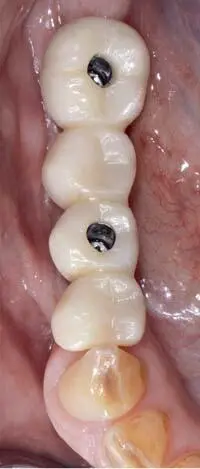
Fig 1-3-9c Try-in of the monolithic zirconium oxide FDP (Lava Plus, 3M, Seefeld, Germany) with super glue, temporarily cemented to the titanium-base abutments (Vario-Base, Straumann).
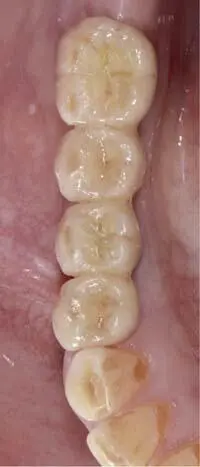
Fig 1-3-9d Final view of the superficial individualization (Ivocolor, Ivoclar Vivadent) of the monolithic zirconium oxide prior to cementation to the titanium-base abutments.
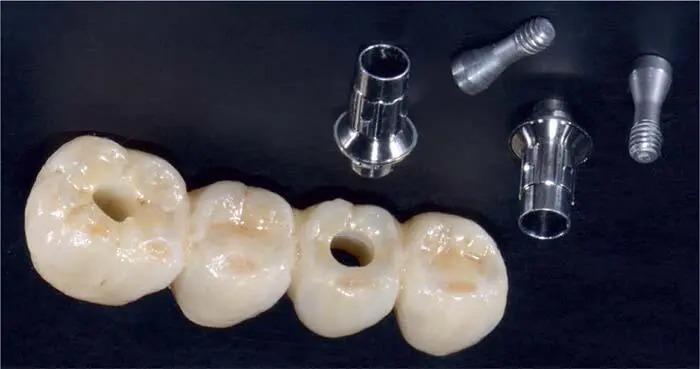
Fig 1-3-9e Final occlusal view of the direct screw-retained, monolithic zirconium oxide FDP on titanium-base abutments (Vario-Base, Straumann).
Options for surface modification
If the reference teeth exhibit pronounced surface microtexture (eg, perikymata), the mimicking may be technically difficult with monolithic ceramics. Reinforced glassceramics and zirconia exhibit high surface hardness and can only be surface-individualized with diamond-coated instruments; the texture may then be smoothened by the application of glaze ceramic. The facial application of softer veneering ceramic is recommended in these situations.
Abrasion/wear properties
The monolithic materials are industrially fabricated and exhibit optimal quality and integrity, with no pores 16 , 17. Yet, their hardness has been questioned and a higher risk for abrasion and wear of the antagonists was assumed for the monolithic restorations (Fig 1-3-10).

Fig 1-3-10a Detailed microscopic image of a conventionally veneered zirconium oxide restoration after a simulated 5 years of aging. The traces of abrasion and the exposure of individual porosities can already be seen very clearly.
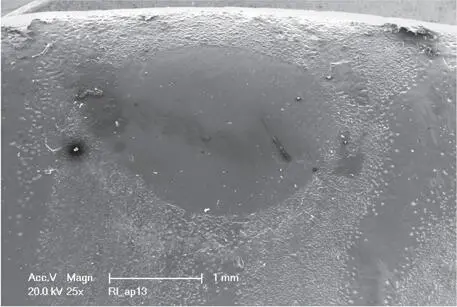
Fig 1-3-10b Detailed microscopic image of a monolithic zirconium oxide restoration after a simulated 5 years of aging.
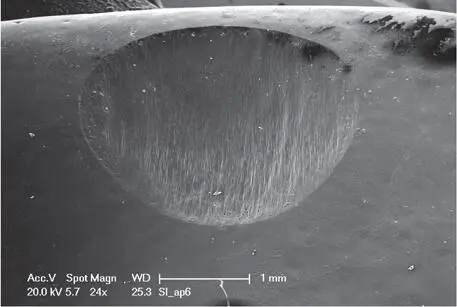
Fig 1-3-10c Detailed microscopic image of a monolithic lithium-disilicate restoration after a simulated 5 years of aging.
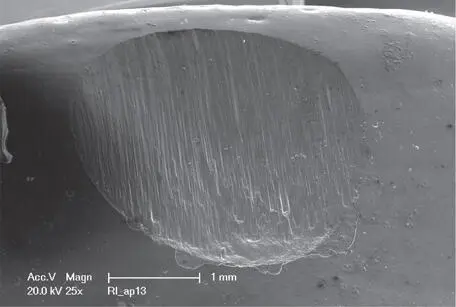
Fig 1-3-10d Detailed microscopic image of a monolithic PICN restoration after a simulated 5 years of aging.
It has been shown, indeed, that these technical processing steps are crucial for the abrasiveness of monolithic restorations. High-gloss polished lithium-disilicate and zirconia lead to very low abrasions with the antagonistic teeth or restorative materials 18 , 19. Yet, intaglio, rough, and stained and glazed monolithic ceramics induce pronounced wear of the antagonists, as studies have shown.
1.3.5 Conclusions
Hence, monolithic restorations should always only be high gloss polished in the occlusal and functional areas, and may be veneered, colored, and/or glazed on the buccal and oral parts.
1.3.6 References
1.Beuer F, Schweiger J, Edelhoff D. Digital dentistry: an overview of recent developments for CAD/CAM generated restorations. Br Dent J 2008;204:505–511.
2.Miyazaki T, Hotta Y, Kunii J, Kuriyama S, Tamaki Y. A review of dental CAD/CAM: current status and future perspectives from 20 years of experience. Dent Mater J 2009;28:44–56.
3.van Noort R. The future of dental devices is digital. Dent Mater 2012;28:3–12.
4.Schenk R. Biogeneric – another step closer to nature. Int J Comput Dent 2010;13:169–174.
5.Rengier F, Mehndiratta A, von Tengg-Kobligk H, et al. 3D printing based on imaging data: review of medical applications. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2010;5:335–341.
6.Cohen A, Laviv A, Berman P, Nashef R, Abu-Tair J. Mandibular reconstruction using stereolithographic 3-dimensional printing modeling technology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009;108:661–666.
7.Fehmer V, Muhlemann S, Hammerle CH, Sailer I. Criteria for the selection of restoration materials. Quintessence Int 2014;45:723–730.
8.Pjetursson BE, Sailer I, Zwahlen M, Hammerle CH. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of all-ceramic and metal-ceramic reconstructions after an observation period of at least 3 years. Part I: single crowns. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18 Suppl 3:73–85.
9.Sailer I, Pjetursson BE, Zwahlen M, Hammerle CH. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of all-ceramic and metal-ceramic reconstructions after an observation period of at least 3 years. Part II: fixed dental prostheses. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18 Suppl 3:86–96.
10.Vichi A, Ferrari M, Davidson CL. Influence of ceramic and cement thickness on the masking of various types of opaque posts. J Prosthet Dent 2000;83:412–417.
11.Kolakarnprasert N, Kaizer MR, Kim DK, Zhang Y. New multi-layered zirconias: composition, microstructure and translucency. Dent Mater 2019;35:797–806.
12.Elsaka SE. Optical and mechanical properties of newly developed monolithic multilayer zirconia. J Prosthodont 2019;28: e279–e284.
13.Kurbad A. Microveneering technique for esthetic enhancement of monolithic zirconia restorations. Int J Comput Dent 2016;19:165–178.
14.Tabatabaian F, Shabani S, Namdari M, Sadeghpour K. Masking ability of a zirconia ceramic on composite resin substrate shades. Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2017;14:389–394.
15.Bacchi A, Boccardi S, Alessandretti R, Pereira GKR. Substrate masking ability of bilayer and monolithic ceramics used for complete crowns and the effect of association with an opaque resin-based luting agent. J Prosthodont Res 2019;63:321–326.
16.Gwon B, Bae EB, Lee JJ, et al. Wear characteristics of dental ceramic CAD/CAM materials opposing various dental composite resins. Materials (Basel) 2019;12.
17.Zhang F, Spies BC, Vleugels J, et al. High-translucent yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics are wear-resistant and antagonist-friendly. Dent Mater 2019;35:1776–1790.
18.Kontonasaki E, Rigos AE, Ilia C, Istantsos T. Monolithic zirconia: an update to current knowledge. Optical properties, wear, and clinical performance. Dent J (Basel) 2019;7: pii: E90.
19.Zarone F, Di Mauro MI, Ausiello P, Ruggiero G, Sorrentino R. Current status on lithium disilicate and zirconia: a narrative review. BMC Oral Health 2019;19:134.
CHAPTER 4
Diagnostics
1.4.1 Introduction
In this chapter:
■ Esthetic parameters to be evaluated: step-by-step checklist
■ Time points for diagnostics, diagnostic tools
■ Conventional procedures
■ Digital procedures
■ Augmented reality in dentistry
■ Diagnostics for fixed implant-supported restorations, surgical stents
Pretreatment diagnostics is essential for predictable treatment outcomes in prosthodontics. Agreeing on the appearance of the final restoration in this early phase of the treatment is key to obtain satisfactory results in comprehensive restorative dentistry 1 – 4.
Читать дальше



















