Myron B. Allen, III - The Mathematics of Fluid Flow Through Porous Media
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Myron B. Allen, III - The Mathematics of Fluid Flow Through Porous Media» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Mathematics of Fluid Flow Through Porous Media
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
The Mathematics of Fluid Flow Through Porous Media: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Mathematics of Fluid Flow Through Porous Media»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
, distinguished professor and mathematician Dr. Myron B. Allen delivers a one-stop and mathematically rigorous source of the foundational principles of porous medium flow modeling. The book shows readers how to design intelligent computation models for groundwater flow, contaminant transport, and petroleum reservoir simulation.
Discussions of the mathematical fundamentals allow readers to prepare to work on computational problems at the frontiers of the field. Introducing several advanced techniques, including the method of characteristics, fundamental solutions, similarity methods, and dimensional analysis,
is an indispensable resource for students who have not previously encountered these concepts and need to master them to conduct computer simulations.
Teaching mastery of a subject that has increasingly become a standard tool for engineers and applied mathematicians, and containing 75 exercises suitable for self-study or as part of a formal course, the book also includes:
A thorough introduction to the mechanics of fluid flow in porous media, including the kinematics of simple continua, single-continuum balance laws, and constitutive relationships An exploration of single-fluid flows in porous media, including Darcy’s Law, non-Darcy flows, the single-phase flow equation, areal flows, and flows with wells Practical discussions of solute transport, including the transport equation, hydrodynamic dispersion, one-dimensional transport, and transport with adsorption A treatment of multiphase flows, including capillarity at the micro- and macroscale Perfect for graduate students in mathematics, civil engineering, petroleum engineering, soil science, and geophysics,
also belongs on the bookshelves of any researcher who wishes to extend their research into areas involving flows in porous media.

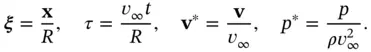
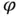 ,
,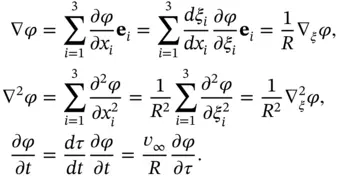
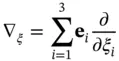
 .
.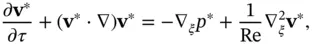
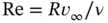 .
.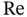 in Eq. (2.16)is the Reynolds number, named after Irish‐born fluid mechanician Osborne Reynolds [128]. This number serves as a unit‐free gauge of the ratio of inertial effects to viscous effects and, heuristically, as an index of mathematical intractability. We associate the regime
in Eq. (2.16)is the Reynolds number, named after Irish‐born fluid mechanician Osborne Reynolds [128]. This number serves as a unit‐free gauge of the ratio of inertial effects to viscous effects and, heuristically, as an index of mathematical intractability. We associate the regime 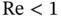 with slow flows in which viscous effects dominate those associated with inertia. When
with slow flows in which viscous effects dominate those associated with inertia. When 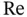 is much smaller than 1, it is common to neglect the inertial terms.
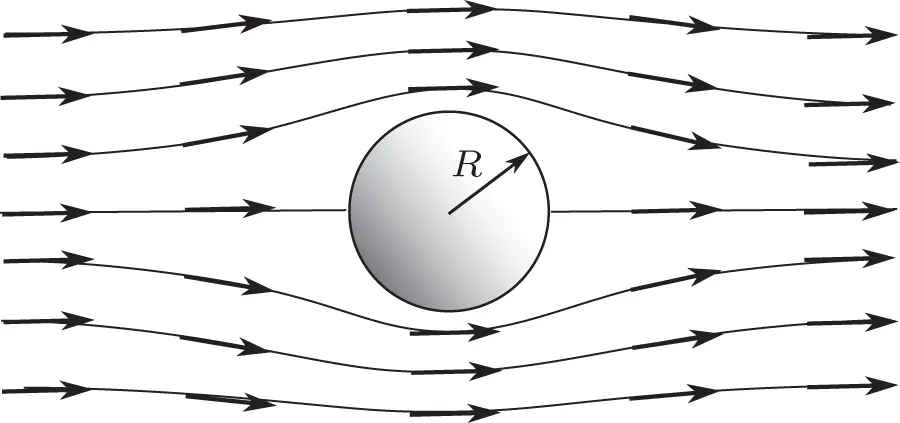
is much smaller than 1, it is common to neglect the inertial terms.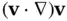 . We now examine two such problems in fluid mechanics that bear on the analysis of flows in porous media. Each serves as a highly simplified model of fluid flow in the interstices of a porous medium, and each involves significant reductions in complexity compared with the full Navier–Stokes equation. The Hagen–Poiseuille problemis a simple model of fluid flows in a straight, cylindrical tube, which one can envision as an idealized pore channel. The Stokes problemmodels slow, viscous flows around a solid sphere, which one can imagine as an idealized solid grain.
. We now examine two such problems in fluid mechanics that bear on the analysis of flows in porous media. Each serves as a highly simplified model of fluid flow in the interstices of a porous medium, and each involves significant reductions in complexity compared with the full Navier–Stokes equation. The Hagen–Poiseuille problemis a simple model of fluid flows in a straight, cylindrical tube, which one can envision as an idealized pore channel. The Stokes problemmodels slow, viscous flows around a solid sphere, which one can imagine as an idealized solid grain. . Let the fluid's density and viscosity be constant. Orient the Cartesian coordinate system so that the
. Let the fluid's density and viscosity be constant. Orient the Cartesian coordinate system so that the 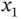 ‐axis coincides with the axis of the tube.
‐axis coincides with the axis of the tube.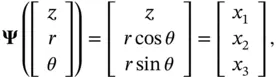
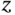 represents position along the axis of the tube,
represents position along the axis of the tube, 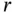 represents distance from the axis, and the angle
represents distance from the axis, and the angle 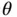 represents the azimuth about the axis. In this coordinate system, the Laplace operator has the form
represents the azimuth about the axis. In this coordinate system, the Laplace operator has the form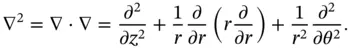
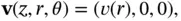
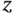 .
. vanishes. Work in Cartesian coordinates .
vanishes. Work in Cartesian coordinates .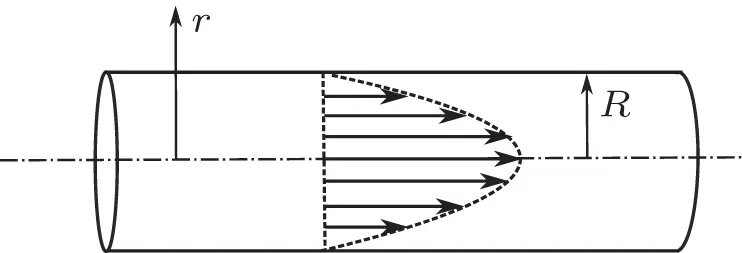
 .
.