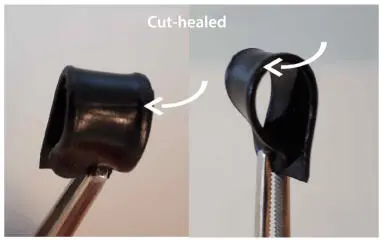
Figure 2.7The images of cured Poly(Si-Bz)/FeCl 3film after healing. Arrow indicates the contact edges.
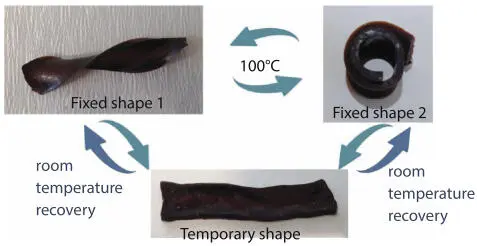
Figure 2.8Images of shape recovery behavior of cured Poly(Si-Bz)/FeCl 3film.
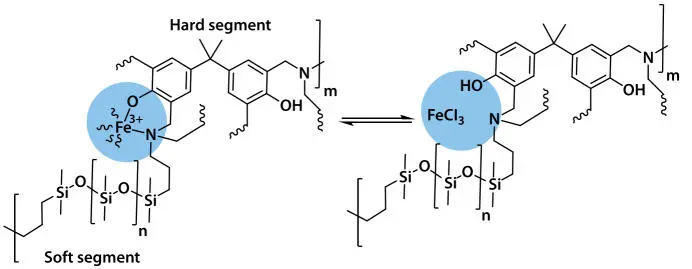
Scheme 2.13 Metal–ligand bond breakage and reforming at certain temperature changes.
In this chapter, self-healing and shape memory systems based on benzoxazines are reviewed. The results demonstrate that it is possible design various different smart materials by using benzoxazines. In general, polybenzoxazines with soft segments such as poly(propylene oxide)s (Jeffamines) can be exhibit self-healing ability with different levels of success. The healing mechanisms can be autonomous or stimuli induced types depending on the design of polybenzoxazines. Especially, in terms of autonomous healing systems, the hydrogen bonds of polybenzoxazines can be exploited. However, from the practical point of view, the hydrogen bonding in polybenzoxazines must augmented for successful results by additives or designing special benzoxazines. Moreover, by mixing benzoxazine resins with suitable polymers shape memory polymers can be obtained easily after a simple curing process. Soft polymers such as polysiloxanes, epoxies, poly(-caprolactone)s were proven to be useful for this purpose. These polymers act as “switch” and polybenzoxazine as hard segments provide the “fix points” in SMPs. As stated in the introduction, the design flexibility of benzoxazine chemistry is vast and just by switching between phenols and primary amines, many different benzoxazines with designed properties can be synthesized. Actually, the potential of benzoxazine chemistry in designing smart materials has not been recognized widely. However, the pioneering studies in this line clearly reveal that there will be intensive studies to develop new smart materials by using benzoxazine resins. Particularly, different healing strategies or SMPs based on benzoxazine resins would be one of the major interest in both academia and industry.
1. Pilato, L., Phenolic resins: A century of progress , Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010.
2. Iredale, R.J., Ward, C., Hamerton, I., Modern advances in bismaleimide resin technology: A 21st century perspective on the chemistry of addition polyimides. Prog. Polym. Sci. , 69, 1, 2017.
3. Nair, C.P.R., Advances in addition-cure phenolic resins. Prog. Polym. Sci. , 29, 401, 2004.
4. Kiskan, B. and Yagci, Y., The journey of phenolics from the first spark to advanced materials. Isr. J. Chem. , 2019, In Press 2020, 60, 20-32. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ijch.201900086.
5. Forsdyke, K.L. and Starr, T.F., Thermoset resins , Rapra Technology Limited, Shawbury, UK, 2002.
6. Ghosh, N., Kiskan, B., Yagci, Y., Polybenzoxazines—New high performance thermosetting resins: Synthesis and properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. , 32, 1344, 2007.
7. Kiskan, B., Ghosh, N., Yagci, Y., Polybenzoxazine-based composites as high-performance materials. Polym. Int. , 60, 167, 2011.
8. Kim, H.J., Brunovska, Z., Ishida, H., Synthesis and thermal characterization of polybenzoxazines based on acetylene-functional monomers. Polymer , 40, 6565, 1999.
9. Lin, C.H., Chang, S.L., Shen, T.Y., Shih, Y.S., Lin, H.T., Wang, C.F., Flexible polybenzoxazine thermosets with high glass transition temperatures and low surface free energies. Polym. Chem. , 3, 935, 2012.
10. Xu, R.J., Schreiber, H.P., Huang, M., Ishida, H., Polybenzoxazine resins: Aspects of interaction and adsorption behavior. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. , 37, 1441, 1999.
11. Ishida, H. and Allen, D.J., Physical and mechanical characterization of nearzero shrinkage polybenzoxazines. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. , 34, 1019, 1996.
12. Ishida, H. and Lee, Y.H., Synergism observed in polybenzoxazine and poly(epsilon-caprolactone) blends by dynamic mechanical and thermogravimetric analysis. Polymer , 42, 6971, 2001.
13. Cid, J.A., Wang, Y.X., Ishida, H., Cationic polymerization of benzoxazine monomers by boron trifluoride complex. Polym. Polym. Compos. , 7, 409, 1999.
14. Zhang, K., Tan, X., Wang, Y., Ishida, H., Unique self-catalyzed cationic ring-opening polymerization of a high performance deoxybenzoin-based 1,3-benzoxazine monomer. Polymer , 168, 8, 2019.
15. Dunkers, J. and Ishida, H., Reaction of benzoxazine-based phenolic resins with strong and weak carboxylic acids and phenols as catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. , 37, 1913, 1999.
16. Andreu, R., Reina, J.A., Ronda, J.C., Carboxylic acid-containing benzoxazines as efficient catalysts in the thermal polymerization of benzoxazines. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. , 46, 6091, 2008.
17. Hamerton, I., McNamara, L.T., Howlin, B.J., Smith, P.A., Cross, P., Ward, S., Examining the initiation of the polymerization mechanism and network development in aromatic polybenzoxazines. Macromolecules , 46, 5117, 2013.
18. Ishida, H. and Rodriguez, Y., Curing kinetics of a new benzoxazine-based phenolic resin by differential scanning calorimetry. Polymer , 36, 3151, 1995.
19. Su, Y.C., Yei, D.R., Chang, F.C., The kinetics of b-a and p-a type copolybenzoxazine via the ring opening process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. , 95, 730, 2005.
20. Liu, C., Shen, D., Sebastián, R.M.a., Marquet, J., Schönfeld, R., Mechanistic studies on ring-opening polymerization of benzoxazines: A mechanistically based catalyst design. Macromolecules , 44, 4616, 2011.
21. Liu, C., Shen, D., Sebastián, R.M., Marquet, J., Schönfeld, R., Catalyst effects on the ring-opening polymerization of 1,3-benzoxazine and on the polymer structure. Polymer (United Kingdom) , 54, 2873, 2013.
22. Imran, M., Kiskan, B., Yagci, Y., Concise synthesis and characterization of unsymmetric 1, 3-benzoxazines by tandem reactions. Tetrahedron Lett. , 54, 4966, 2013.
23. Kaya, G., Kiskan, B., Yagci, Y., Phenolic naphthoxazines as curing promoters for benzoxazines. Macromolecules , 51, 1688, 2018.
24. Kaya, G., Kiskan, B., Yagci, Y., Coumarines as masked phenols for amide functional benzoxazines. Polym. Chem. , 10, 1268, 2019.
25. Andreu, R., Espinosa, M.A., Galia, M., Cadiz, V., Ronda, J.C., Reina, J.A., Synthesis of novel benzoxazines containing glycidyl groups: A study of the crosslinking behavior. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. , 44, 1529, 2006.
26. Zuniga, C., Larrechi, M.S., Lligadas, G., Ronda, J.C., Galia, M., Cadiz, V., Polybenzoxazines from renewable diphenolic acid. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. , 49, 1219, 2011.
27. Oie, H., Sudo, A., Endo, T., Acceleration effect of n-allyl group on thermally induced ring-opening polymerization of 1,3-benzoxazine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. , 48, 5357, 2010.
28. Agag, T. and Takeichi, T., Synthesis and characterization of novel benzoxazine monomers containing allyl groups and their high performance thermosets. Macromolecules , 36, 6010, 2003.
Читать дальше















