1 ...7 8 9 11 12 13 ...16 The proof of [1.13]is based on the “so-called” probability space method (Belorusov 2012).
Let us note that condition 1.4 may be provided in various ways. For instance, assume that blocked (or available) period has an exponential phase and
[1.14] 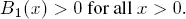
Then Q is a regenerative process with points of regeneration 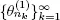 that is a subsequence of the sequence
that is a subsequence of the sequence 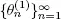 such that
such that 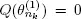 and all servers are in the exponential phase of their blocked (or available) periods. Now condition 1.4 follows directly from theorem 1 in Afanasyeva and Tkachenko (2014). We also note that in this case Q is a stable process if ρ < 1. If only assumption [1.14]takes place with the help of the majorising system Sδ , we obtain the stochastic boundedness Q when ρ < 1. ■
and all servers are in the exponential phase of their blocked (or available) periods. Now condition 1.4 follows directly from theorem 1 in Afanasyeva and Tkachenko (2014). We also note that in this case Q is a stable process if ρ < 1. If only assumption [1.14]takes place with the help of the majorising system Sδ , we obtain the stochastic boundedness Q when ρ < 1. ■
1.7. Discrete-time queueing system with interruptions and preemptive repeat different service discipline
Here, we consider the system with interruptions described in the previous section for the discrete-time case. The moments of breakdowns 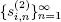 and moments of restorations
and moments of restorations 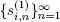 for the i th server satisfy [1.12]. The input flow X is an aperiodic discrete-time regenerative flow with rate λX .
for the i th server satisfy [1.12]. The input flow X is an aperiodic discrete-time regenerative flow with rate λX .
We consider the preemptive repeat different service discipline that means that the service is repeated from the start after restoration of the server and the new service time is independent of the original service time (Gaver 1962).
To define the process Yi for the i th server in the auxiliary system S 0, we introduce the collection 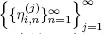 of independent sequences
of independent sequences 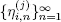 consisting of iid random variables with distribution function Bi . Of course, we assume that
consisting of iid random variables with distribution function Bi . Of course, we assume that 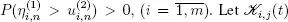 Let
Let 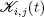 be the counting process associated with the sequence
be the counting process associated with the sequence 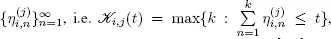
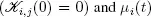 be the number of cycles for the i th server during [0 ,t ], i.e.
be the number of cycles for the i th server during [0 ,t ], i.e. 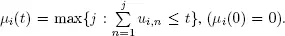 Then the process Yi is defined by the relation
Then the process Yi is defined by the relation
[1.15] 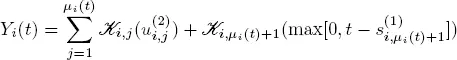
and 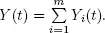 We denote by Hi ( t ) the renewal function for
We denote by Hi ( t ) the renewal function for 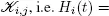
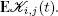
LEMMA 1.2.– There exists the limit
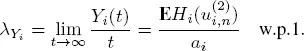
The proof easily follows from the evident inequalities
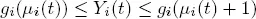
where 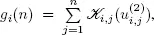 the strong law of large numbers and convergence
the strong law of large numbers and convergence 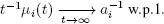
From lemma 1.2, we have
[1.16] 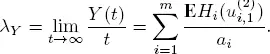
We introduce the counting processes
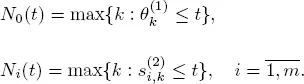
CONDITION 1.8.– The counting processes 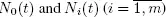 are aperiodic.
are aperiodic.
Then Y is a regenerative aperiodic flow with points of regeneration
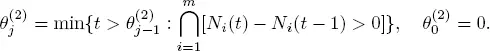
In other words, 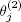 is a point of regeneration of Y if all the servers get out of the order simultaneously at this moment. Taking into account condition 1.8, we conclude from lemma 1.1 that
is a point of regeneration of Y if all the servers get out of the order simultaneously at this moment. Taking into account condition 1.8, we conclude from lemma 1.1 that 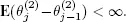 Now we construct the sequence
Now we construct the sequence 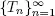 of common points of regeneration for processes X and Y with the help of [1.3]. Because of lemma 1.1
of common points of regeneration for processes X and Y with the help of [1.3]. Because of lemma 1.1 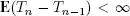 and the traffic rate ρ of the system is defined by [1.7].
and the traffic rate ρ of the system is defined by [1.7].
COROLLARY 1.2.– Let condition 1.8 be fulfilled. Then
1 i)
2 ii) Q(t) is a stochastically bounded process if ρ < 1.
PROOF.– The first statement follows from theorem 1.1 since conditions 1.2 and 1.3 are realized.
Let ρ < 1. For the system S , we introduce the embedded process  where Qn is the number of customers in the system on time Tn and ζi(n) = 1 if there is a customer on the i th server and ζi ( n ) = 0 otherwise. In a view of the service discipline after service restoration and properties of the synchronization epochs
where Qn is the number of customers in the system on time Tn and ζi(n) = 1 if there is a customer on the i th server and ζi ( n ) = 0 otherwise. In a view of the service discipline after service restoration and properties of the synchronization epochs 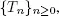 the process
the process 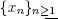 is a Markov chain with countable set of states
is a Markov chain with countable set of states 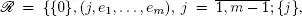 j > m }. Let R 0be the set of unessential states and
j > m }. Let R 0be the set of unessential states and 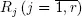 irreducible classes of communicating states. It follows from the condition ρ < 1 that the number of classes r < ∞ .
irreducible classes of communicating states. It follows from the condition ρ < 1 that the number of classes r < ∞ .
Читать дальше

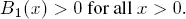
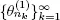 that is a subsequence of the sequence
that is a subsequence of the sequence 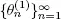 such that
such that 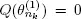 and all servers are in the exponential phase of their blocked (or available) periods. Now condition 1.4 follows directly from theorem 1 in Afanasyeva and Tkachenko (2014). We also note that in this case Q is a stable process if ρ < 1. If only assumption [1.14]takes place with the help of the majorising system Sδ , we obtain the stochastic boundedness Q when ρ < 1. ■
and all servers are in the exponential phase of their blocked (or available) periods. Now condition 1.4 follows directly from theorem 1 in Afanasyeva and Tkachenko (2014). We also note that in this case Q is a stable process if ρ < 1. If only assumption [1.14]takes place with the help of the majorising system Sδ , we obtain the stochastic boundedness Q when ρ < 1. ■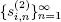 and moments of restorations
and moments of restorations 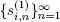 for the i th server satisfy [1.12]. The input flow X is an aperiodic discrete-time regenerative flow with rate λX .
for the i th server satisfy [1.12]. The input flow X is an aperiodic discrete-time regenerative flow with rate λX .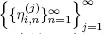 of independent sequences
of independent sequences 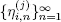 consisting of iid random variables with distribution function Bi . Of course, we assume that
consisting of iid random variables with distribution function Bi . Of course, we assume that 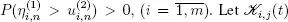 Let
Let 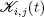 be the counting process associated with the sequence
be the counting process associated with the sequence 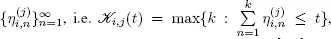
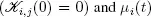 be the number of cycles for the i th server during [0 ,t ], i.e.
be the number of cycles for the i th server during [0 ,t ], i.e. 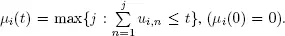 Then the process Yi is defined by the relation
Then the process Yi is defined by the relation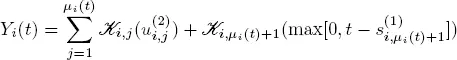
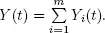 We denote by Hi ( t ) the renewal function for
We denote by Hi ( t ) the renewal function for 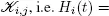
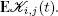
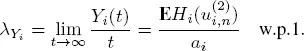
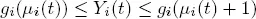
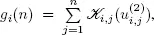 the strong law of large numbers and convergence
the strong law of large numbers and convergence 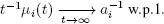
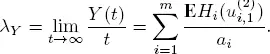
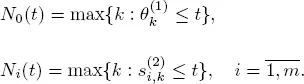
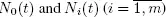 are aperiodic.
are aperiodic.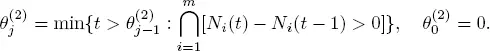
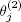 is a point of regeneration of Y if all the servers get out of the order simultaneously at this moment. Taking into account condition 1.8, we conclude from lemma 1.1 that
is a point of regeneration of Y if all the servers get out of the order simultaneously at this moment. Taking into account condition 1.8, we conclude from lemma 1.1 that 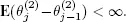 Now we construct the sequence
Now we construct the sequence 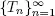 of common points of regeneration for processes X and Y with the help of [1.3]. Because of lemma 1.1
of common points of regeneration for processes X and Y with the help of [1.3]. Because of lemma 1.1 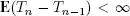 and the traffic rate ρ of the system is defined by [1.7].
and the traffic rate ρ of the system is defined by [1.7]. where Qn is the number of customers in the system on time Tn and ζi(n) = 1 if there is a customer on the i th server and ζi ( n ) = 0 otherwise. In a view of the service discipline after service restoration and properties of the synchronization epochs
where Qn is the number of customers in the system on time Tn and ζi(n) = 1 if there is a customer on the i th server and ζi ( n ) = 0 otherwise. In a view of the service discipline after service restoration and properties of the synchronization epochs 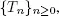 the process
the process 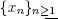 is a Markov chain with countable set of states
is a Markov chain with countable set of states 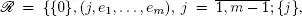 j > m }. Let R 0be the set of unessential states and
j > m }. Let R 0be the set of unessential states and 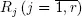 irreducible classes of communicating states. It follows from the condition ρ < 1 that the number of classes r < ∞ .
irreducible classes of communicating states. It follows from the condition ρ < 1 that the number of classes r < ∞ .










