ λ 2, and the unavailable time u 2is the period of the system M |G|∞ being busy.
In relation to the process Q 1( t ), we have a single-channel service system with an unreliable server. The operating time u 1has an exponential distribution with the parameter λ 1+ λ 2, and the unavailable time u 2is the period of the system M |G|∞ being busy.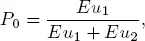
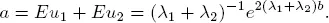
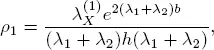
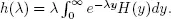
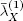 is defined as
is defined as