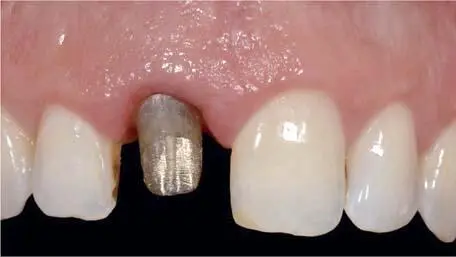
Fig 1-3-5c Extremely discolored abutment tooth with dark gold build-up and strong discoloration of marginal gingiva: maximal need to mask. To be restored with a classic porcelain-fused-to-metal crown to achieve predictable esthetic outcome.
1.3.4 Monolithic and veneered restorations
Lithium-disilicate and zirconia ceramics are available in different shades and levels of translucency today, allowing for a monolithic application of both ceramics in most clinical situations (for more details, see Part I, Chapter 1). Lithium-disilicate is solely indicated for the restoration of single teeth (overlay, crowns) or single implants, while zirconia can be used for the fabrication of tooth- and implant-supported single- and multiple-unit fixed dental prostheses. These indications result out of the differences in mechanical stability of the different ceramics (see Part I, Chapter 1).
Until recently, zirconia was only available as yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals – a non-esthetic, rather opaque whitish framework material which had to be veneered. As presented in Parts III and IV of this book, very high rates of chipping of the veneering ceramic were reported in the scientific literature leading to rising doubts with respect to this restorative material. Due to modifications of the crystalline structure of zirconia (tetragonal –> cubic zirconia) increased translucency of the ceramic was achieved. Furthermore, color modifications improved its esthetic appearance. Therefore, a monolithic or microveneered application of zirconia is possible today. However, as the mechanical stability of the translucent and shaded zirconia types differ significantly between the grades of translucency/shade and, even more, between the manufacturers. This leads to indications and limitations for the clinical application 11. To avoid complications like catastrophic fracture, clinicians and technicians need to be aware of the recommendations by the respective manufacturers.
Five factors need to be considered for the selection between monolithic and veneered restorations:
■ Esthetic factors
■ Position in the dental arch
■ Material-specific limitations
■ Options for surface modification
■ Abrasion/wear properties.
Esthetic factors
The individual characteristics of the remaining dentition used as a reference play an important role for the selection between monolithic and veneered restorations. The more complex the optical properties of the reference teeth, eg, the more internal and superficial structure and staining they have, the more difficult (or even impossible) will be their mimicking with monolithic materials. Multilayer ingots may improve the esthetic appearance to a certain extent 12. With very translucent reference teeth, a buccal cut-back of the monolithic restorative material and microveneering needs to be planned 13.
With discolored teeth, it has to be considered that all ceramic materials including zirconia may be unable to mask strong discolorations 14, if not certain thicknesses of the ceramic can be provided. Monolithic ceramics are, hence, mostly indicated for non-discolored or slightly discolored situations 15.
With very discolored abutment teeth, either a more invasive preparation needs to be provided, or a masking of the discoloration with opaque composite materials needs to be performed. This, however, implies a more invasive reduction of the tooth substance to gain space. Alternatively, metal-ceramic restorations may be preferred.
Position in the dental arch
The second factor to be evaluated is the position of the restoration in the dental arch. In posterior regions, highly esthetic results can be achieved with monolithic materials, even more with aid of multilayer ingots. In the posterior area, the application of veneering ceramic can be avoided and the risk for chipping of the ceramic during occlusion and function may be reduced (Fig 1-3-6).
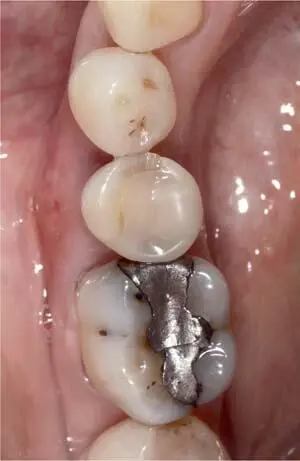
Fig 1-3-6a Occlusal view of the initial situation of a non-preservable second premolar due to a fracture.
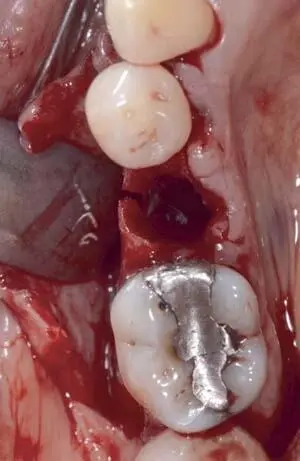
Fig 1-3-6b Occlusal view after extraction of the fractured premolar.
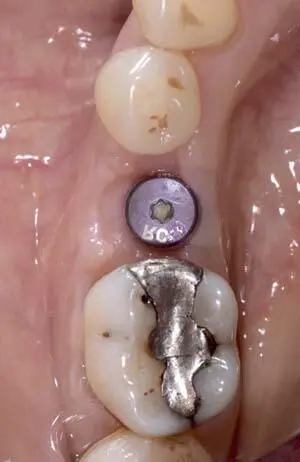
Fig 1-3-6c Occlusal view before final impression.
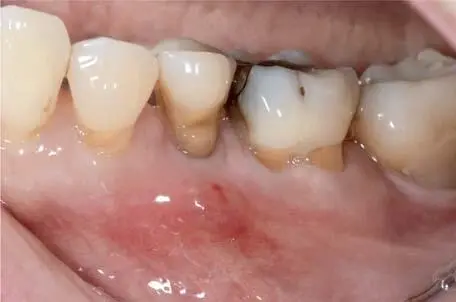
Fig 1-3-6d Buccal view of the initial situation of a non-preservable second premolar due to a fracture.
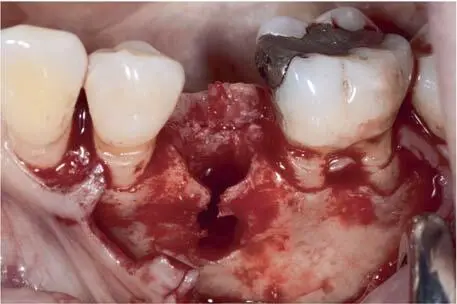
Fig 1-3-6e Buccal view before implantation of the BLT 4.1 mm implant (Straumann, Basel, Switzerland).
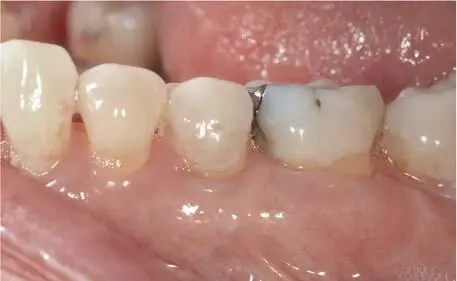
Fig 1-3-6f Final buccal view of the direct screw-retained, monolithic lithium-disilicate restoration based on a titaniumbase abutment (Vario-Base, Straumann) after 3 years of clinical function.
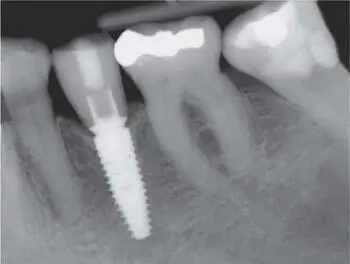
Fig 1-3-6g Radiographic control after 3 years of clinical function.
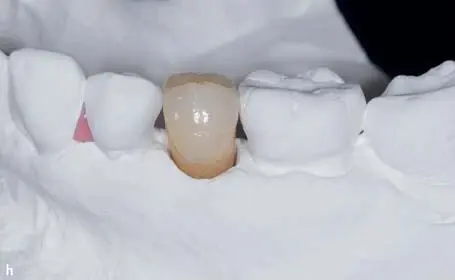

Fig 1-3-6h and 1-3-6i Final buccal and occlusal view of the directly screw-retained, monolithic lithium-disilicate restoration on the master cast.

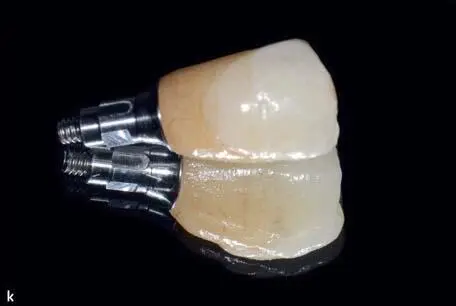
Figs 1-3-6j and 1-3-6k Final view of the monolithic lithium-disilicate restoration cemented to the titanium-base abutment with Multilink Hybrid Abutment HO-0 (Ivoclar Vivadent).
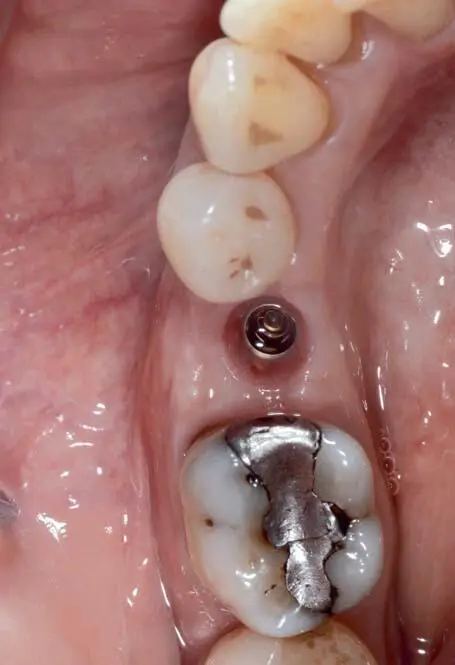
Fig 1-3-6l Occlusal view before placement of the direct screw-retained implant restoration.
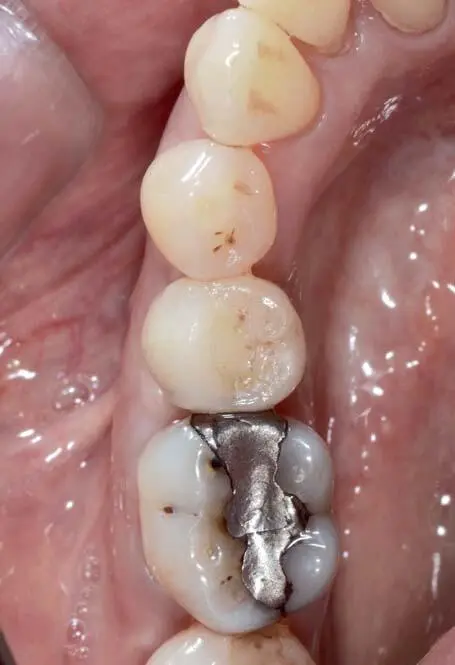
Fig 1-3-6m Final occlusal view of the direct screw-retained, monolithic lithium-disilicate restoration on a titanium-base abutment (Vario-Base, Straumann), after 3 years of clinical function. Individualized only by the application of ceramic stains and glaze (Ivocolor, Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein).
Читать дальше


























