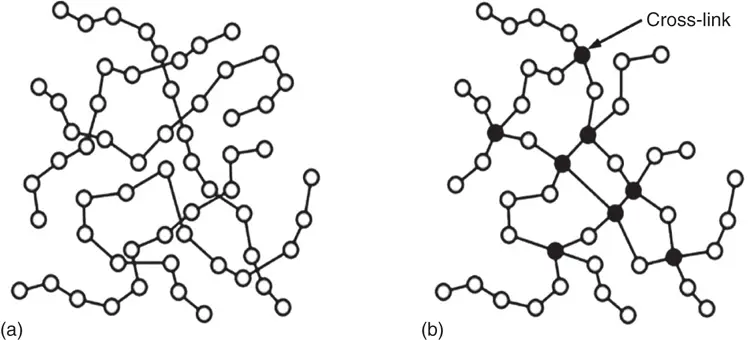
Figure 1.1 Descriptive molecular structure of both (a) thermoplastic and (b) thermoset polymers.
Source: Bergstrom [7]. © 2015, Elsevier
Figure 1.1a,bdepicts the molecular structure of thermoplastic and thermosetting resins, respectively. The cross‐links in the molecular structure of the thermosetting resins (shaded molecules) are depicted in Figure 1.1b.
There are different categories that exist for the manufacturing process of polymer matrix composites (PMCs). These include squeeze flow methods, short‐fiber suspension methods, and porous media methods [4]. Table 1.3depicts some partial and complete natural and synthetic hybrid FRP composites, their resins/matrices, and manufacturing methods.
It is well known that there is no single engineering material that can be all‐encompassing in terms of its applicability to operations and processes. Therefore, natural FRP composites have some limitations, despite their outstanding benefits. Table 1.4presents some of the benefits as well as disadvantages of natural FRP composites.
The key elements that affect the mechanical response of natural FRP hybrid composites are subsequently identified [5]:
Fiber selection, which includes the type, method of extraction, time of harvest, natural fiber aspect ratio, content, as well as its treatment
Interfacial strength
Matrix choice
Fiber distribution
Composite manufacturing process
Fiber arrangement [9]
Void presence/porosity, among others.
Table 1.3 Manufacturing processes of some hybrid (mainly natural) FRP composites.
Source: Sathishkumar et al. [8]. © 2014, SAGE Publications.
| Hybrid fiber |
Resin |
Curing agent Catalyst |
Accelerator |
Manufacturing methods |
| Pineapple/sisal/glass |
Polyester |
MEKP |
Cobalt napthenate |
Hydraulic press |
| Sisal/silk |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up technique |
| Kenaf/glass |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up and cold press |
| Woven jute/glass |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up |
| Banana/Kenaf |
Polyester |
|
|
Hydraulic compression molding process |
| Banana/sisal |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up method followed by compression molding |
| Glass/palmyra |
Polyester |
|
|
Hydraulic compression molding process |
| Jute/glass |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up |
| Roselle/sisal |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay/up technique |
| Silk/sisal |
Polyester |
|
|
Hand lay‐up technique |
| Banana/sisal |
Epoxy |
|
|
Hydraulic compression molding process |
| Glass/glass |
Epoxy |
HY95 I hardener |
|
Hand lay‐up technique |
| Carbon/glass |
Epoxy |
HY225 Hardener |
|
Hand lay‐up technique |
| Oil palm/jute |
Epoxy |
Hardener |
|
Compression molding process |
| Chicken feather/glass |
Epoxy |
n ‐ tert ‐Butyl peroxybenzoate |
|
Hot press |
| Basalt/Hemp |
Polypropylene |
|
|
Hot pressing |
| Flax, Hemp, and jute |
Polypropylene |
|
|
Hydraulic press |
| Flax/wood fiber |
HDPE |
|
|
Twin screw extrusion |
| Banana/glass |
Polypropylene |
|
|
Twin screw extrusion |
| Cork/coconut |
HDPE |
|
|
Screw extrusion and compression molding |
| Kenaf/pineapple |
HDPE |
|
|
Mixing and compression molding |
| Bamboo/glass |
Polypropylene |
|
|
Injection molding |
| Cordenka/jute |
Polypropylene |
|
|
Injection molding |
| Bamboo/cellulose |
Poly lactic acid |
|
|
Injection molding |
| OPEFB/glass |
Vinyl ester |
|
|
Resin transfer molding |
| Aramid/sisal |
Phenolic |
|
|
Stirring, drying, compression |
HDPE, high‐density polyethylene; MEKP, methyl ethyl ketone peroxide; and OPEFB, oil palm empty fruit punch.
Table 1.4 Benefits and drawbacks of natural FRP hybrid composites.
Source: Modified from Pickering et al. [5]. © 2014, SAGE Publications.
| Benefits |
Drawbacks |
| Renewable source of fibers/matrices and sustainabilityLow danger/risk during manufacturing processesLow density, stiffness, and high specific strengthLow process/production energy and environmental friendlinessLower production cost when compared with synthetic fibers, such as carbon and glassLow release of harmful fumes when heating and during end of life process (incineration)Lower abrasive attack on processing tools, when compared with synthetic FRP compositesPossibility of predicting better balanced mechanical behaviors, such as toughness |
Lower responses, especially impact strength in comparison with the synthetic FRP compositesHigher variability of behaviors, due to discrepancies in sources and qualitiesLower durability in comparison with synthetic FRP composites. However, it can be enhanced significantly using treatmentsPoor fiber orientation and/or layer stacking sequence, causing weak fiber–matrix interfacial adhesionHigh water/moisture absorption, consequently causes swelling effectLower processing parameters, such as degradability temperatures. Hence, it causes limiting matrix and fiber options and structural applications |
1.3 Hybrid Natural Fiber‐Reinforced Polymeric Biocomposites
Fiber hybridization could offer a further alternative in composites. Hybrid composites are derived by a combination of two or more various fiber types in a common matrix [10]. The fibers can be arranged in different layer pattern/orientations and stacking sequences. Figure 1.2presents some common arrangements (layering patterns) of natural FRP hybrid composites. This introduces wider spread in their properties than in the regular composite materials, which comprises only one kind of reinforcement. It also enables manufacturing engineers to channel the properties of the composite to the required structural properties. This can possibly be achieved once the hybrid composite behavior can be predicted from the constituent composites.
Operationally, producing hybrid natural FRP composites suggests an intermediate intervention to reduce the negative environmental impact of glass and carbon (synthetic) fibers on the environment, by partially replacing the glass and carbon fibers with such alternatives as the vegetable fibers jute, flax, hemp, kenaf, sisal, among others [12, 13]. In these substitutions, the limits are revealed by simulating the service performance in such a dynamic testing, including fatigue and impact [14, 15].
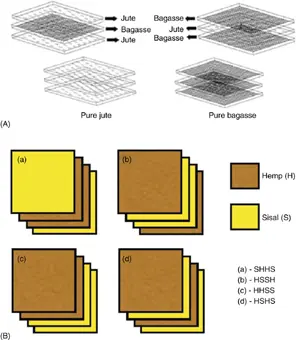
Figure 1.2 Schematic illustration of different orientations and stacking sequences of natural FRP hybrid composites.
Source: Refs. [9, 11]. © 2012; John Wiley and Sons.
Читать дальше














