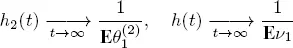
Because of X and Y independence
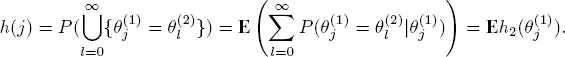
Since 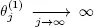 w.p.1, then
w.p.1, then 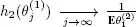 w.p.1. Therefore, from Lebesgue s dominated convergence theorem, we obtain
w.p.1. Therefore, from Lebesgue s dominated convergence theorem, we obtain 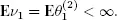 ■
■
Later we consider both cases (discrete-time and continuous-time) together. We only have to take condition 1.2 instead of condition 1.1.
Let
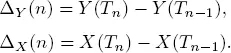
Then
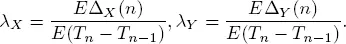
We define the traffic rate as follows:
[1.7] 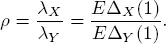
We think of λX and λγ as the arrival and service rate, respectively. Intuitively, it is clear that the number of customers in the system S is a stochastically bounded process if ρ < 1 and it is not the case if ρ ≥ 1. The main stability result of this chapter consists of the formal proof of this fact.
We define the stochastic flow 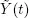 as the number of customers served at the system S during time interval [0, t ).
as the number of customers served at the system S during time interval [0, t ).
CONDITION 1.3.– The following stochastic inequalities take place:
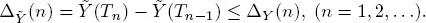
Let Q ( t ) be the number of customers in the system S including the customers on the servers at time t so that
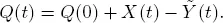
CONDITION 1.4.– There are two possible cases:
1 i) Q(t) is a stochastically bounded process, i.e.
2 ii)
CONDITION 1.5.– If 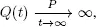 , then for any ϵ > 0 there exists nϵ such that for n > n ϵ
, then for any ϵ > 0 there exists nϵ such that for n > n ϵ
[1.8] 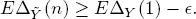
1.4. Instability result for the case ρ ≥ 1
THEOREM 1.1.– Let conditions 1.3 and 1.1 (1.2) for the continuous-time (for the discrete-time) case be fulfilled. If ρ ≥ 1, then
[1.9] 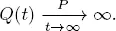
PROOF.– Consider the embedded process Qn = Q(Tn) and denote 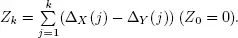
Define the auxiliary sequence 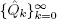 recursion
recursion
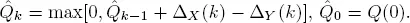
Because of the equality 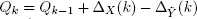 and condition 1.3 we get the stochastic inequality
and condition 1.3 we get the stochastic inequality 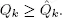 It is well known (Feller 1971) that
It is well known (Feller 1971) that
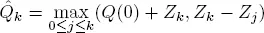
and in distribution
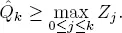
For ρ ≥ 1, the sequence 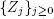 is a random walk with a non-negative drift. Hence, except when
is a random walk with a non-negative drift. Hence, except when  ( c is a constant),
( c is a constant), 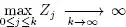 (w.p.1) (Feller 1971) that completes the proof. ■
(w.p.1) (Feller 1971) that completes the proof. ■
1.5. Stochastic boundedness for the case ρ < 1
Our objective here is to establish stochastic boundedness of the process Q when the traffic rate ρ < 1. Under some additional assumptions providing the regenerative structure of the process Q , this property has its stability as a consequence.
THEOREM 1.2.– Let conditions 1.4and 1.5 and condition 1.1 (1.2) for the continuoustime (for the discrete-time) case be fulfilled. If ρ < 1, then Q is a stochastically bounded process.
PROOF.– Because of condition 1.4 there are two possible cases: Qn = Q ( Tn ) is either stochastically bounded or 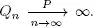 Assume that the second case takes place and ρ < 1. Because of condition 1.5 for
Assume that the second case takes place and ρ < 1. Because of condition 1.5 for 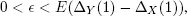 there is nϵ such that for n > nϵ
there is nϵ such that for n > nϵ
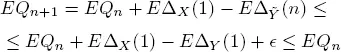
that contradicts our assumption that 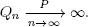 ■
■
In the next sections, we discuss some examples to verify our results and to compare them with previous works. First, we consider two queueing models with service interruptions. These models occur in numerous applications and there is extensive literature concerning queueing system with interruptions. Let us mention some papers in which detail description of the literature in this sphere is given (Krishnamoorthy et al . 2012; Fiems and Bruneel 2013; Pechinkin et al . 2009; Morozov et al . 2011). However, to the best of our knowledge there are no papers that study the stability problem for multichannel systems with heterogeneous servers for the non-Markovian case: with general input flow and general distribution of blocked and available periods.
Читать дальше

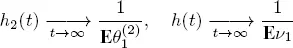
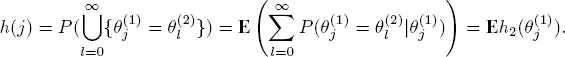
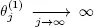 w.p.1, then
w.p.1, then 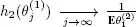 w.p.1. Therefore, from Lebesgue s dominated convergence theorem, we obtain
w.p.1. Therefore, from Lebesgue s dominated convergence theorem, we obtain 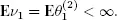 ■
■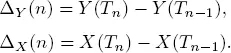
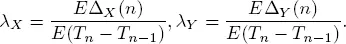
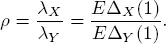
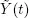 as the number of customers served at the system S during time interval [0, t ).
as the number of customers served at the system S during time interval [0, t ).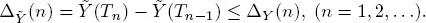
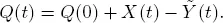
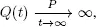 , then for any ϵ > 0 there exists nϵ such that for n > n ϵ
, then for any ϵ > 0 there exists nϵ such that for n > n ϵ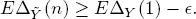
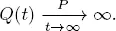
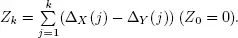
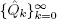 recursion
recursion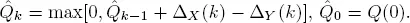
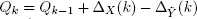 and condition 1.3 we get the stochastic inequality
and condition 1.3 we get the stochastic inequality 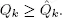 It is well known (Feller 1971) that
It is well known (Feller 1971) that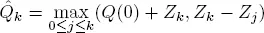
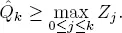
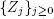 is a random walk with a non-negative drift. Hence, except when
is a random walk with a non-negative drift. Hence, except when  ( c is a constant),
( c is a constant), 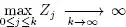 (w.p.1) (Feller 1971) that completes the proof. ■
(w.p.1) (Feller 1971) that completes the proof. ■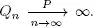 Assume that the second case takes place and ρ < 1. Because of condition 1.5 for
Assume that the second case takes place and ρ < 1. Because of condition 1.5 for 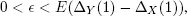 there is nϵ such that for n > nϵ
there is nϵ such that for n > nϵ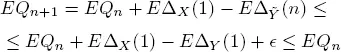
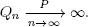 ■
■










